UPSC Articles
PLACID Trials: convalescent plasma therapy shows no positive effects
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Science and Technology
In news
- Recently, the PLACID Trial, a multicentre randomized controlled trial (RCT), has shown that convalescent plasma (CP) therapy for Covid-19 patients gave no positive effects and did not improve the outcome of the patients.
Key takeaways of the trial
- The trial results indicate that there was no difference in the 28-day mortality.
- Progression of Covid-19 from moderate to severe in patients treated with CP along with basic standard care had no difference when compared to basic standard care alone.
- The use of CP seemed to improve the resolution of shortness of breath and fatigue in patients with moderate Covid-19. However, this did not translate into a reduction in 28-day mortality or progression to severe disease.
- The ICMR is now considering removing the option of CPT from the national guidelines.
Important value additions
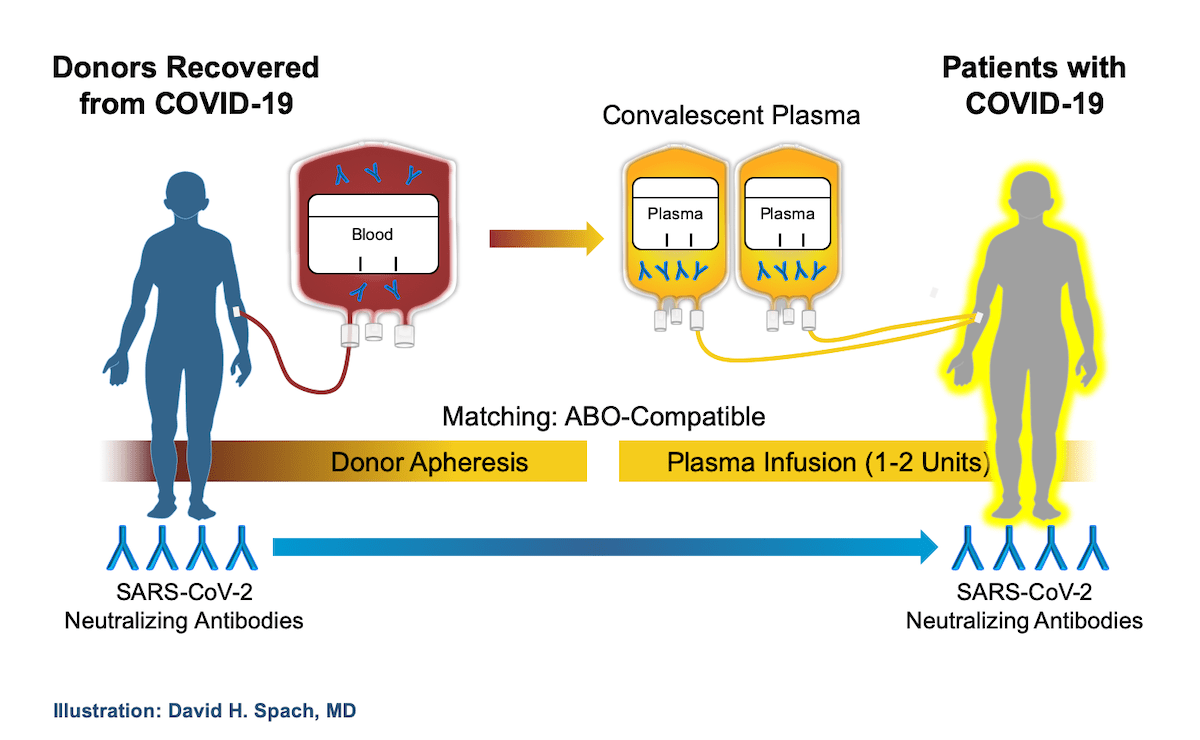
Convalescent Plasma Therapy
- Convalescent Plasma, extracted from the blood of patients recovering from an infection, is a source of antibodies against the infection.
- The therapy uses blood from people who have recovered from an illness to help others recover.
- Blood donated by people who have recovered from Covid-19 has antibodies to the virus that causes it.
- The donated blood is processed to remove blood cells, leaving behind liquid (plasma) and antibodies. These can be given to people with Covid-19 to boost their ability to fight the virus.
- The plasma donor would have to be a documented case of Covid-19 and healthy for 28 days since the last symptoms.
PLACID Trial
- It was conducted by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
- Aim: To investigate CPT’s effectiveness for the treatment of Covid-19.
- It is the first and largest randomised control trial to be completed in the world.
Do you know?
- RCT is a trial in which subjects are randomly assigned to one of two groups.
- One (the experimental group) receiving the intervention that is being tested, and the other (the comparison group or control) receiving an alternative (conventional) treatment.