IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
WHO’s 2019 Global Health Estimates
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health
In news
- The WHO’s 2019 Global Health Estimates was released recently.
Key takeaways
- According to the report, non-communicable diseases now make up 7 of the world’s top 10 causes of death, an increase from 4 of the 10 leading causes in 2000.
- The new data cover the period from 2000 to 2019.
- Heart disease: (1) It has remained the leading cause of death at the global level for the last 20 years; (2) It now represents 16% of total deaths from all causes; (3) The number of deaths from heart disease increased by more than two million since 2000 to nearly 9 million in 2019.
- Diabetes and dementia are also among the world’s top 10 causes of death.
- HIV/AIDS dropped from the 8th leading cause of death in 2000 to the 19th in 2019.
- Tuberculosis is also no longer in the global top 10, falling from 7th place in 2000 to 13th in 2019, with a 30% reduction in global deaths.
- In 2019, people were living more than 6 years longer than in 2000, with a global average of more than 73 years in 2019 compared to nearly 67 in 2000.
- There has been a global decline in deaths from communicable diseases, which however, still remain a major challenge in low- and middle-income countries.
Do you know?
- In 2019, pneumonia and other lower respiratory infections were the deadliest group of communicable diseases and together ranked as the fourth leading cause of death.
Post Matric Scholarship To Students Belonging To Scheduled Castes (PMS-SC)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and Interventions
In news
- The Union Cabinet has recently approved major changes in the Centrally Sponsored Scheme ‘Post Matric Scholarship to students belonging to Scheduled Castes (PMS-SC)’ to benefit more than 4 Crore SC students in the next 5 years so that they can successfully complete their higher education.
Key takeaways
- A campaign will be launched to enrol the students, from the poorest households passing the 10th standard, in the higher education courses of their choice in the next 5 years.
- The scheme will be run on an online platform with robust cyber security measures that would assure transparency and timely delivery of the assistance.
- The States will undertake fool-proof verification of the eligibility, caste status, Aadhar identification and bank account details on the online portal.
- Transfer of financial assistance to the students under the scheme shall be on DBT mode, and preferably using the Aadhar Enabled Payment System.
- It shall start from from 2021-22.
- The Central share shall be 60% in the scheme.
- Monitoring mechanism will be further strengthened through conduct of social audits, annual third party evaluation, and half-yearly self-audited reports from each institution.
- The Central Assistance which was around Rs 1100 crore annually during 2017-18 to 2019-20 would be increased more than 5 times to be around Rs 6000 core annually during 2020-21 to 2025-26.
Medium Range Surface To Air Missile (MRSAM) launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Defence and Security
In news
- DRDO recently achieved a major milestone with the maiden launch of Medium Range Surface to Air Missile (MRSAM), Army Version from Integrated Test Range, Chandipur, off the Coast of Odisha.

Key takeaways
- The missile completely destroyed a high speed unmanned aerial target which was mimicking an aircraft with a direct hit.
- Army version of MRSAM is a surface to Air Missile developed jointly by DRDO, India and IAI, Israel for use of the Indian Army.
- MRSAM Army weapon system comprises of Command post, Multi-Function Radar and Mobile Launcher system.
India and World Bank sign USD 500 million worth project for Green National Highway Corridors
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Infrastructure
In news
- The Indian Government and the World Bank signed a USD 500 million project to build safe and green national highway corridors in Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Andhra Pradesh.
Key takeaways
- The Green National Highways Corridors Project will support the Road Transport and Highways Ministry to construct 783 kilometres of highways in various geographies by integrating safe and green technology designs such as local and marginal materials, industrial by-products and other bioengineering solutions.
- The project will help reduce GHG emissions in the construction and maintenance of highways.
- The project will also enhance the capacity of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways in mainstreaming safety and green technologies.
- The $500 million loan from the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) has a maturity of 18.5 years including a grace period of five years.
Important value additions
The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD)
- It is an international financial institution.
- Established in: 1944
- Headquarter: Washington, D.C., USA
- It is the lending arm of World Bank Group.
- It offers loans to middle-income developing countries.
- It is the first of five member institutions that compose the World Bank Group.
- The IBRD and its concessional lending arm, the International Development Association (IDA), are collectively known as the World Bank as they share the same leadership and staff.
Baroda Military Salary Package
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy; Defence and Security
In news
- Indian Army and Bank of Baroda have entered into a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for ‘Baroda Military Salary Package’.
Key takeaways
- The MoU lays down the basis on which banking services would be provided by Bank of Baroda to serving and retired personnel of Indian Army.
- Services under ‘Baroda Military Salary Package’ will be offered to serving and retired personnel of Indian Army through the Bank’s network.
- The benefits include: Free Personal Accidental Insurance cover, Permanent Total Disability cover, Partial disability Cover and Higher Education Cover and Girl Child Marriage Cover on death in case of serving personnel.
- Other offerings: Unlimited free ATM transactions at all bank ATMs, waivers or concessions on various service charges in retail loans, free remittance facility through RTGS/NEFT, free Demand Draft/Banker’s Cheque, substantial discount in locker rentals, and various additional benefits in usage of Cards.
Miscellaneous
Shaheen-IX
-
Shaheen-IX is joint air exercise between China and Pakistan.
- China defended “Shaheen-IX” exercise with Pakistan air force as a routine arrangement, which experts believe is reflective of a larger strategic posture towards India.
- It is being held in Pakistan’s southern Sindh province near Indian border.
- India recently hosted the Malabar 2020 naval exercise with the U.S., Japan and Australia which was termed by a Chinese state media as an ill-intentioned attempt to corner China.
Abdul Rahim Khan-I-Khana
- Rahim Khan’s tomb was opened to the public after six years of restoration work — perhaps the largest conservation project ever undertaken for any monument of national importance in India.

- Abdul Rahim Khan-i-Khana (1556 – 1627), popularly known as simply Rahim, was a poet who lived in India during the rule of Mughal emperor Akbar.
- Abdul Rahim was the son of Bairam Khan, Akbar’s trusted guardian and mentor.
- He was one of the nine important ministers (dewan) in Akbar’s court, also known as the Navaratnas.
- Rahim is known for his Hindi dohe (couplets) and his books on astrology.
- Rahim also translated Babar’s memoirs, Baburnama from Chagatai language to Persian language.
- In Sanskrit, he wrote two books on astrology, Khetakautukam and Dwatrimshadyogavali.
Tomb of Abdul Rahim Khan-I-Khana
- His tomb is situated near Humayun’s Tomb, in New Delhi.
- It was built by him for his wife in 1598, and his body was placed in it in 1627.
- It was the first Mughal tomb built for a woman.
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development.
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
Cairn Arbitration case
Context: The Permanent Court of Arbitration at The Hague has ruled that the Indian government was wrong in applying retrospective tax on Cairn. In its ruling, the international arbitration court said that Indian government must pay roughly Rs 8,000 crore in damages to Cairn.
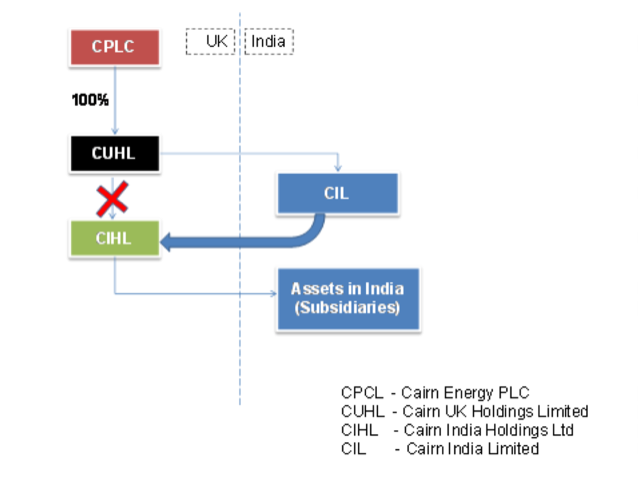
What is the dispute all about?
- The dispute between the Indian government and Cairn relates to retrospective taxation.
- Before 2006 (listing in BSE), the India operations of Cairn Energy were owned by a company called Cairn India Holdings Ltd (CIHL) incorporated in Jersey, UK.
- Cairn India Holdings Ltd (CIHL) was a fully owned subsidiary of Cairn UK Holdings (CUHL), in turn a fully owned subsidiary of Cairn Energy (CPLC).
- At the time of the IPO (2006), the ownership of the India assets was transferred from Cairn UK Holdings to a new company, Cairn India Ltd(CIL).
- In 2006, Cairn India Ltd. (CIL) acquired the entire share capital of Cairn India Holdings (CIHL) from Cairn UK Holdings (CUHL). In exchange, 69 per cent of the shares in Cairn India were issued to Cairn UK Holdings (CUHL). Hence, Cairn Energy (CPLC), through Cairn UK Holdings (CUHL), held 69 per cent in Cairn India.
- Later, in 2011, Cairn Energy sold Cairn India to mining billionaire Anil Agarwal’s Vedanta group, barring a minor stake of 9.8 per cent. It wanted to sell the residual stake as well but was barred by the I-T department from doing so. The government also froze payment of dividend by Cairn India to Cairn Energy.
- In 2012, government introduces retrospective tax amendment in finance bill and in 2014 the IT authorities launches a retrospective tax probe into transactions undertaken prior to IPO.
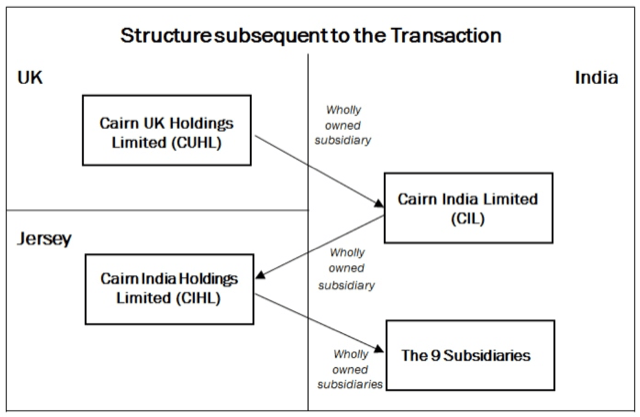
What were the objections by IT Authorities?
- The Income Tax authorities then contented that Cairn UK had made capital gains and slapped it with a tax demand of Rs 24,500 crore.
- Owing to different interpretations of capital gains, the company refused to pay the tax, which prompted cases being filed at the Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT) and the High Court.
- While Cairn had lost the case at ITAT, a case on the valuation of capital gains is still pending before the Delhi High court.
- In 2015, Cairn’s claim was brought under the terms of the UK-India Bilateral Investment Treaty, the legal seat of the tribunal was the Netherlands, and the proceedings were under the registry of the Permanent Court of Arbitration.
What has the arbitration court said?
- The Permanent Court of Arbitration at The Hague has maintained that the Cairn tax issue is not a tax dispute but a tax-related investment dispute and, hence, it falls under its jurisdiction.
- India’s demand in past taxes, it said, was in breach of fair treatment under the UK-India Bilateral Investment Treaty.
- The tribunal ordered the government to return the value of shares it had sold, dividends seized and tax refunds withheld to recover the tax demand.
- The government was asked to compensate Cairn “for the total harm suffered” together with interest and cost of arbitration.
What has been the government response?
- The Solicitor General of India has opined that an “arbitral tribunal can’t render a law passed by a sovereign Parliament ineffective,
- While senior government functionaries have asserted India’s sovereign taxation rights “can’t be subservient to bilateral investment treaties,” PM Modi had assured global investors that “concerns over retrospective taxation would be taken care of”.
- Also, Finance minister Nirmala Sitharaman has on record said that, “we won’t use retrospective taxation for income generation”.
- The verdict came barely three months after India lost arbitration to Vodafone Plc over the retrospective tax legislation amendment.
Connecting the dots:
- Vodafone case: Click here
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE/ RIGHTS
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Fundamental Rights
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
Wistron (Apple Supplier) Violence
Context: Worker unrest following the non-redressal of payment and overtime issues at a new factory of Wistron Infocomm Manufacturing India Pvt Ltd, that manufactures iPhones for Apple and other products, resulted in a riot at the plant on December 12.
Production at the plant in Kolar district, Karnataka around 60 km from Bengaluru, employing 1,343 regular workers and 8,490 contract workers, was suspended following the violence.
Wistron’s investment
- Wistron, which makes devices and peripheral systems for major global tech companies, has manufacturing facilities and R&D centres at two dozen locations around the world.
- The company started a small pilot plant in Bengaluru in 2017 to make the iPhone and, in 2018, decided to make a large investment (Rs 3,000 crore) in India for a full-fledged plant.
- The company got environmental clearance in mid-2019 and, in 2020, announced investments to the tune of Rs 1,220 crore in equipment and machinery for the Kolar plant, which is designated as a service and manufacturing centre.
- In August 2020, the plant became fully operational, with around 5,000 employees to manufacture the iPhone SE (2020) and iPhone 7 models.
What factors led to Labour unrest in the facility?
- Rapid Expansion of Contractual Labour: Wistron rapidly scaled up its contractual employee strength from around 3,000 to nearly 8,500 between September 2020 and December 2020.
- The contract employees were hired and paid through six manpower supply contractors, but their work was supervised and managed by Wistron officials
- Overtime Work: The manufacturing facility also moved from eight-hour to 12-hour shifts. workers were working in two compulsory 12-hour shifts. The factory was being operated like a sweatshop.
- Irregular Payment: Initial police investigations have revealed that the contractors were not paying the workers their full wages as per their contracts, or for overtime work. “While wages were slashed from Rs 22,000 to Rs 8,000 in some cases, wages for November were not paid until December 12.
- Labour Rights Compromised: With no employee grievance redressal system in place at the firm or a union, workers were constantly asking company officials for their dues.
- Immediate Trigger for Violence: An official of the labour department said the trigger for the violence during a 6 am shift change on December 12 was an argument over the attendance system not capturing the exact work hours logged by the workers.
- Overblown Damages: Wistron officials initially estimated the damage at Rs 437 crore, but later revised it downward to about Rs 43 crore saying the “violence did not cause any material damage to major manufacturing equipment and warehouses”.
What has been the reaction of Apple?
- Apple has put Wistron on probation, and said the company will get no more orders until it fixes the problems
- Apple employees, along with independent auditors, will monitor their progress.
- Increasingly, following pressure from the consumers’ side and also being highly conscious of its brand image, Apple has provided a ‘Code of Conduct’ to all its suppliers, seeking to monitor and audit compliance of labour standards and safeguards
- Pressured by Apple’s response, Wistron has also been forced to apologise to the workers, remove its Vice-President in charge of India operations, and initiate corrective measures to address workers’ grievances.
What are the Key Takeways of the Incident?
- Voices of Labour subdued in Liberal era: That it took violence for the workers to be ‘seen’ and ‘heard’, and for corrections to be undertaken points to the realities of high-tech manufacturing outsourced through supply chains in the global south that is built on precarities of labour involved in them.
- Wilful Violation of Labour rights: In fact, many of the suppliers subcontracting in the high-end electronics sector including those for Apple, have been involved in wilful violations of labour standards and practices
- Complexities of Contractual Labour: The prevailing norms of work arrangements practised by many industries was through hired labour from multiple subcontractors/third party work supply firms. This process creates ambiguity in identifying the primary employer and thereby, seriously constrains the workers from getting effective redress of their grievances.
- Ensuring Accountability: Until recently, the default response of the brands has been evasion of responsibility by either shifting the onus to the subcontracting firms or keeping things in silent mode. However, Apple’s actions are a step forward in corporate accountability and ethical business operations.
- Traumatic Experience for Workers: Forcing workers to do overtime in harsh conditions without much breaks, and under constant disciplinary monitoring by supervisors are matched by low pay and little or no social security, leading to strain and traumatic experiences, both physical and mental
- Dangers of Student Internship: Another prevalent phenomenon is that of unpaid, forced student internships to fill shortages in labour supply and offset costs; students from vocational educational institutions are compulsorily employed, and subjected to the same exploitative conditions as the workers. Since they are not legally classified as workers, there are no obligations to offer social protections.
Conclusion
In the absence of avenues for workers to channelise their grievances — representative associations and unions — and adequate collective bargaining mechanisms as well as social dialogue, frequent labour unrest including to the extent of violent confrontations, could very well be a daily reality in these high-end manufacturing facilities.
Connecting the dots:
- New Labour Codes: Click here
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding WHO’s 2019 Global Health Estimates which was released recently:
- Heart disease remains the leading cause of death.
- Cases of HIV/AIDS have increased ten times as compared to 2000.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Abdul Rahim Khan-I-Khana was a well-known poet who lived in the court of which of the following Mughal Emperor?
- Akbar
- Shah Jahan
- Humayun
- Jahangir
Q.3 International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) is the lending arm of which of the following?
- International Monetary Fund
- World Bank
- World Economic Forum
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
ANSWERS FOR 23rd December 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | C |
Must Read
About an anti-science lawsuit:
About Sister Abhaya Murder case:
About US in post- Trump era:













