IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
First direct flight between Kalaburagi to Tirupati flagged off under UDAN
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and Interventions & GS-III – Infrastructure
In news
- Star Air has commenced the direct daily flight operations from Kalaburagi, Karnataka to Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh under the RCS-UDAN (Regional Connectivity Scheme – Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik).
Important value additions
Tirupati city
- It is also called as the ‘Spiritual Capital of Andra Pradesh’.
- It is home to the most famous Sri Venkateshwara Swamy Temple popularly called ‘Tirupati Balaji Temple’ which has its name in the most-visited shrine across the globe.
- Apart from the Tirupati Balaji temple, the place is also famous for other historical temples, Sri Venkateshwara National Park, Deer Park, Tirupati, & Talakona Waterfalls.
- The Tirumala Hills in Tirupati is the second oldest rock mountain hills in the world.
- Tirupati Laddu received Geographical indication tag which entitles that only Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams can make and sell it.
UDAN (Ude Desh ka Aam Naagrik)
- It is a regional airport development and “Regional Connectivity Scheme” (RCS) of Government of India
- Objective: Letting the common citizen of the country fly
- Aim: (1) Making air travel affordable and widespread; (2) To boost inclusive national economic development, job growth and air transport infrastructure development of all regions and states of India.
- Ministry: Ministry of Civil Aviation
Do you know?
- Inaugurated under the UDAN scheme, Kalaburagi airport recently completed a successful 1 year of service.
- The airport has become the fastest growing airport in the country.
Risk Based Internal Audit (RBIA) Framework
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- RBI has issued Risk Based Internal Audit (RBIA) Framework for Strengthening Governance arrangements of banks.
Key takeaways
In order to bring uniformity in approach followed by the banks and to align the expectations on Internal Audit Function with the best practices, banks are advised as under:
- Authority, Stature and Independence: The Head of Internal Audit (HIA) shall be a senior executive of the bank who shall have the ability to exercise independent judgement.
- Tenor for appointment of HIA: The HIA shall be appointed for a reasonably long period, preferably for a minimum of three years.
- Reporting Line: The HIA shall directly report to either the Audit Committee of the Board (ACB) / MD & CEO or Whole Time Director (WTD).
- Staff Rotation: Except for the entities where the internal audit function is a specialised function and managed by career internal auditors, the Board should prescribe a minimum period of service for staff in the Internal Audit function.
- The internal audit function shall not be outsourced.
- However, where required, experts, including former employees, could be hired on contractual basis subject to the ACB being assured that such expertise does not exist within the audit function of the bank.
Payment Infrastructure Development Fund (PIDF) scheme
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- The RBI recently announced the operationalisation of the payment infrastructure development fund (PIDF) scheme.
Key takeaways
- Objective: To subsidise deployment of payment acceptance infrastructure in tier-3 to tier-6 cities, with a special focus on the north-eastern states of the country.
- An advisory council (AC) under the chairmanship of RBI deputy governor BP Kanungo has been constituted for managing the PIDF.
- The fund will be operational for three years effective from January 1, 2021 and may be extended for two more years.
- The implementation of targets shall be monitored by the RBI with assistance from card networks, the Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) and the Payments Council of India (PCI).
Do you know?
- The PIDF presently has a corpus of Rs 345 crore, with Rs 250 crore contributed by the RBI and Rs 95 crore by the major authorised card networks in the country.
- The authorised card networks shall contribute in all Rs 100 crore.
- The card issuing banks shall also contribute to the corpus based on the card issuance volume.
- Besides, the PIDF shall also receive annual contributions from card networks and card issuing banks.
Academic advisory council for College Of Supervisors (COS) set up
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- The RBI has set up an academic advisory council with former deputy governor N S Vishwanathan as the chairperson to advise the full-time director of the central bank’s College of Supervisors (CoS).
- Functions: (1) Identify areas where skill building/up-skilling is required; (2) Plan and develop curricula of all programmes; (3) Benchmark the programmes with international standards/best practices; (4) Develop appropriate teaching methods, etc.
Important value additions
College of Supervisors (CoS)
- Set up by: RBI
- It was set up as part of the measures to further strengthen Supervision over regulated entities.
- Objective: To augment and reinforce supervisory skills among its regulatory and supervisory staff both at entry level and on a continuous basis.
- While the CoS was functioning in a limited way in virtual mode since May 2020, it is now being fully operationalised.
- This will further contribute to effective oversight of the regulated entities by augmenting and ensuring a consistent quality of supervisory resources pool.
- The CoS will have a full-time Director supported by an Academic Advisory Council (AAC).
- Rabi Narayan Mishra, former Executive Director, RBI has been appointed as the Director of CoS.
Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) Introduced
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- The RBI has introduced the Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) for Large Value Transactions in Centralised Payment Systems.
Key takeaways
- The LEI is a 20-digit number used to uniquely identify parties to financial transactions worldwide.
- Objective: To improve the quality and accuracy of financial data systems for better risk management post the Global Financial Crisis.
- The RBI has now decided to introduce the LEI system for all payment transactions of value Rs.50 crore and above undertaken by entities (non-individuals) using RBI-run Centralised Payment Systems viz. Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) and National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT).
- The LEI has been introduced by the RBI in a phased manner for participants in the over the counter (OTC) derivative and non-derivative markets as also for large corporate borrowers.
- In India, LEI can be obtained from Legal Entity Identifier India Ltd. (LEIL), which is also recognised as an issuer of LEI by the Reserve Bank under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
Period Room Set Up For Menstruating Women in Thane district, Maharashtra
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I – Society
In news
- In a bid to help the women residing in congested slums during their menstruation days, a ‘period room’ has been set up at a public toilet in Maharashtra’s Thane city.
Key takeaways
- Equipped with several basic facilities, the period room aims to facilitate menstrual hygiene among women dwelling in slums.
- The facility is set up keeping in mind the women living in small houses, who do not have a separate bathing section.
- Many times they find it difficult to change during periods.
- This facility will be a boon for such women and go a long way in promoting good hygiene.
- Claimed to be the first-of-its-kind initiative, the much-needed facility has been set up by the Thane Municipal Corporation in collaboration with an NGO, at a slum in Shanti Nagar locality of Wagle Estate area in Thane.
- The 45,000 rupees low-cost facility will be replicated in all 120 community toilets in the city.
Related articles:
- Menstruation and associated stigma: Click here
- Period Products (Free Provision) Scotland Bill: Click here
Miscellaneous
World Hindi Day
- World Hindi Day was recently observed on 10th January.
- The day is commemorated every year with the objective to promote use of Hindi language abroad.
- On this day in 2006, the First World Hindi Conference was held in Nagpur.
- Since then, every year 10th January is being observed as the World Hindi Day.
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
K-shaped economic recovery
Context: Economists states the prospects of a K-shaped recovery from COVID are increasing both in India and across the world.
India’s economic recovery is being characterised by three distinct forces that need to be disentangled
- Controlling COVID-19 has led to better recovery
- Successful Controlling of Virus Spread: India has broken the link between virus proliferation and mobility earlier and more successfully than many countries. Rising mobility and normalising economic activity, rather than sparking another wave of infections, have coincided with COVID cases falling by 80 per cent since September.
- Recovery much sooner than expected: Consequently, the progressive return towards pre-COVID activity levels has occurred much sooner than expected. Activity jumped back up to 95 per cent of pre-COVID levels by October, and has been inching up since
- Supportive actions by Government: Sooner than expected recovery is being complemented by the much-awaited pick-up in central government spending, which surged in November and is expected to remain strong for the rest of the year
- Recovery not led by labour and wages
- Lingering Unemployment Problem: CMIE’s labour market survey still reveals 18 million fewer employed (about 5% of the total employed) compared to pre-pandemic levels. The employment rate gradually improved till September but has weakened since then, even as the economy has progressively opened up.
- This also shows up in the PMI surveys where employment is lagging activity, and in demand for MGNREGA jobs which are still 50 per cent higher than the previous year
- Impacts recovery prospects: These labour market pressures increase risks of medium-term economic scarring, and are not incompatible with a sharper near-term rebound because the recovery appears to be led by capital and profits, not labour and wages.
- Differential Impact on Labourers: Even within labour, blue-collar workers are likely to have been disproportionately impacted vis-à-vis their white-collar counterparts.
- Greater Scale and Formalisation
- Weak Resilience of Smaller Firms: A third phenomenon is large firms have endured the crisis better and are gaining market share at the expense of smaller firms. It’s, therefore, important to interpret the data carefully because some variables will reflect this substitution effect as much as the pace of the recovery.
- Benefits of having larger firms: To the extent there is a migration of activity from the informal/SME firms to larger firms, tax collections and Sensex/Nifty earnings should get a boost, even holding the economic pie constant.
- Associated Risks: Greater scale and formalisation undoubtedly augur well for medium-term productivity but could increase near-term labour market frictions and boost pricing power.
All this, therefore, increases prospects of a K-shaped recovery from COVID, a phenomenon playing out globally.
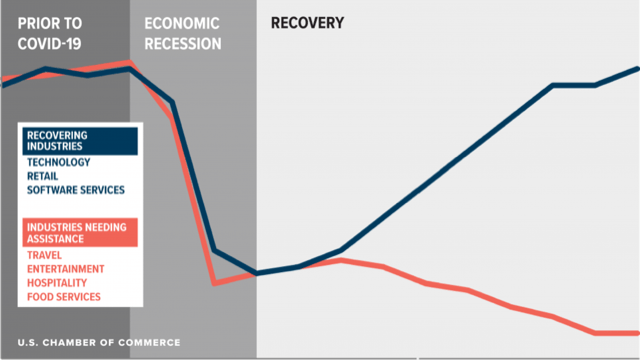
What is a K-shaped recovery?
- A K-shaped recovery happens when different sections of an economy recover at starkly different rates.
- Households at the top of the pyramid are likely to have seen their incomes largely protected, and savings rates forced up during the lockdown, increasing “fuel in the tank” to drive future consumption.
- Meanwhile, households at the bottom are likely to have witnessed permanent hits to jobs and incomes.
- Example: Passenger vehicle registrations (proxying upper-end consumption) have grown about 4 per cent since October while two-wheelers have contracted 15 per cent.
What are the macro implications of a K-shaped recovery?
- Recurring drag on the demand if labour market doesn’t heal faster
- With the top 10% of India’s households responsible for 25-30% of total consumption, one could argue consumption would get a boost as this pent-up demand expresses itself.
- But it’s important not to conflate stocks with flows, and levels with changes. Upper-income households have benefitted from higher savings for two quarters. What we are currently witnessing is a sugar rush from those savings being spent. This is, however, a one-time effect.
- To the extent that households at the bottom have experienced a permanent loss of income in the forms of jobs and wage cuts, this will be a recurring drag on demand, if the labour market does not heal faster.
- Marginal Propensity to consume if high at bottom
- To the extent that COVID has triggered an effective income transfer from the poor to the rich, this will be demand-impeding because the poor have a higher marginal propensity to consume i.e. they tend to spend (instead of saving) a much higher proportion of their income.
- Inequality and impact on productivity
- Third, if COVID-19 reduces competition or increases the inequality of incomes and opportunities, it could impinge on trend growth in developing economies by hurting productivity and tightening political economy constraints.
Way Ahead
- Plan ahead by incentivising Private Investment: Policy will, therefore, need to look beyond the next few quarters and anticipate the state of the macro economy post the sugar rush. The key, of course, is to incentivize the private sector to start re-investing and re-hiring, thereby setting the economy onto a more virtuous path.
- Manufacturing can benefit from export led growth: With manufacturing utilisation rates below 70 per cent pre-COVID, an investment revival, in turn, will depend crucially on the demand dynamics. Exports should benefit from strengthening global growth as the world gets progressively vaccinated
- Seize the Opportunity: It’s against this backdrop that the upcoming budget presents India with its New Deal moment. An unprecedented infrastructure push under the New Deal in 1935 created millions of jobs and regenerated regional economic development in the US. India must seek inspiration from this.
Conclusion
India’s faster-than-expected rebound is very encouraging. But given labour market pressures and prospects of a K-shaped recovery around the world, the economy will need to be carefully nurtured and stoked.
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- International Events
Bridging the Gulf: On Gulf reconciliation summit
Context: The Gulf reconciliation summit, in Al-Ula, Saudi Arabia, where the kingdom and its allies decided to end their blockade of Qatar, has brought to an end, for now, their long feud.
What was the feud between Qatar and Saudi allies?
- Accusation of Qatar funding Terrorism: In 2017, Saudi Arabia, under the leadership of Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman (MBS), the UAE, Bahrain and Egypt imposed the blockade and severed diplomatic ties, accusing the tiny Gulf country of supporting terrorism.
- List of Demands for Normalisation: They also issued 13 demands for it to be lifted, which included shutting down the Qatar-funded TV network, Al Jazeera, closing a Turkish military base and reducing diplomatic relations with Iran.
Did Qatar submit to the coercive tactics of Saudi Arabia & its allies?
- Qatar did not budge despite the heavy economic cost.
- When the Saudi and Emirati airspaces were closed, Iran offered Qatar global connectivity.
- Al Jazeera is still live.
- Qatar has invited more Turkish troops, bolstering its ties with Ankara, which is eager to play a bigger role in West Asia.
- Moreover, it played an important role in the U.S.-Taliban deal and continued to host talks between Taliban representatives and the Afghan government.
- If the original Saudi plan was to isolate Qatar and make it kneel, it has backfired.
- And in the last weeks of the Trump administration, MBS and his allies seem to have realised their strategic folly.
What steps were announced by both sides in reconciliation summit to end the feud?
- Qatar has made few concessions to reach the reconciliation.
- The 13 specific demands were replaced by a broad agreement on non-intervention in other countries’ internal affairs and cooperating to ensure regional stability and security, which can be open to different interpretations for different sides.
- After the summit, Qatar’s Foreign Ministry has said that the country had no intention of altering ties with Iran and Turkey.
- In practice, the Saudi side stepped down from its demands and made amends with an unshaken Qatar.
What are the reasons for Saudi Arabia stepping down from its demands?
The Saudi U-turn could be the result of a genuine tactical rethink.
- The rift in the Gulf helped Iran and Turkey, Riyadh’s main rivals, while it failed to scuttle Qatar’s standing. Iran, reeling under U.S. sanctions, also got some financial relief from Qatari payouts for using its airspace.
- By lifting the air and sea blockades, the Saudis and the Emiratis could deny Iran of those funds and also try to put economic pressure on Iran.
- Saudi Arabia also tries to up a united Arab regional front as Joe Biden is preparing to renegotiate the Iran nuclear deal.
- The Saudis may also be hoping that bridging the Gulf between two American allies (Saudi Arabia & Qatar) would help them warm up to the Biden administration.
Conclusion
- While ending the feud is welcome, it cannot be overlooked that this unnecessary crisis was born out of an ill-thought-out Saudi-Emirati strategy of coercion. It reflects poorly on them.
- Saudi & its allies should learn from the mistakes and build ties based on mutual interests and cooperation, not on threats and coercion.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the following is the second oldest rock mountain hills in the world?
- Tirumala Hills
- Anantagiri Hills
- Parvati Hill
- Susunia Hills
Q.2 Which of the following is responsible for UDAN scheme?
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Civil Aviation
- National Highway Authority of India
- Ministry of External Affairs
Q.3 College of Supervisors (CoS) has been set up with which of the following objective?
- Strengthening Supervision over regulated entities in the banking sector.
- Strengthening Supervision over Central universities.
- Strengthening Supervision over trading sector
- Strengthening Supervision over IAS and IFS officers.
ANSWERS FOR 11th January 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | C |
| 4 | A |
Must Read
About how deliberations with Civil Society reduced NREGA wages rejections:
On wages for housework and its limitations:
About reframing India’s foreign Policy priorities:











