IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Nord Stream 2 Pipeline
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- II – International Relations
In news
- In a development that could increase tensions between the USA and Germany, the association which is building the Nord Stream 2 pipeline has said that it has resumed work on the controversial project.
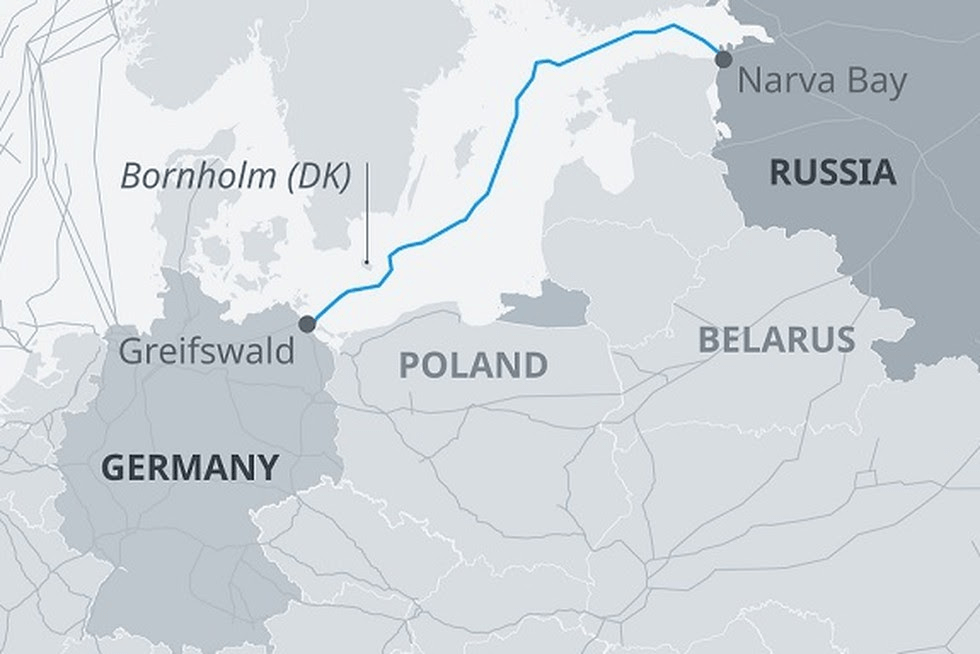
Key takeaways
- In 2015, Gazprom and 5 other European energy firms decided to build Nord Stream 2, valued at around $11 billion.
- The 1,200 km pipeline will run from Ust-Luga in Russia to Greifswald in Germany.
- It will carry 55 billion cubic meters of gas per year.
- The under-construction pipeline will run along with the already-completed Nord Stream 1 system, and the two together will supply an aggregate of 110 billion cubic meters of gas to Germany per year.
Why is the pipeline controversial?
- Nord Stream 2 has drawn criticism from the US, where it is believed that the project would increase Europe’s dependence on Russia for natural gas, thus strengthening its President.
- Currently, EU countries already rely on Russia for 40% of their gas needs.
Parliament informed about Agricultural Mechanization
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- III – Economy; Agriculture
In news
- The government of India informed Parliament about the initiatives to Promote Farm Mechanization.
Key takeaways
- A special dedicated scheme ‘Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM)’ has been introduced by the Government of India in 2014-15.
- Aim: To make farm machines accessible and affordable for the small and marginal farmers (SMFs) through the establishment of Custom Hiring Centers(CHCs), creating Hubs for hi-tech & high-value farm equipment and Farm Machinery Banks.
- Distribution of various subsidized agricultural equipment and machines to individual farmers is also one of the activities under the scheme.
- For 2021-22 Rs. 1050 crore budget has been allocated for SMAM which is higher than the last year.
- Significance: Agricultural mechanization is crucial in the agriculture sector as it contributes towards improving the efficiency of the inputs used in crop production thereby also increasing the productivity of crops.
World’s Smallest Reptile discovered in Madagascar
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- III – Biodiversity
In news
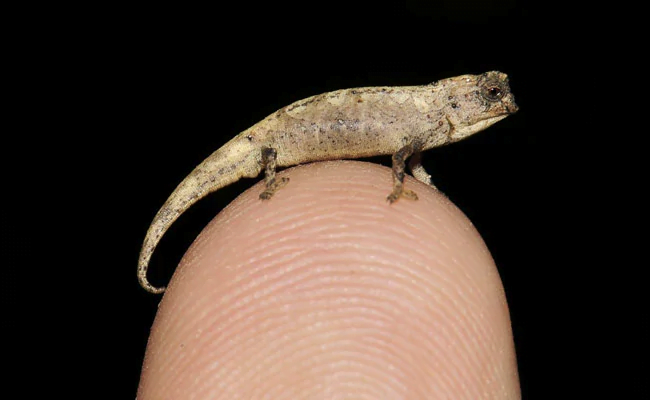
- A chameleon discovered in Madagascar by scientists from Germany and Madagascar may be the world’s smallest adult reptile.
- The discovery has been reported in the journal Scientific Reports.
Key takeaways
- The team found one male and one female of the species, named Brookesia nana, during an expedition in 2012.
- The male has a length (snout to vent) of 13.5 mm and a total length of 21.6 mm when the tail is included.
- Previously, the chameleon species Brookesia Micra was thought to be the smallest.
Do you know?
- The longest, the reticulated python, at 6.25 m is almost as long as 289 Brookesia nanas.
- Madagascar is home to tiny lizards and also the smallest species of snakes.
- One possible reason for such small species is the so-called “island effect” that causes species on small islands to get smaller.

Properties of the 99th element in the periodic table reported
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- III – Sci & Tech
In news
- A team of scientists at the Berkeley Lab has reported some of the properties of element 99 in the periodic table called “Einsteinium”, named after Albert Einstein.
Key takeaways
- For the first time, researchers have been able to characterise some of the properties of this element.
- It was discovered in 1952 in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb (the detonation of a thermonuclear device called “Ivy Mike” in the Pacific Ocean).
- The most common isotope of the element, einsteinium 253 has a half-life of 20 days.
- Because of its high radioactivity and short half-life of all einsteinium isotopes, even if the element was present on Earth during its formation, it has most certainly decayed.
- This is the reason that it cannot be found in nature and needs to be manufactured using very precise and intense processes.
National AYUSH Mission (NAM)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- II – Health
In news
- Central Government is implementing Centrally Sponsored Scheme of National AYUSH Mission (NAM) through States/UTs for development and promotion of AYUSH systems of medicine including Ayurvedic system.
Key takeaways
The Mission inter-alia makes the following provisions for the promotion of AYUSH systems including the Ayurvedic system:
- Co-location of AYUSH facilities at Primary Health Centers (PHCs), Community Health Centers (CHCs), and Districts Hospitals (DHs).
- Up-gradation of exclusive State Government AYUSH Hospitals and Dispensaries.
- Setting up of up to 50 bedded integrated AYUSH Hospital.
- Upgradation of State Government Under-Graduate and Post-Graduate Educational Institutions.
- Setting up of new State Government AYUSH Educational Institutions in the States where it is not available in Government Sector.
- Strengthening of State Government/State Government Co-operatives/PSUs for manufacturing of quality medicines in AYUSH Systems.
- Strengthening of State Drug Testing Laboratories
- Support for the cultivation of Medicinal Plant including processing and post-harvest management to ensure supply of quality raw material for AYUSH medicine and other products.
Lithium Reserves in Karnataka
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – I – Geography & GS- III – Resources
In news
- Atomic Minerals Directorate issues clarification on media reports about Lithium Reserves in Karnataka.
Key takeaways
- Atomic Minerals Directorate for Exploration and Research (AMD), a constituent unit of the Department of Atomic Energy and Geological Survey of India are two agencies that are involved in mineral exploration.
- Lithium is a key element for new technologies.
- It finds its use in ceramics, glass, telecommunication, and aerospace industries.
- The thermonuclear application makes Lithium a “Prescribed substance” under the Atomic Energy Act, 1962 which permits AMD for exploration of Lithium in various geological domains of the country.
- Recently, news items on Lithium exploration and resource of Allapatna – Marlagalla sector, Mandya district, Karnataka have been published in various media.
- In some media, the estimates of lithium metal have been quoted to be as high as 14,100 tonnes in a small patch of the surveyed area in Mandya district.
- The Directorate has clarified that exploration efforts have so far established ~1600 tonnes of lithium in the inferred category (low level of confidence).
National Research Centre For Makhana
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- III – Agriculture
In news
- Union Minister of Agriculture informed Lok Sabha about National Research Centre for Makhana.
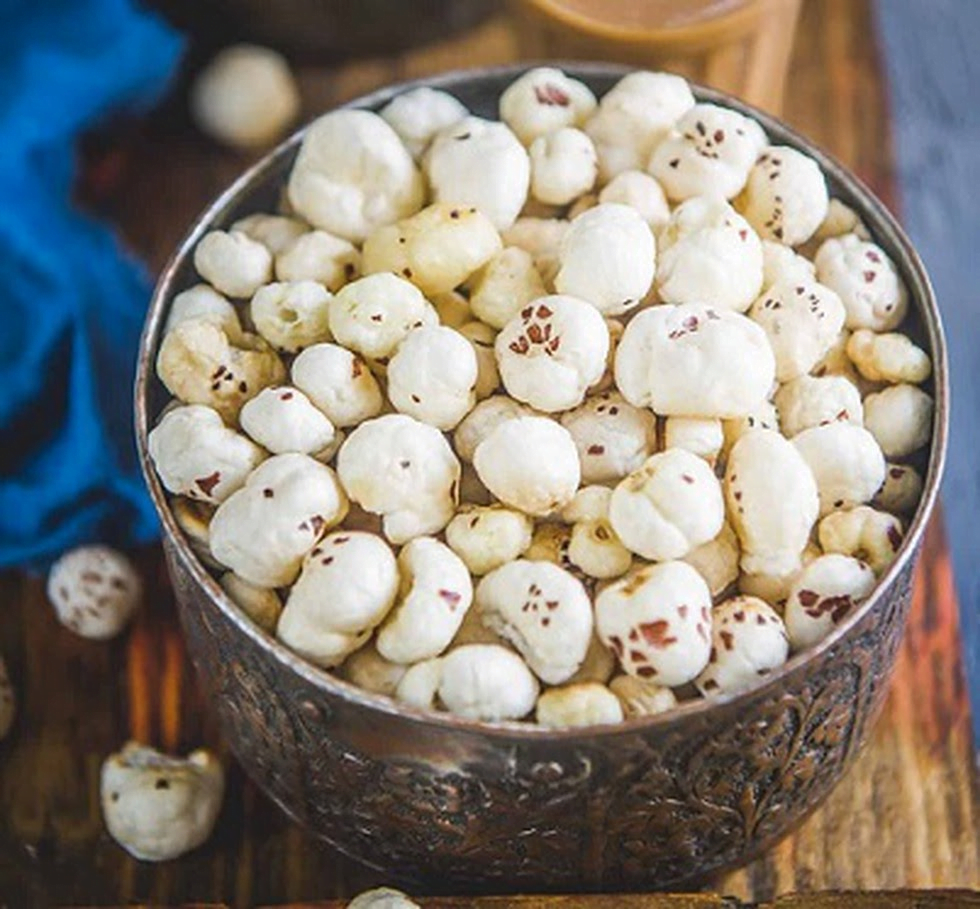

Key takeaways
- ICAR-National Research Centre (NRC) for Makhana, Darbhanga (Bihar) was sanctioned by the Department of Agricultural Research & Education, Govt. of India, as a new scheme during the 9th Five Year Plan period (1997–2002) for Conservation, Research & Development of the Makhana crop.
- However, during the 10th plan period (2002-2007), the NRC for Makhana was merged and brought under the administrative control of ICAR-Research Complex for Eastern Region (RCER), Patna, without changing the mandate.
- Darbhanga in particular and Mithila, in general, is the major Makhana producing region in the country.
Important value additions
- In India, makhana cultivation takes place mainly in West Bengal, Bihar, Manipur, Tripura, Assam, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and UP.
- But, Bihar alone is the largest producer of Makhana with 90 percent of overall production across the world.
- It belongs to the Nymphaeaceae family.
- It is a perennial plant.
- It grows in stagnant water like ponds, swamps, and wetlands in the tropical climatic areas very much similar to the lotus.
MoU signed for the construction of the Lalandar Dam
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – International Relations
In news
- MoU was signed for the construction of the Lalandar [Shatoot] Dam between India and Afghanistan recently.
Key takeaways
- The project is a part of the New Development Partnership between India and Afghanistan.
- Benefits: (1) Meet the safe drinking water needs of Kabul City; (2) Provide irrigation water to nearby areas; (3) Rehabilitate the existing irrigation and drainage network; (4) Aid in flood protection and management efforts in the area; (5) Provide electricity to the region.
Do you know?
- This is the second major dam being built by India in Afghanistan, after the India- Afghanistan Friendship Dam [Salma Dam], which was inaugurated by the Prime Minister and the President in June 2016.
National Monsoon Mission
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – I – Geography & GS-III – Sci & Tech
In news
- Minister of Earth Science informed Rajya Sabha about National Monsoon Mission.
Key takeaways
- Under the Monsoon Mission, Ministry has developed state-of-the-art weather and climate prediction models, which are now in operational use.
- These models include models for short-range to medium range (1-10 days), extended-range (10days to 30 days), and seasonal (up to one season).
Targets of Monsoon Mission:
- Development of a seamless prediction system using monsoon mission model, on different time scales, like Seasonal, Extended range, Short-range prediction.
- Initiate and coordinate the working partnership between Indian and foreign institutes to develop a system for the prediction of extremes and climate applications
- Develop and implement a system for climate applications having social impacts (such as agriculture, flood forecast, extreme events forecast, wind energy, etc.)
- Advanced data assimilation system for preparing high-quality data for model predictions.
Major achievements of NMM during the last three years:
- Setting up of an advanced prediction system for Seasonal prediction; Extended range prediction and Very high-resolution Short-range prediction.
- Commissioning of a Global Ensemble Forecast System (GEFS) for short and medium-range prediction at 12km.
UAE’s Hope Mission
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- III – Sci & Tech; Space
In news
- The UAE’s first mission to Mars entered its orbit, seven months after the UAE’s ‘Hope Probe’ was launched from Tanegashima in Japan.
Key takeaways
- With this, the UAE has become the fifth country after the US, Russia, China, the EU, and India, to reach the Martian orbit.
- The unmanned spacecraft is called ‘Al-Amal’ — the Arabic word for hope.
- The historic event was timed to coincide with the 50th anniversary of the unification of the UAE’s seven emirates.
- Carrying three instruments, including a high-resolution camera and a spectrometer, the spacecraft is on an orbital mission to collect data on Martian climate dynamics and help scientists understand why Mars’s atmosphere is decaying into space.
- Hope is the UAE’s fourth space mission and first interplanetary one.
- The previous three were all Earth-observation satellites.
- Its overall mission life is one Martian year, which is about 687 days on Earth.
Community in news: Koch Rajbangshis
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – I – Society
In news
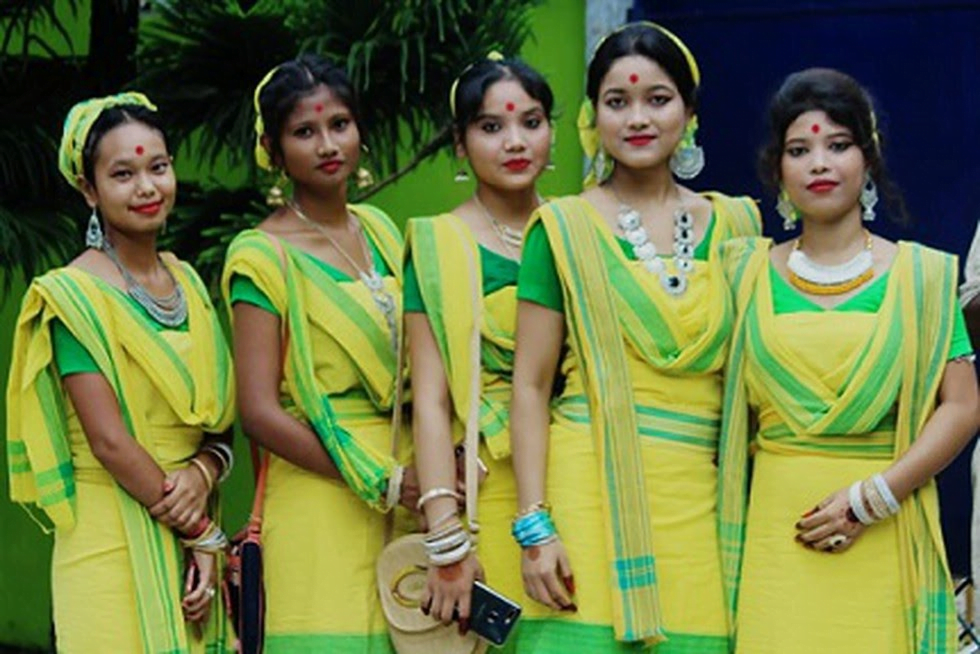
- The Koch Rajbongshis community was in news recently.
Important value additions
- They are a community that traces its roots to the Kamata kingdom, which comprised parts of Assam, West Bengal, and adjoining territories.
- In the medieval period, the community was dominant and ruled their territory of Kamatapur, which comprised a large part of Bangladesh, West Bengal, Bihar, and India’s north-east.
- After Independence, the princely state of Cooch Behar became part of West Bengal.
- Today, Koch Rajbongshis are found in Assam, Meghalaya, West Bengal, and Bihar, and in Bangladesh, Nepal, and some parts of Bhutan.
- They are estimated to number over 33 lakh in West Bengal, mostly the northern districts, and have a large presence in Assam.

(Mains Focus)
INTERNATIONAL / RIGHTS/ GOVERNANCE
Topics:
- GS-2: Fundamental Rights: Freedom of Speech
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
- GS-3: Role of media and social networking sites in internal security challenges
US Lawsuit on Fox News: Press Freedom Vs Disinformation
Context: Smartmatic, which makes voting machines, has filed a $2.7 billion defamation lawsuit against American media powerhouse Fox News for false election claims they had made.
What is the case about?
- In a 258-page lawsuit, the company claimed that the Fox news media invented a story that the election was stolen from Trump and made disparaging statements against Smartmatic, alleging that its machines and software platforms hacked to allow Democrats to seize the election.
- In one show, Smartmatic was represented by Fox News as a “Venezuela company under the control of corrupt dictators from socialist countries.”
- Although these claims did not change the result of the election, Smartmatic claimed that the news media organisation and its hosts profited in ratings and advertisements from spreading this narrative
- On the other hand, the company suffered a loss of reputation and also received hate mails and death threats from those who believed in these claims
- Fox News moved the court seeking to dismiss the lawsuit claiming it is an attempt to chill First Amendment Rights under the Constitution (express recognition of freedom of press)
Significance of the case
- Fight against fake News: The lawsuit claiming such huge damages is being seen as a test case for fighting disinformation.
- Corrective actions of Fox News causes doubt: Even before the lawsuit has had a hearing, Fox News’ cancellation of the show in which the host is a defendant in case, is seen as a course-correction measure.
- Previous measures yielded little results: Advertising boycotts, and mass campaigns against fake news have had little impact over the years.
- Freedom of Press Vs Defamation Law: With the First Amendment protections, defamation law is rather unsympathetic to the plaintiff (person filing case), especially public figures and those holding public offices. However, it is significant that the lawsuit has been brought about by a private party, which relatively has a higher degree of protection than public figures to protect its rights.
- Judicial Precedence in Defamation Law: In the US, the landmark 1964 case New York Times Co. v. Sullivan redefined libel(defamation) law in favour of media. The case set the standard that to win a libel suit in matters involving public concerns, it is not enough to simply prove that a false statement of fact was made but they would be required to prove either malice -a deliberate attempt to harm the plaintiff or a “reckless disregard” for facts. So Smartmatic Company has tough battle to fight
- Judgement Global Precedence: Although the express recognition of freedom of press in the First Amendment to the US Constitution places the American media in a unique position, the case is expected to have seminal consequence for balancing press freedoms and penalising disinformation across the globe.
Do You Know?
- India’s Constitution, unlike in the US, does not distinguish the press in guaranteeing free speech.
- Article 19(1)(a), which recognises freedom of speech and expression, is for every citizen. The press doesn’t qualify as a separate category for rights, but the collective right to free speech includes every individual journalist.
- Compared to the US law, India’s civil defamation law is in favour of the plaintiff. The plaintiff would just need to prove that the statement made against him results in lowering his or her reputation and proof of Intent to defame is not required.
Connecting the dots:
- On regulation of Digital media (Sudarshan TV Case): Click here
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment; Government Budgeting
- GS-3: Government Budgeting
Privatisation of Banks
Context: In the Union Budget for 2021-22, the government has announced taking up the privatisation of two public sector banks (in addition to IDBI Bank) and one general insurance company in the upcoming fiscal.
Laying down a clear policy roadmap for disinvestment, the government has identified four strategic sectors in which it will have bare minimum presence.
- Atomic energy,space and defence;
- Transport and telecommunications;
- Power, petroleum, coal and other minerals;
- Banking, insurance and financial services.
All CPSEs in other sectors will be privatised.
Do You Know?
- PSU banks are under dual control, with the RBI supervising the banking operations and the Finance Ministry handling ownership issues.
- Many committees had proposed bringing down the government stake in public banks below 51% — the Narasimham Committee proposed 33% and the P J Nayak Committee suggested below 50%.
Which are the two PSBs that will be Privatised?
- Currently, there are ten nationalised banks in addition to IDBI Bank and SBI.
- While the government is unlikely to touch the top three including SBI, smaller and middle-level banks are likely to be privatised.
- Government has not disclosed which two banks will be privatised this fiscal.
- The two banks that will now be privatised will be selected through a process in which NITI Aayog will make recommendations, which will be considered by a core group of secretaries on disinvestment and then the Alternative Mechanism (or Group of Ministers).
Reasons for Privatising Public Sector Banks
- Previous reform measures have not yielded results: Years of capital injections and governance reforms have not been able to improve the financial position of in public sector banks significantly. Many of them have higher levels of stressed assets than private banks, and also lag the latter on profitability, market capitalisation and dividend payment record.
- Aligned with Long Term Goal: Privatisation of two public sector banks will set the ball rolling for a long-term project that envisages only a handful of state-owned banks, with the rest either consolidated with strong banks or privatised.
- Reduces Government Burden: Privatisation will free up the government, the majority owner, from continuing to provide equity support to the banks year after year. The government front-loaded Rs 70,000 crore into government-run banks in September 2019, Rs 80,000 crore in in FY18, and Rs 1.06 lakh crore in FY19 through recapitalisation bonds.
- Rationalisation of Banks in Post-COVID Scenario: After the Covid-related regulatory relaxations are lifted, banks are expected to report higher NPAs and loan losses. This would mean the government would again need to inject equity into weak public sector banks. The government is trying to strengthen the strong banks and also minimise their numbers through privatisation.
- Changed Approach to Financial Sector Problems: Privatisation and proposal of setting up an asset reconstruction company entirely owned by banks, underline an approach of finding market-led solutions to challenges in the financial sector.
- Private Participation promotes innovation in market: Private banks’ market share in loans has risen to 36% in 2020 from 21.26% in 2015, while public sector banks’ share has fallen to 59.8% from 74.28%. They have expanded the market share through new innovative products, latest technology, and better services.
What are the challenges associated with increasing Privatisation of Banks?
- Private banks are not without faults
- In the last couple of years, some questions have arisen over the performance of private banks, especially on governance issues.
- ICICI Bank MD and CEO Chanda Kochhar was sacked for allegedly extending dubious loans.
- Yes Bank CEO Rana Kapoor was not given extension by the RBI and now faces investigations by various agencies.
- Lakshmi Vilas Bank faced operational issues and was recently merged with DBS Bank of Singapore.
- Former Axis Bank MD Shikha Sharma too was denied an extension.
- Moreover, when the RBI ordered an asset quality review of banks in 2015, many private sector banks, including Yes Bank, were found under-reporting NPAs.
- Dangers of private banks repeating the mistakes of 1960s
- There is widespread perception that the private sector then was not sufficiently aware of its larger social responsibilities and was more concerned with profit.
- This made private banks unwilling to diversify their loan portfolios as this would raise transaction costs and reduce profits.
- The expansion of branches was mostly in urban areas, and rural and semi-urban areas continued to go unserved
Conclusion
The initial plan of the government was to privatise four. Depending on the success with the first two, the government is likely to go for divestment in another two or three banks in the next financial year.
Connecting the dots:
- Corporates as Banks: Click here
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding ‘Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM)’:
- It targets small and marginal farmers (SMFs).
- Subsidized agricultural equipment and machines shall also be distributed under the scheme.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 World’s smallest adult reptile was recently discovered in which of the following country?
- Israel
- Madagascar
- Mozambique
- Bhutan
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding the 99th Element which was recently seen in the news :
- It is named after Issac Newton
- It is not found naturally.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4 Which of the following are the uses of Lithium?
- Ceramics
- Glass
- Telecommunication
- Aerospace industries
Select the correct code:
- 1,2 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
ANSWERS FOR 10th February 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | D |
Must Read
On disinformation as cybersecurity threat:
On ED searches at NewsClick office:
About how India’s farm crisis is of middle peasant and not of chhota Kisan:











