UPSC Articles
Historic heat wave in Canada caused due to Heat Dome
Part of: GS Prelims and GS I – Geography
In news
- Recently, the Pacific Northwest and some parts of Canada recorded temperatures around 47 degrees, causing a “historic” heat wave.
- This is a result of a phenomenon referred to as a “heat dome”.
- The western Pacific ocean’s temperatures have increased in the past few decades and are relatively more than the temperature in the eastern Pacific.
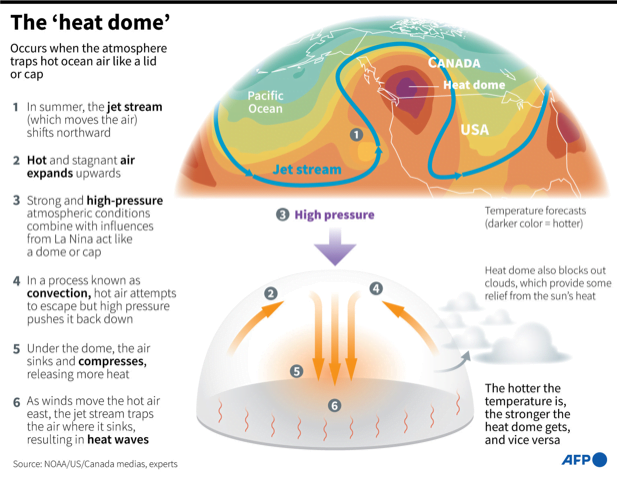
Phenomenon of heat dome
- A heat dome is an area of high pressure that parks over a region like a lid on a pot, trapping heat.
- The phenomenon begins when there is a strong change in ocean temperatures.
- The gradient causes more warm air, heated by the ocean surface, to rise over the ocean surface (Convection).
- As prevailing winds move the hot air east, the northern shifts of the jet stream trap the air and move it toward land, where it sinks, resulting in heat waves.
- This strong change in ocean temperature from the west to the east causes heat dome (HD).
- HD also prevents clouds from forming, causing more Sun’s radiation to reach the Earth’s surface.
- They are more likely to form during La Niña years like 2021, when waters are cool in the eastern Pacific and warm in the western Pacific.
Effects of Heat Dome
- The temperatures of homes rise unbearably high, leading to sudden fatalities, if such homes do not have AC.
- Damage crops, dry out vegetation and droughts.
- Rise in energy demand, especially electricity, leading to pushing up rates.
- Fuel to wildfires, which destroys a lot of land area in the US every year.
What are Jet streams?
- Jet streams are relatively narrow bands of strong wind in the upper levels of the atmosphere.
- The winds blow from west to east in jet streams but the flow often shifts to the north and south.
Pic courtesy: Barrons











