Science and Technology
In News: A case detected in United Kingdom
- Health authorities in the United Kingdom have confirmed a case of monkey pox, in an individual who recently travelled to that country from Nigeria
Monkey Pox
- It is a rare viral infection similar to smallpox
- Monkeypox is a zoonosis, that is, a disease that is transmitted from infected animals to humans.
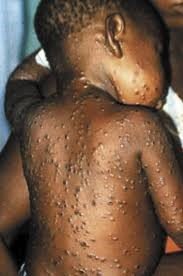
Monkeypox virus
- The monkeypox virus is an orthopoxvirus, which is a genus of viruses that also includes the variola virus, which causes smallpox, and vaccinia virus, which was used in the smallpox vaccine.
- Monkeypox continues to occur in a swathe of countries in Central and West Africa
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), two distinct clade are identified: the West African clade and the Congo Basin clade, also known as the Central African clade
Transmission
- Monkeypox is a zoonosis
- Monkeypox virus infection has been detected in squirrels, Gambian poached rats, dormice, and some species of monkeys.
- Human-to-human transmission is limited
- Transmission can be through contact with bodily fluids, lesions on the skin or on internal mucosal surfaces, such as in the mouth or throat, respiratory droplets and contaminated objects
Symptoms
- Monkey pox begins with a fever, headache, muscle aches, back ache, and exhaustion.
- It also causes the lymph nodes to swell (lymphadenopathy), which smallpox does not.
Treatment
- There is no safe, proven treatment for monkeypox yet. The WHO recommends supportive treatment depending on the symptoms.
Source: Indian Express
Q.1) Which of the following statements is not correct?
- Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV
- Hepatitis B, unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine
- Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses are several times more than those infected with HIV
- Some of those infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years











