IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs – International Relations
In News: The recently held 12th Ministerial Conference of the WTO agreed to a series of deals relating to the temporary waivers on Covid-19 vaccines, a moratorium on e-commerce trade, food security and setting limits on harmful fishing subsidies.
- Together these agreements are referred to as the “Geneva Package”.
Ministerial Conference
- The Ministerial Conference is the WTO’s top decision-making body and usually meets every two years.
- All members of the WTO are involved in the MC and they can take decisions on all matters covered under any multilateral trade agreements.
- The WTO’s 12th Ministerial Conference was held in Geneva
Key takeaways
Curtailing harmful fishing subsidies
- A multilateral agreement was passed to curb ‘harmful’ subsidies on illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing for the next four years, to better protect global fish stocks.
Note:
- Overfishing refers to exploiting fishes at a pace faster than they could replenish themselves — currently standing at 34% as per the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
- Declining fish stocks threaten to worsen poverty and endanger communities that rely on aquatic creatures for their livelihood and food security.
Global Food Security
- Members agreed to a binding decision to exempt food purchased by the UN’s World Food Programme (WFP) for humanitarian purposes, from any export restrictions.
- However, countries would be allowed to restrict food supplies to ensure domestic food security needs.
Covid-19 vaccine production
- Members agreed to temporarily waive intellectual property patents on Covid-19 vaccines without the consent of the patent holder for 5 years, so that they can more easily manufacture them domestically
- The waiver did not cover all medical tools like diagnostics and treatments
E-commerce transactions
- All members agreed to continue the long standing moratorium on custom duties on e-commerce transmissions until the subsequent Ministerial Conference
India’s interest secured
- India and other developing countries were able to win some concessions on fishing subsidies
- They successfully lobbied to remove a section of the proposal that would threaten some subsidies which would assist small-scale artisanal fishing
- The agreements hold that there would be no limitation on subsidies granted or maintained by developing or least-developed countries for fishing within their exclusive economic zones (EEZ)
Current moratoriums on electronic transmissions been extended
- Member countries agreed to extend the current moratorium on not imposing customs duties on electronic transmission (ET) until MC13
- ETs consist of online deliveries such as music, e-books, films, software and video games. They differ from other cross-border e-commerce since they are ordered online but not delivered physically.
- Proponents had put forth that the moratorium would help maintain certainty and predictability for businesses and consumers particularly in the context of the pandemic.
- India and South Africa, citing data from the UN Conference on Trade and Development submitted that extending duty-free market access due to the moratorium resulted in a loss of $10 billion per annum globally — 95% of which was borne by developing countries.
Source: The Hindu, Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2016)
- India has ratified the Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) of WTO.
- TFA is a part of WTO’s Bali Ministerial Package of 2013.
- TFA came into force in January 2016.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
In News: India will be taking over an ambitious hydropower project in Nepal — West Seti — nearly four years after China withdrew from it
- India’s National Hydro Power Corporation (NHPC) has already begun preliminary engagement of the site in far-western Nepal
- The CWE Investment Corporation, a subsidiary of China Three Gorges Corporation, had informed the Nepal Government in August 2018 that it would not be able to execute the 750-MW West Seti Hydropower Project it had undertaken on the ground that it was “financially unfeasible and its resettlement and rehabilitation costs were too high”
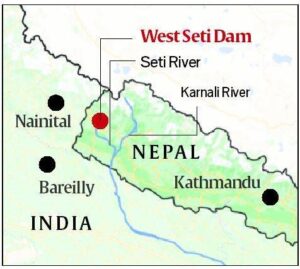
India -Nepal power relations
- Nepal is rich in power sources with around 6,000 rivers and an estimated potential for 83,000 MW.
- India is viewed as a feasible market for Nepal, but there has been some uncertainty in Nepal over India’s inability to deliver projects on time
- For instance – an ambitious Mahakali treaty was signed back in 1996, to produce 6,480 MW, but India has still not been able to come out with the Detailed project Report.
- What has helped build faith recently is India’s success in executing the 900-MW Arun Three project in eastern Nepal’s Sankhuwa Sabha
West Seti success is expected to restore India’s image in Nepal and give it weightage in future considerations for hydropower projects, when competition is bound to be tough. West Seti, therefore, has the potential to be a defining model for Nepal India’s power relations in future.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (2019)
- Japan
- Russia
- The United Kingdom
- The United States of America
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
In News: 7th round of India-Bangladesh Joint Consultative Commission was held recently
- India extended its assistance in management of the annual flood in Bangladesh
- And also stated its wish to work with Bangladesh on Artificial Intelligence, start-ups, Fintech and cybersecurity
India-Bangladesh relations
India was one of the first countries to recognize Bangladesh and establish diplomatic relations immediately after its independence in December 1971
Economic Relations:
- Bangladesh is India’s biggest trade partner in South Asia and India is the second biggest trade partner of Bangladesh.
- In the FY 2019-20, India’s exports to Bangladesh were $8.2 bn and imports were $1.26 bn
Connectivity:
- Both countries jointly inaugurated the newly restored railway link between Haldibari (India) and Chilahati (Bangladesh).
- Agreed to an early operationalization of the Bangladesh-Bhutan-India-Nepal (BBIN) initiative Motor Vehicles Agreement through the expeditious signing of the Enabling MoU
- The second addendum to the Protocol on Inland Water Transit and Trade (PIWTT) was signed recently
- Kolkata-Dhaka-Agartala Bus Service also launched in 2015. This reduced the distance between Kolkata and Agartala from 1,650 km to just 500 km.
Cooperation over Rivers:
- India and Bangladesh share 54 common rivers.
- A bilateral Joint Rivers Commission (JRC) has been working since June 1972 to maintain liaison between the two countries to maximize benefits from common river systems.
Defence Cooperation:
- Border Management: India and Bangladesh share 7 km. of border, which is the longest land boundary that India shares with any of its neighbours.
- The India-Bangladesh Land Boundary Agreement (LBA) came into force following the exchange of instruments of ratification in June 2015.
- Various Joint exercises of Army (Exercise Sampriti) and Navy (Exercise Milan) take place between the two countries
Medical tourism
- Bangladesh accounts for more than 35% of India’s international medical patients.
- Bangladesh alone contributes to more than 50% of India’s revenue from medical tourism
Co operation in multilateral platforms
- Members of major regional organisations like South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) and the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC)
- Solidarity at global platforms like UNSC, working together in achieving SDGs
- Cooperation to tackle the challenge of COVID-19 pandemic – participation of Bangladesh in SAARC leaders Video Conference in March 2020 and for creation of the SAARC Emergency Response Fund to counter effects of the global pandemic in the South Asian region.
Recent Advancements
- Recently, India and Bangladesh signed seven agreements and also inaugurated three projects to deepen their partnership.
- The use of the Chattogram and Mongla ports in Bangladesh for movement of goods to and from India, particularly from Northeastern India.
- Use of Bangladesh’s Feni River for drinking water supply in Tripura.
Challenges
The Teesta river water dispute:
- The 2011 interim deal aims to share the Teesta river water between India and Bangladesh about 42.5 per cent and 37.5 per cent respectively.
- But, the state of West Bengal object to this demand and never signed the deal, and strain in this issue goes on
The issue of Illegal migrants:
- Bangladesh has already raised concerns over roll out of the National Register of Citizens (NRC) in Assam, an exercise carried out to identify genuine Indian citizens living in Assam and weed out illegal Bangladeshis
China Factor
- Bangladesh is an active partner of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) that India has not signed up to.
- Bangladesh is also a major recipient of Chinese military inventory, including submarines.
Other issues
- Armed Dacoity in border districts, fake money transfer, cattle smuggling is also a cause of concern for India.
- Trafficking of Illegal migrants and involving them in terrorist activities, prostitution in India is also a challenge in India-Bangladesh relations.
- Apart from that, Bangladesh is also opposing India’s proposed the Tapaimukh Dam on the Barak River in Manipur and the Interlinking of the rivers project by India.
Way forward
- The early resolution of river water disputes like Teesta is the better way to boost India-Bangladesh relations.
- Involvement of joint forces to reduce border issues such as illegal trading, trafficking, cattle smuggling, etc
- Strengthening of regional groups like SAARC, BIMSTEC etc and focusing on Neighbourhood First policy.
Good relation between India and Bangladesh is essential for the development of North-east region, exploring the Indo-Pacific region and for greater connectivity to South Asian countries.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography (Places in news)
Sierra de la Culebra
- Zamora province, Spain
- In News: Wildfires has engulfed the entire region
- Firefighters in Spain struggled to contain wildfires in several parts of the country, which is suffering a heat wave unusual for this time of the year.
Oromia
- Oromia, Ethiopia
- In News: Ethnic attack
- More than 200 ethnic Amhara have been killed in an attack in the country’s Oromia region
- Ethiopia is experiencing widespread ethnic tensions in several regions, most of them over historical grievances and political tensions.
- The Amhara people, the second-largest ethnic group among Ethiopia’s more than 110 million populations, have been targeted frequently in regions like Oromia.
- Ethnic Amhara settled in the area about 30 years ago in resettlement programs
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2022)
Regions in News Country
- Anatolia – Turkey
- Amhara – Ethiopia
- Cabo Delgado – Spain
- Catalonia – Italy
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Syllabus
- Mains – GS (Agriculture)
Context: Supply disruptions during the pandemic and the Russia-Ukraine war have led many nations to think about self-sufficiency in critical food items
- Examples include Russia’s export ban on wheat and sunflower oil, Ukraine’s ban on exports of food staples, Indonesia’s ban on palm oil exports, Argentina’s ban on beef exports, Turkey, Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan’s ban on a variety of grain products, and India’s wheat export ban.
- Sudden actions such as these exacerbate the pressure on global trade leading to a spike in the prices of these commodities, threatening the food security of net food-importing countries.
- Thus such disruptions in supply chain had made India to rethink about self-sufficiency in critical food items or at least reduce their excessive dependence on imports of essential food products.
Stats
- India agri-exports in FY22 touched $ 50.3 billion against its agri-imports of $ 32.4 billion.
- This means that Indian agriculture is largely globally competitive.
- But its biggest agri-import item, edible oil, accounts for 59 per cent of India’s agri-import basket.
- India’s edible oil import bill in 2021-22 (FY22) crossed $19 billion
- Palm oil comprises more than 50 per cent of India’s edible oil imports, followed by soybean and sunflower.
- India imports 55 to 60 per cent of its edible oil requirements.
- The excessive dependence on imports has raised the pitch for atmanirbharta in edible oil.
- Thus the GoI launched National Edible Oil Mission-Oil Palm (NEOM-OP) in 2021
National Edible Oil Mission-Oil Palm (NEOM-OP) in 2021
- It aims raise the domestic production of palm oil by three times to 11 lakh MT by 2025-26.
- This will involve raising the area under oil palm cultivation to 10 lakh hectares by 2025-26 and 16.7 lakh hectares by 2029-30.
Features:
- The special emphasis of the scheme will be in India’s north-eastern states and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands due to the conducive weather conditions in the regions.
- Under the scheme, oil palm farmers will be provided financial assistance and will get remuneration under a price and viability formula.
Significance of the Scheme:
- Reduction in Import dependence – India is the largest consumer of vegetable oil in the world.
- Rise in Yields – India produces less than half of the roughly 2.4 crore tonnes of edible oil that it consumes annually, with financial assistance and guidance there will be rise in the yield.
- Food Security
Concerns
- Achieving atmanirbharta in edible oils would require an additional area of about 39 million hectares under oilseeds.
- Such a large tract of land will not be available without cutting down the area under key staples (cereals) – this could endanger the country’s food security
- Long gestation period crop it takes four to six years to come to maturity affecting farmers income
- Price volatility
Way Forward
- A rational policy to reduce import dependence in edible oils and achieve food security without affecting other essential crops
- Supporting farmers during gestation period with incentives and opportunity cost of their lands
- Proper pricing formula that take into account the price volatility
- Declare oil palm as a plantation crop and allow the corporate players to own/lease land on a long-term basis
- Development of processing units
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS (Economy)
Context: A petty patents regime could encourage domestic enterprises to undertake minor adaptive innovations
- India’s rank of 46 in WIPO’s Global Innovation Index (GII) 2021, up from 81 in 2015, is encouraging.
- India, which aspires to emerge as one of the largest economies of the world, needs to move up further in the innovation rankings, for building self-reliance in technology, especially in the context of the incipient digital revolution.
Stats
R&D
- Gross R&D expenditure (GERD) as a percentage of GDP at 0.7% is low.
- Only about 30% of the GERD is spent by business enterprises, despite the generous tax incentives offered by the government.
- This suggests that Indian enterprises have not got into an R&D culture.
Innovation
- The number of patents registered by residents is another indicator of innovative activity.
- In India the bulk of innovative activity is conducted by a handful of companies in the pharma and auto sectors
- The patent filings by Indian enterprises and other institutions have increased from 8,841 in 2011 to 23,141 in 2020 (WIPO). However, patents granted have been only 776 and 4,988 respectively.
What’s need to be done to boost the R&D activities of Indian enterprises?
Partial funding
- In India, R&D activities have been encouraged mainly through weighted tax deductions.
- Partial funding by government for specific R&D projects undertaken by business enterprises may be desirable to develop products or processes, thus strengthening competitiveness.
Petty patents
- Another policy to promote local innovation could be to protect minor innovations through the so-called utility models or petty patents, as has been done by several East Asian countries.
- The patent system fails to encourage minor innovations since the criteria for inventiveness tend to look at the novelty of the invention.
- Petty patents and industrial design patents could be effective means of encouraging domestic enterprises to undertake minor adaptive innovations
- India should consider adopting a petty patents regime that provides limited protection to minor incremental innovations made, especially those by MSMEs, often called jugaad.
- The utility models or petty patents typically provide a limited period of protection (5-10 years in contrast to 20 years in case of patents) and have less stringent requirements and procedures.
India’s rising rank in the global innovation league suggests its potential, opportunity, and stakes in boosting the R&D culture among business enterprises to strengthen their competitiveness. R&D funding and petty patents could help India climb the ladder.
Source: The Hindu
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements
- The Ministerial Conference is the WTO’s top decision-making body
- In the 12th Ministerial Conference multilateral agreement to curb harmful subsidies on illegal fishing was signed by member countries
Choose the correct statements:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Which of the below given pairs are correctly matched?
| Places in News | Country |
| 1. Oromia | Spain |
| 2. Sierra de la Culebra | Portugal |
| 3. Luhansk | Moldova |
Choose the correct code:
- 1 and 2
- 1 only
- 2 only
- None
Q.3) In which of the following country is India has undertaken West Seti power project?
- Bhutan
- Bangladesh
- Nepal
- Sri Lanka
Baba’s Explainer – FATF & Pakistan

Syllabus
- GS-2: Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
- GS-3: Security
Context:
Recently, Pakistan got a reprieve from the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) as FATF announced that the country could be removed from the grey list.
- FATF is expected to decide whether to take Pakistan off the ‘grey’ list at the end of its plenary session in Berlin in October.
- Pakistan has been on the FATF grey list continuously since June 2018.
Read Complete Details on FATF & Pakistan
ANSWERS FOR 18th JUNE 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – a











