International Relations
In News: India is hosting the two-day conclave to mark the 30th anniversary of its relations with the 10-nation Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
- The foreign ministers of India and ASEAN countries to uphold multilateralism in jointly responding to the regional and global challenges
- They reaffirmed the commitment to multilateralism founded on the principles of the international law, including the Charter of the United Nations, the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and other relevant UN treaties and conventions, maintain an open and inclusive regional cooperation framework, support ASEAN Centrality in the evolving rules-based regional architecture, uphold multilateralism in jointly responding to regional and global challenges
- Myanmar did not participate in the India-ASEAN foreign ministers’ meeting
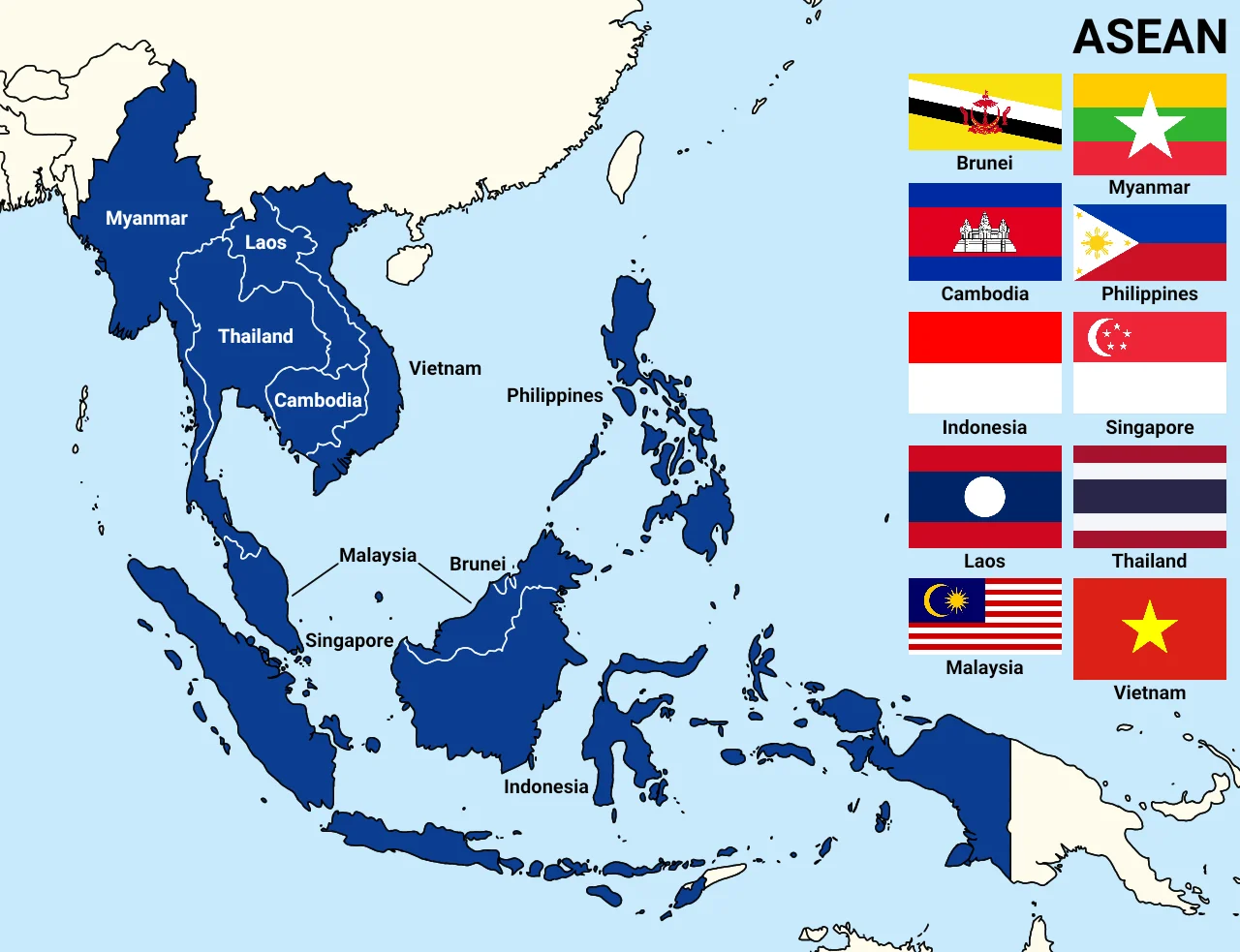
ASEAN
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations was established on 8 August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand, with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration)
- The motto of ASEAN is “One Vision, One Identity, One Community”.
- Founding Members Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
- Brunei Darussalam (1984), Vietnam (1995), Lao PDR and Myanmar (1997), and Cambodia (1999), joined the ASEAN later.
- ASEAN Secretariat – Indonesia, Jakarta.
Significance
- It is the 3rd largest market in the world
- It is the 6th largest economy in the world, 3rd in Asia.
- The Free-trade agreements (FTAs) with China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia and New Zealand.
ASEAN-led Forums
- ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF): Launched in 1993, the twenty-seven-member multilateral grouping was developed to facilitate cooperation on political and security issues to contribute to regional confidence-building and preventive diplomacy.
- ASEAN Plus Three: The consultative group initiated in 1997 brings together ASEAN’s ten members, China, Japan, and South Korea.
- East Asia Summit (EAS): The summit seeks to promote security and prosperity in the region and is usually attended by the heads of state from ASEAN, Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Russia, South Korea, and the United States.
India and ASEAN
- India’s relationship with ASEAN has emerged as a key cornerstone of our foreign policy.
- The relationship has evolved from the ‘Look East Policy’ enunciated in early 1990s which led India to become a Sectoral Partner of ASEAN in 1992, a Dialogue Partner in 1996 and a Summit-level Partner in 2002.
- The India-ASEAN Strategic Partnership acquired a new momentum with the announcement of “Act-East Policy” in the 12th Summit in 2014.
- India and ASEAN already has 25 years of Dialogue Partnership, 15 years of Summit Level interaction and 5 years of Strategic Partnership with ASEAN.
Economic Cooperation:
- ASEAN is India’s fourth largest trading partner.
- India’s trade with ASEAN stands at approx. 10.6% of India’s overall trade.
- India’s export to ASEAN stands at 11.28% of our total exports. The ASEAN-India Free Trade Area has been completed.
Socio-Cultural Cooperation:
- Programmes to boost People-to-People Interaction with ASEAN, such as inviting ASEAN students to India, Special Training Course etc
Delhi Declaration:
- To identify Cooperation in the Maritime Domain as the key area of cooperation under the ASEAN-India strategic partnership.
Delhi Dialogue:
- Annual Track 1.5 event for discussing politico-security and economic issues between ASEAN and India.
ASEAN-India Centre (AIC):
- To undertake policy research, advocacy and networking activities with organizations and think-tanks in India and ASEAN.
Political Security Cooperation:
- India places ASEAN at the centre of its Indo-Pacific vision of Security and Growth for All in the Region.
Financial Assistance
Financial assistance has been provided to ASEAN countries from the following Funds:
- ASEAN-India Cooperation Fund
- ASEAN-India S&T Development Fund
- ASEAN-India Green Fund
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
- 1, 2, 4 and 5
- 3, 4, 5 and 6
- 1, 3, 4 and 5
- 2, 3, 4 and 6











