Environment & Ecology
In news: A Varanasi district court has issued notice regarding carbon-dating of the disputed structure known to have been found inside the premises of the Gyanvapi mosque.
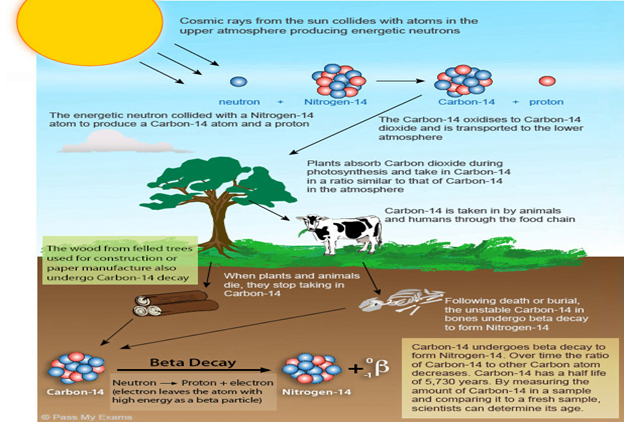
What is Carbon Dating?
- Carbon dating, also called radiocarbon dating is method of age determination that depends upon the decay to nitrogen of radiocarbon (Carbon-14).
- This method was developed by the American physicist Willard F. Libby about 1946.
- Carbon-14 is continually formed in nature by the interaction of neutrons with nitrogen-14 in the Earth’s atmosphere.
- The neutrons required for this reaction are produced by cosmic rays interacting with the atmosphere.
How it works?
- Radiocarbon present in molecules of atmospheric carbon dioxide enters the biological carbon cycle: it is absorbed from the air by green plants and then passed on to animals through the food chain.
- Radiocarbon decays slowly in a living organism, and the amount lost is continually replenished as long as the organism takes in air or food.
- Once the organism dies, however, it ceases to absorb carbon-14, so that the amount of the radiocarbon in its tissues steadily decreases.
The half-life concepts:
- Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5,730 ± 40 years—i.e., half the amount of the radioisotope present at any given time will undergo spontaneous disintegration during the succeeding 5,730 years.
- Because carbon-14 decays at this constant rate, an estimate of the date at which an organism died can be made by measuring the amount of its residual radiocarbon.
Its uses:
- It has proved to be a versatile technique of dating fossils and archaeological specimens from 500 to 50,000 years old.
- The method is widely used by geologists, anthropologists, archaeologists, and investigators in related fields.
Source: Indian Express











