Governance
In News: India ranks 107th out of 121 countries on Global Hunger Index.
About the Global Hunger Index:
- The Global Hunger Index (GHI) is a tool for comprehensively measuring and tracking hunger at global, regional, and national levels.
- Annual Report: Jointly published by Concern Worldwide and Welthungerhilfe.
- It was first produced in 2006. It is published every October. The 2022 edition marks the 17th edition of the GHI.
Aim: To comprehensively measure and track hunger at the global, regional, and country levels.
Calculation: It is calculated on the basis of four indicators:
- Undernourishment: Share of the population with insufficient caloric intake.
- Child Wasting: Share of children under age five who have low weight for their height, reflecting acute undernutrition.
- Child Stunting: Share of children under age five who have low height for their age, reflecting chronic undernutrition.
- Child Mortality: The mortality rate of children under the age of five.
Scoring:
- Based on the values of the four indicators, the GHI determines hunger on a 100-point scale where 0 is the best possible score (no hunger) and 100 is the worst.
- Each country’s GHI score is classified by severity, from low to extremely alarming.
Indian Scenario:
- India also ranks below Sri Lanka (64), Nepal (81), Bangladesh (84), and Pakistan (99). Afghanistan (109) is the only country in South Asia that performs worse than India on the index.
- India’s score of 29.1 places it in the ‘serious’ category.
- India’s child wasting rate, at 3%, is worse than the levels recorded in 2014 (15.1%) and even 2000 (17.15%), and is the highest for any country in the world and drives up the region’s average owing to India’s large population.
- Prevalence of undernourishment, has also risen in the country from 14.6% in 2018-2020 to 16.3% in 2019-2021. This translates into 3 million people in India considered undernourished out of the total 828 million people undernourished globally.
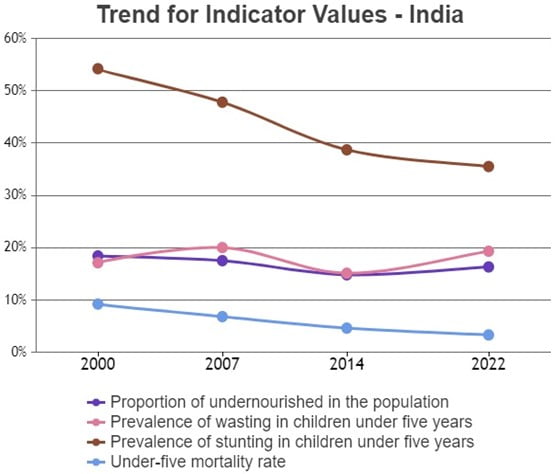
- India has shown improvement in the other two indicators – child stunting has declined from 38.7% to 35.5% between 2014 and 2022 and child mortality has also dropped from 4.6% to 3.3% in the same comparative period.
- On the whole, India has shown a slight worsening with its GHI score increasing from 28.2 in 2014 to 29.1 in 2022.
Global Scenario
- Globally, progress against hunger has largely stagnated in recent years.
- The 2022 GHI score for the world is considered “moderate”, but 18.2 in 2022 is only a slight improvement from 19.1 in 2014.
- This is due to overlapping crises such as conflict, climate change, the economic fallout of the COVID-19 pandemic as well as the Ukraine war, which has increased global food, fuel, and fertiliser prices and is expected to “worsen hunger in 2023 and beyond.”
- There are 44 countries that currently have “serious” or “alarming” hunger levels and “without a major shift, neither the world as a whole nor approximately 46 countries are projected to achieve even low hunger as measured by the GHI by 2030”.
Initiatives taken by the government
- National Food Security Act, 2013: It legally entitled up to 75% of the rural population and 50% of the urban population to receive subsidized food grains under the Targeted Public Distribution System.
- Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) Scheme: Launched on 2nd October, 1975, the ICDS Scheme offers a package of six services (Supplementary Nutrition, Pre-school non-formal education, Nutrition & health education, Immunization, Health check-up and Referral services) to children in the age group of 0-6 years, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana: A centrally sponsored scheme executed by the Ministry of Women and Child Development, is a maternity benefit programme being implemented in all districts of the country with effect from 1st January, 2017.
- POSHAN Abhiyan: Launched by the Ministry of Women and Child Development in 2018, it targets to reduce stunting, undernutrition, anemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls).
- Food Fortification: Food Fortification or Food Enrichment is the addition of key vitamins and minerals such as iron, iodine, zinc, Vitamin A & D to staple foods such as rice, milk and salt to improve their nutritional content.
Must Read: Malnutrition
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) The Global Competitiveness Report is published by the (2019)
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
- World Economic Forum
- World Bank
Q.2) Rule of Law Index” is released by which of the following? (2018)
- Amnesty International
- International Court of Justice
- The office of UN Commissioner for Human Rights
- World Justice Project











