Environment & Ecology
In news: Methane emission to rise 13% by 2030 without global pledge, said the United States Special Presidential Envoy for Climate citing an upcoming report by the United Nations Environment Programme during his speech at the Global Methane, Climate and Clean Air Forum 2022 being held in Washington, DC.
About:
- The Global Methane Pledge, launched in 2021, aims to keep alive the 1.5 degrees Celsius goal.
- Over 100 countries have committed to reducing global methane emissions by at least 30 per cent by 2030 from 2020 levels. This reduction could eliminate over 0.2˚C warming by 2050.
- India is among top 5 methane emitters globally and is not a part of the pledge. Most emissions can be traced back to agriculture.
About Methane:
- Methane is a short-lived climate pollutant like hydrofluorocarbons and stays in the Earth’s atmosphere for a few years, unlike carbon dioxide.
- Their potential to warm the atmosphere could be 80-1,500 times greater.
- Methane has contributed to about one-third of the current anthropogenic greenhouse gas-driven warming.
- Methane enters the atmosphere due to leaks in oil and gas industries, rearing livestock and the decomposition of waste in landfills.
- Mitigating methane and other short-lived climate pollutants is essential to achieving decarbonisation goals. It will enable further carbon dioxide removal.
- Currently, only 2 per cent of global climate finance goes to methane.
- Global methane emissions in 2030, can be reduced by 57 per cent using available strategies and technologies. This reduction can cause lower global warming by around 0.25°C in 2050 and 0.5°C by the end of the century.
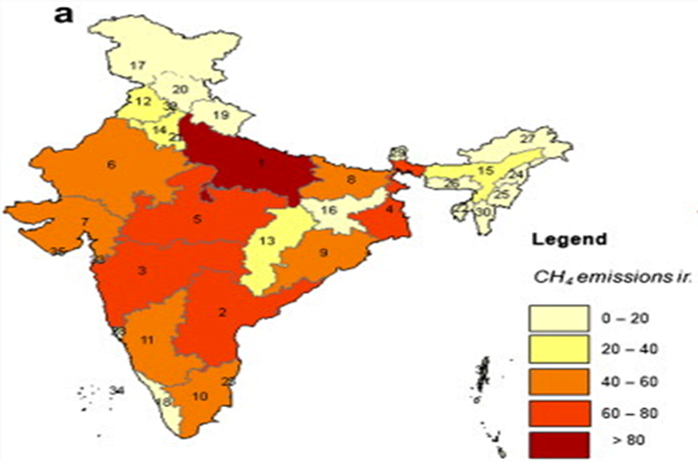
- Methane Emissions in India are as follows:
About The Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC):
- CCAC is a voluntary partnership of governments, intergovernmental organizations, businesses, scientific institutions and civil society organizations committed to improving air quality and protecting the climate through actions to reduce short-lived climate pollutants.
- It was formed in 2012 by the governments of Bangladesh, Canada, Ghana, Mexico, Sweden and the United States, along with the UNEP.
- Aim: To support fast action and deliver benefits on several fronts at once: climate, public health, energy efficiency, and food security
- 76 countries are its partner including India.
- CCAC 2030 Vision: To achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement and hold warming to 1.5˚C. Methane emissions can be reduced by 40% and black carbon by 70% by 2030 (from 2010 levels). Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) can be virtually eliminated with the potential for a 99.5% reduction by 2050 (from 2010 levels).
About Global Methane Initiative(GMI):
- It was launched in 2004.
- It is an international public-private initiative that advances cost-effective, near-term methane abatement and recovery and use of methane as a valuable energy source in three sectors: biogas (including agriculture, municipal solid waste, and wastewater), coal mines, and oil and gas systems.
- It focuses on collective efforts and a cost-effective approach to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and increase energy security, enhance economic growth, improve air quality and improve worker safety.
- GMI includes 46 Partner Countries, which together represent approximately 75 percent of the world’s estimated man-made methane emissions.
- Active involvement by private sector entities, financial institutions, and other non-governmental organizations is essential to build capacity, transfer technology, and promote private investment.
About International Energy Agency (IEA):
- It was established in the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in 1974 in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis.
- IEA is an autonomous intergovernmental organisation.
- Its mission is guided by four main areas of focus: energy security, economic development, environmental awareness and engagement worldwide.
- Headquarters: Paris, France.
- Roles and functions:
- to help its members respond to major oil supply disruptions, a role it continues to fulfil today
- tracking and analysing global key energy trends,
- promoting sound energy policy,
- fostering multinational energy technology cooperation.
- Composition: It has 30 members at present. IEA family also includes eight association countries. A candidate country must be a member country of the OECD. But all OECD members are not IEA members.
- Three countries are seeking accession to full membership: Chile, Israel, and Lithuania.
Reports by IEA:
- Global Energy & CO2 Status Report.
- World Energy Outlook.
- World Energy Statistics.
- World Energy Balances.
- Energy Technology Perspectives.
Source: DownToEarth
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Consider the following statements:
- Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC) to Reduce Short Lived Climate Pollutants is a unique initiative of G20 group of countries.
- The CCAC focuses on methane, black carbon and hydrofluorocarbons.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2 (2017)












