Geography, International Relations
In News: Sweden discovered the fourth leak in the two damaged offshore pipelines that comprise the crucial Nord Stream pipelines (Nord Stream 1 and Nord Stream 2). Two other leaks were found near Denmark earlier this week, Reuters reported.
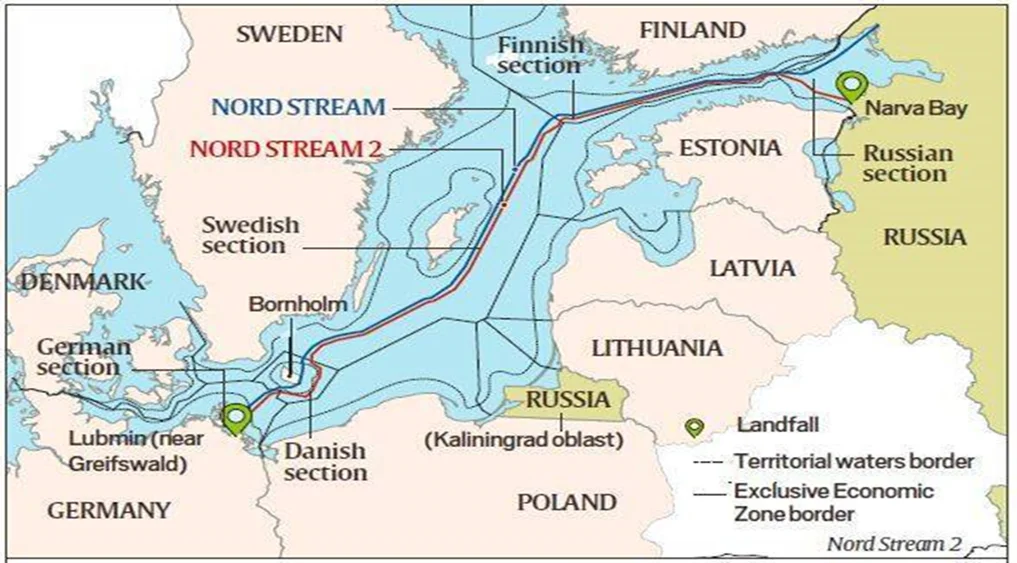
About Nord stream:
- It is a pair of 2 offshore natural gas pipelines that runs across the Baltic Sea from Russia to Germany.
- Nord Stream 1 was completed in 2011 and runs from Vyborg in Russia to Lubmin near Greifswald, Germany.
- Nord Stream 2 runs from Ust-Luga in Leningrad to Lubmin Germany and was completed in September 2021. It has the capacity to handle 55 billion cubic meters of gas per year.
- The twin pipelines together can transport a combined total of 110 billion cubic metres of gas a year to Europe for at least 50 years.
- The Nord Stream crosses the Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs) of several countries including Russia, Finland, Sweden, Denmark and Germany, and the territorial waters of Russia, Denmark, and Germany. In Germany, the pipeline connects to the OPAL (Baltic Sea Pipeline) and NEL (North European Pipeline) which further connects to the European grid.
Significance:
- Russia has the largest natural gas reserves in the world and around 40% of its budget comes from sales of gas and oil.
- Nord Stream 2 eliminates the risks related with sending gas through transit countries, cuts operating costs by doing away with transit fees and gives direct access to its most important European customer, Germany.
- It increases Europe’s dependence on Russia (around 40% of its gas comes from Russia) while giving it a reliable customer. Germany is Russia’s biggest European gas consumer, and most of it comes through the Nord Stream.
- This gas is used for heating homes, factories, and offices in the harsh, long European winters and also for power generation.
- Further, Germany’s transition to cleaner fuels by phasing out nuclear power and cutting reliance on coal has increased its dependence on Russian gas.
- Russia has been accused of leveraging Europe’s dependency on its energy, as retaliation against the Western sanctions imposed on it since the Ukraine war began.
Source: Indian Express












