International Relations
Context: Recently, the grouping of the world’s largest oil-producing countries, the Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and its allies, together known as OPEC+, decided to cut oil production by 2 million barrels per day (bpd).
This is the largest cut since the beginning of the Covid-19 pandemic. Brent crude, the international benchmark, was up 28 cents or 0.3%, at $92.08 a barrel after the cut was announced.
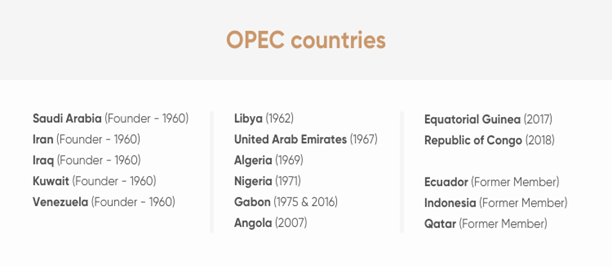
Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC):
- Established in 1960 by founding members Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela, OPEC has since expanded and has 13 member states.
- With the addition of another 11 allied major oil-producing countries that include Russia, the grouping is known as OPEC+.
- e., OPEC+ is a group of 24 oil-producing nations.
- OPEC+ format was born in 2017 with a deal to coordinate oil production among the countries in a bid to stabilize prices.
- The OPEC bloc is nominally led by Saudi Arabia, the group’s largest oil producer, while Russia is the biggest player among the non-OPEC countries.
Objective of OPEC Countries:
- To coordinate and unify the petroleum policies of its Member Countries;
- To ensure the stabilization of oil markets;
- To secure an efficient, economic, and regular supply of petroleum to consumers, a steady income to producers
- To ensure a fair return on capital for those investing in the petroleum industry.
Significance of OPEC Bloc:
- OPEC bloc accounts for roughly 40 per cent of the world’s crude oil and 80 per cent of the globe’s oil reserves, according to estimates from 2018.
- They usually meet every month to determine how much oil the member states will produce.
- However, many allege that OPEC behaves like a cartel, determining the supply of oil and influencing its price in the world market.
Reason for slashing production of oil:
- Oil prices skyrocketed after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in February, and have since begun to soften over the past few months.
- In September 2022, it dropped to $90 due to fears of a recession in Europe and reduced demands from China because of its lockdown measures.
- OPEC+ members are concerned that a faltering global economy would reduce the demand for oil, and the cuts are seen as a way to protect profits.
- Experts have also raised the possibility that Russia might be influencing OPEC, to make it more expensive for the West.
- Prices rise will make it more challenging for Europe to proceed with its sanctions on Russian oil in December.
Impact of slashing oil production:
- Impact on EU’s plan to put a price cap on Russian oil
- Recently, European Union had announced its plan to implement a price cap on oil exports from Russia.
- Under the plan, countries will only be permitted to purchase Russian oil and petroleum products transported via sea that are sold at or below the price cap.
- However, the recent decision to reduce the supply is likely to keep the global oil prices high, allowing Russia to continue aiming for significant revenue from its crude export.
Who is against this decision?
- Within the group, there are countries who opposed to such significant cuts in oil production
- As a meeting of OPEC+ technocrats was cancelled on Tuesday because of disagreements that reportedly only a gathering of oil ministers could resolve
- United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Kuwait, in particular, are said to be concerned that extended cuts would interfere with their plans to increase oil output capacity
Weaponization of energy:
- The West has accused Russia of weaponizing energy, creating a crisis in Europe that could trigger gas and power rationing this winter.
- Moscow accuses the West of weaponizing the dollar and financial systems, such as SWIFT, in retaliation for the invasion of Ukraine in February.
OPEC+’ or ‘Vienna Group’:
OPEC and non-OPEC oil producing nations (10 other countries including Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Oman, Russia, South Sudan, and Sudan.) made an agreement in 2016 to jointly cut production for stabilization of prices. This grouping is informally known as ‘OPEC+’ or ‘Vienna Group’.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
- Argentina, Mexico, South Africa, and Turkey
- Australia, Canada, Malaysia, and New Zealand
- Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and Vietnam
- Indonesia, Japan, Singapore, and South Korea












