Science and Technology
Context: Recently researchers from Hyderabad have rescued a nine year old boy from a rare progressive genetic disease identified as Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis or CTX at an early stage.
About Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis (CTX):
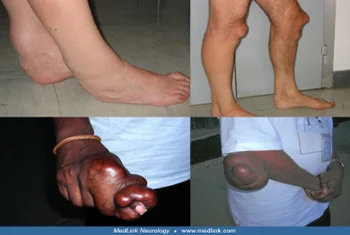
- Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX) is a lipid storage disease characterized by infantile-onset Diarrhea, childhood-onset cataract, adolescent- to young adult-onset tendon xanthomas, and adult-onset progressive neurologic dysfunction (dementia, psychiatric disturbances, pyramidal and/or cerebellar signs, dystonia, atypical parkinsonism, peripheral neuropathy, and seizures).
- Patients with CTX are unable to break down different forms of cholesterol, which build up in certain areas of the body.
- CTX is characterized by fatty yellow nodules (xanthomas) located in the connective tissues within the brain.
- These deposits can cause progressive damage to the brain and other areas of the body.
- Patients with CTX do not have elevated levels of cholesterol in their blood; however, they do have elevated levels in their tissues.
Symptoms:
- For infants and children, symptoms may include: Chronic Diarrhea during infancy, Cataracts in late childhood, Frequent bone fractures due to brittle bones
- When a patient with CTX enters into adulthood, they may begin to notice the following neurological symptoms: Dementia, Seizures, Hallucinations, Depression, Difficulty with coordination, Difficulty with speech
- The fatty deposits can also result in cardiovascular disease or stroke if they limit or block the blood flow to the heart or brain.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis is caused by a change in the CYP27A1 gene, which is involved in the production of an enzyme that breaks down cholesterol.
- The condition is inherited, and both parents need to pass on the genetic abnormality in order for their child to have the condition.
- If the child only receives one copy of the abnormal gene, then they are a carrier for CTX but will not have any symptoms.
- The condition is rare and occurs in an estimated 3 to 5 out of every 100,000 people.
- The condition affects all genders and ethnicities; however, it is most common in the Moroccan Jewish population.
Treatment:
- There is no cure for CTX, however, if the condition is treated early, its progression can be slowed or stopped.
- The first treatment generally prescribed is chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) replacement therapy, which works to normalize the body’s ability to break down cholesterol.
- Other medications, known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, may be prescribed to help lower cholesterol levels by blocking the enzyme responsible for the production of cholesterol.
- In CTX patients, cataract surgery also is often required by the age of 50.
- For patients who have experienced a stroke, the Stroke Program provides a multidisciplinary treatment approach through a personalized treatment plan tailored to each patient.
- Patient care is generally broken down into three categories: stroke prevention, treatment immediately after a stroke, and post-stroke rehabilitation.
Source: Times of India
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Consider the following statements: DNA Barcoding can be a tool to:
- assess the age of a plant or animal.
- distinguish among species that look alike.
- identify undesirable animal or plant materials in processed foods.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3













