Environment & Ecology
In News: International Crops Research Institute for The Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) has published a modelling study that revealed how the right combination of fertilisers, biochar, and irrigation could potentially increase soil carbon by 300%.
- The study was conducted in some districts of Maharashtra and Odisha with semi-arid climate (annual rainfall 600 -1,100 mm).
- A new gaming app, ‘Mrida’, has been launched to promote behavioural change among farmers and will be released in English, Marathi and Odiya.
About Carbon sequestration:
- Carbon sequestration is the process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide.
- The carbon sequestration increased by more than 300 per cent in combination with fertiliser, biochar, and irrigation.
- Biochar is a charcoal-like substance that burns organic material (biomass) from agricultural and forestry wastes in a controlled process called pyrolysis.
- Biochar has safely reduced contamination and stored carbon.
- Biochar increased carbon value in the soil by 130-300 per cent over 30 years with little difference in yield.
- Optimal use of fertilizers increased the carbon and output by up to 30 per cent.
- Improved nutrients, crop/variety, landform, minimum tillage and residue addition led to a significant increase in soil carbon.
- Carbon sequestration increased by 100 kg ha per year with the improved practices of landform management, fertilizers and crop varieties over 45 years.
- Two major types: geologic and biologic
- Geologic carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon dioxide (CO2) in underground geologic formations like rocks.
- Biologic carbon sequestration refers to storage of atmospheric carbon in vegetation, soils, woody products, and aquatic environments.
- Carbon sequestration occurs both naturally and as a result of anthropogenic activities.
- The Kyoto Protocol under UNFCCC allows countries to receive credits for their carbon-sequestration activities in the area of land use, land-use change, and forestry.
- Carbon capture and storage (CCS): carbon dioxide is first separated from other gases contained in industrial emissions. It is then compressed and transported to a location that is isolated from the atmosphere for long-term storage.
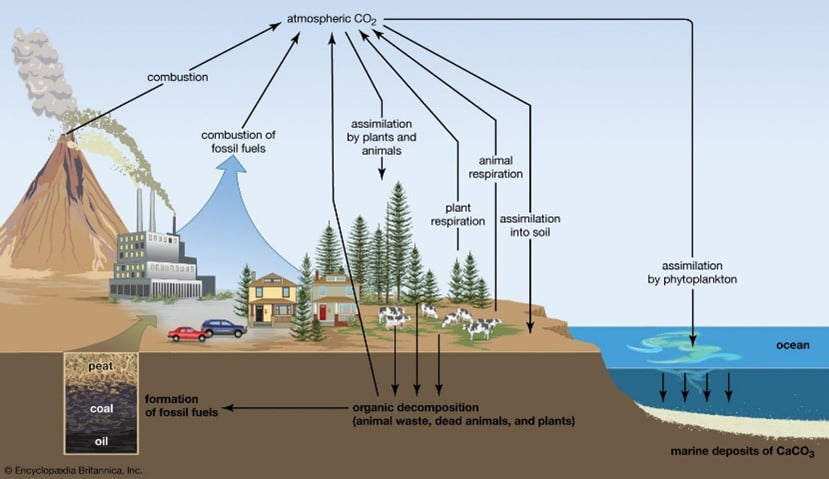
- Carbon cycle is as follows:
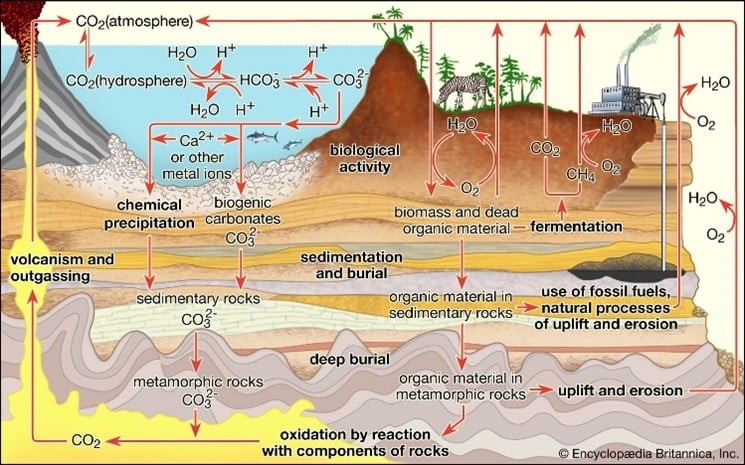
Significance:
- Food systems account for nearly one-third of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- In 2015, food-system emissions amounted to 18 Gt CO2 equivalent per year globally, representing 34 per cent of total GHG emissions.
- Soil carbon is critical for crop yield and climate adaptation or mitigation measures, which are heavily reduced by both intensive agriculture and indiscriminate use of chemicals leading to increased carbon emissions.
- Carbon sequestering can provide an additional source of income for the farmers.
Source: Down To Earth
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which of the following statements best describes “carbon fertilization”? (2018)
- Increased plant growth due to increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Increased temperature of Earth due to increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Increased acidity of oceans as a result of increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Adaptation of all living beings on Earth to the climate change brought about by the increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.














