Governance
Context: Recently, a pedestrian-only suspension bridge collapsed in Gujarat’s Morbi killing over 100 people.
- The bridge is owned by Morbi municipality and maintenance and operations are outsourced to a trust owned by private company Oreva.
- This 19th century bridge, which had been reopened a few days ago after repairs spanning six months, reportedly had over 400 people on it when it collapsed.
- Although the weight limit is not known, a few pre-incident videos seem to suggest the bridge was swaying, possibly because of the large crowd on it.
Suspension Bridge:
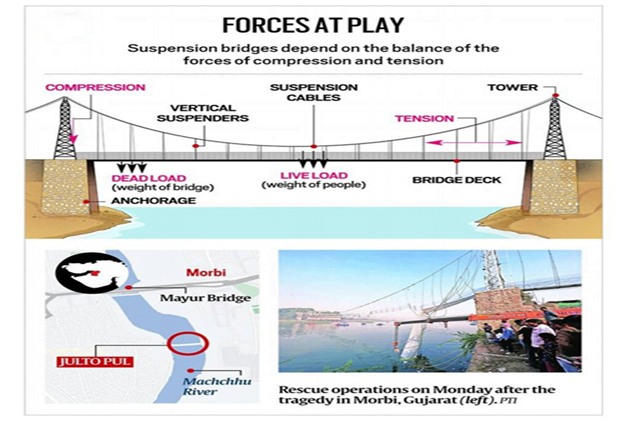
- A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck is hung below suspension cables on vertical suspenders.
- The basic structural components of a suspension bridge system include
- Stiffening girders.
- Two or more main suspension cables.
- Towers and anchorages for cables at either end of the bridge.
- The main cables are suspended between the towers and are connected to the anchorage or the bridge itself.
- The vertical suspenders carry the weight of the deck and the commuter load on it.
- The Golden Gate Bridge and Brooklyn Bridge in the US are examples of suspension bridges.
- India’s longest single-lane motorable suspension bridge — the 725-metre Dobra-Chanti suspension bridge built over the Tehri Lake — was inaugurated in November 2020.
Working of Suspension Bridge:
- The design ensures that the load on the suspension cables is transferred to the towers at the two ends, which transfer them further by vertical compression to the ground by way of the anchorage cables.
- All of this balancing has to happen within the permissible weight restrictions for the bridge, given that the deck is hanging in air, supported by the two sets of cables.
- Given that the most important load bearing members are the main suspension cables, the entire cross-section of the main cable is the mainstay of carrying the load and ensuring that buckling does not happen.
The efficient working is subject to two preconditions:
- There must be no overloading.
- And there should not be any excessive swaying.
Role of vertical support:
- The job of the vertical cables in a suspension bridge is to transfer the weight of the deck, by tension, to the twin suspension cables.
- These cables run horizontally between the two anchorages on either end, which, in turn, transfer the tension to the towers and, through them, to the ground by way of cables whose ends are anchored.
Possible reasons for the Morbi bridge collapse:
- Although an investigation into the accident is pending, the visuals and purported footage prior to the incident suggest that both the conditions of efficient working were possibly tested.
- However, the bridge collapse is unusual from a structural engineering point of view.
- Usually in such incidents one or two suspension cables give way, and the bridge breaks and hangs before the rest of the structure collapses.
- In the present case the vertical cables seem to have snapped entirely from the deck at one end of the bridge, sending part of the unsuspended deck and those on it plunging into the river.
- Most or all the suspension cables were weak or corroded.
- This is possible considering that this was a very old bridge which was recently repaired.
- During the recent repairs, the original wooden deck had possibly been replaced with an aluminum deck.
- It could have involved rewiring the mechanism connecting the vertical cables with the deck.
- Possibility of likely altering the basic structure of the bridge that had endured for well over a century.
- The load from the pedestrians:
- There was overcrowding but there is no information whether capacity was exceeded.
Need of suspension bridge:
- Bridges can be of different types including arch bridges, beam bridges, cantilever bridges, truss bridges and tied-arch bridges.
- While beam bridges are among the simplest and oldest bridges, the reason for the enduring design of the suspension bridge is
- The supporting cables running horizontally between the two far-flung anchorages provide the counterweight and effectively pass on the entire tensional force to the anchorages.
- As a result, suspension bridges can easily cross distances of well over 2,000 metres, beyond the scope of other bridge designs.
Way Forward:
- Although suspension bridges are built using an old, robust technology; overloading and excessive swaying present risks for such structures to fail.
- There is a need to put a multi-layered safety check mechanism in place for such infrastructure structures to avoid such tragic incidents in future.
MUST READ: Machchu River
Source: Indian Express














