Science and Technology
In News: Anti-cancer CAR-T therapy reengineers T cells to kill tumors — and researchers are expanding the limited types of cancer it can target.
About CAR-T therapy:
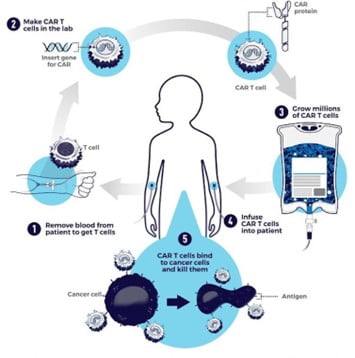
- It is made up of two parts – CAR and T.
- T refers to cytotoxic T cells are a particular kind of white blood cells (WBC)
- CAR-T cell therapy starts with doctors isolating a patient’s T cells from a sample of their blood.
- These T cells are genetically engineered in lab to produce a chimeric antigen receptor, or CAR.
- CARs are synthetic receptors specifically designed to redirect T cells from their usual targets have them recognize and hone in on tumor cells.
- On the outside of a CAR is a binder that allows the T cell to stick to tumor cells.
- Binding to a tumor cell activates the engineered T cell to kill and produce inflammatory cytokines proteins that support T cell growth and function and boost their cancer-killing abilities.
- These CAR-T cells are then stimulated to divide into large numbers over seven to 10 days, then given back to the patient via infusion.
- The infusion process usually takes place at a hospital where clinicians can monitor for signs of an overactive immune response against tumors, which can be deadly for the patient.
Solid tumors:
- While CAR-T cell therapy has seen success in blood cancers, it has faced hurdles when fighting what are called solid tumor cancers like pancreatic cancer and melanoma.
- Unlike cancers that begin in the blood, these types of cancers grow into a solid mass that produces a microenvironment of molecules, cells and structures that prevent T cells from entering into the tumor and triggering an immune response.
- Here, even CAR-T cells engineered to specifically target a patient’s unique tumor are unable to access it, suppressing their ability to kill tumor cells.
- So, a new synthetic receptor that complements the first CAR design is developed.
- This receptor, called synthetic Notch receptor, or synNotch, is based on the natural form of Notch in the body, which plays an important role in organ development across many species.
synNotch vs CAR:
- Like CARs, the outside of synNotch has a binder that allows T cells to stick to tumor cells.
- Unlike CARs, the inside of synNotch has a protein that is released when a T cell binds to the tumor – This protein, or transcription factor, allows researchers to better control the T cell by inducing it to produce a specific protein.
- While, CAR binds to both tumor and healthy cells and induce T cells to kill both; synNotc ensure that engineered T cells are only activated when bound to a tumor cell and not healthy cells.
- Because T cells now require both CAR and synNotch receptors to recognize tumors, this increases the precision of T cell killing.
Uniqueness of synNotch:
- Use synNotch to improve CAR-T cell activity against solid tumors by inducing them to produce more inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-2, that enable them to kill tumor cells.
- These cytokines are highly toxic, there is a limit to how much IL-2 a patient can safely tolerate, limiting their use as a drug.
- Using synNotch, when a CAR-T cell encounters a tumor, it produces IL-2 within the tumor instead of outside it, avoiding causing harm to healthy cells.
- SynNotch modified CAR-T cells were able to trigger IL-2 production without causing toxicity to healthy cells in the rest of the body.
- Because synNotch is able to bypass the barriers tumors put up, it is able to help T cells amp up and maintain the amount of IL-2 they can make, allowing the T cells to keep functioning even in a hostile microenvironment.
- It is being used to treat lymphoma and multiple myeloma, and has shown remarkable response rates where other treatments have failed.
Source: DTE
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body ? (2022)
- They protect the body from environmental allergens.
- They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
- They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
- They protect the body from the diseases caused by pathogens.











