Environment & Ecology
Context: Recently a Finland based company came up with sand-based battery to provide clean energy solution for Europe’s energy crisis. It is currently operational at town of Kankaanpaa in Finland.
About Sand Battery:

- It is a type of energy storage device that uses sand or sand-like materials as the storage medium.
- Sand is a very effective medium for storing heat and loses little over time.
- The sand is charged with electricity and then discharged to produce power.
- Its purpose is to work as a high-power and high-capacity reservoir for renewable energy.
- Sand batteries can help to increase the use of renewable energy by allowing excess/surplus energy produced from renewable sources to be stored and used at a later time.
Key Features: The sand battery has three major interconnected components:
- Steel silo: It contains 100 tonnes of sand where the heat is stored.
- Electric air heater: Resistors are used in regular ovens and an air-to-water heat exchanger.
- Heat Exchanger: It has a mechanical pipe and water.
- Sand stores the heat at around 500 Celsius (the same process that makes electric fires work).
- Sand is at the core and very far from the boundary so the heat stored in the core does not easily get lost
- It can last days or weeks.
- Reservoir is so well-insulated from the outer environment that it can retain temperatures up to 600 degrees Celsius and prevent heat losses over time.
- It can store up to 8 megawatt-hours of energy as heat.
Working conditions:
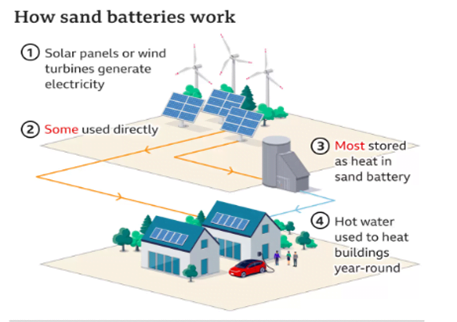
- It receives electricity from grid through cheaper renewable sources like solar and wind.
- Electricity is converted to heat and transferred to sand.
- Air is blown via a fan through the curricular pipe system inside the silo.
- It will enter the electric air heater, where it becomes hot with the help of a resistor located inside.
- Hot air will be circulated by air-to-water heat exchanger through metal structure (pipes).
- There’s no direct contact between air and water.
- Hot water is discharged into district heating system.
- It circulates in close loop from the heat exchanger to the customer and back.
- Energy is stored as heat which is used to heat homes or to provide hot stream and high temperature process heat to industries that are often fossil-fuel dependent.
Source: DownToEarth











