Science and Technology
Context: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is planning to launch the Aditya-L1 mission by June or July 2023.
About Aditya-L1 Mission:
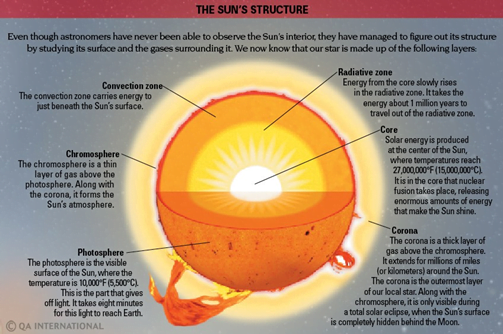
- Aditya-L1 is the first observatory-class space-based solar mission from India.
- A satellite around the L1 point has the major advantage of continuously viewing the Sun without occultation/eclipses.
- This position provides a greater advantage of observing solar activities continuously.
- Aditya-L1 carries seven payloads to observe the photosphere, chromosphere, and the outermost layers of the Sun (the corona) using electromagnetic and particle detectors.
- Four payloads directly view the Sun from the unique vantage point of L1, and the remaining three payloads carry out in-situ studies of particles and fields at the Lagrange point L1.
- The Aditya-L1 mission will be inserted in a halo orbit around the L1 point, which is about 1.5 million km from Earth.
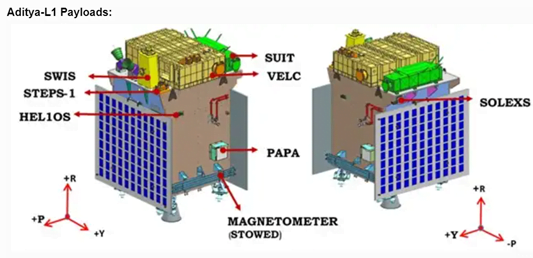
Aditya L1 Payloads: The 1,500 kg satellite carries seven science payloads with diverse objectives.
- Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC): To study the diagnostic parameters of solar corona and dynamics and origin of Coronal Mass Ejections, magnetic field measurement of solar corona.
- Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT): To image the spatially resolved Solar Photosphere and Chromosphere in near Ultraviolet (200-400 nm) and measure solar irradiance variations.
- Aditya Solar wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX): To study the variation of solar wind properties as well as its distribution and spectral characteristics.
- Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA): To understand the composition of solar wind and its energy distribution
- Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS): To monitor the X-ray flares for studying the heating mechanism of the solar corona .
- High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS): To observe the dynamic events in the solar corona and provide an estimate of the energy used to accelerate the particles during the eruptive events.
- Magnetometer: To measure the magnitude and nature of the Interplanetary Magnetic Field.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) If a major solar storm (solar flare) reaches the Earth, which of the following are the possible effects on the Earth? (2022)
- GPS and navigation systems could fail.
- Tsunamis could occur at equatorial regions.
- Power grids could be damaged.
- Intense auroras could occur over much of the Earth.
- Forest fires could take place over much of the planet.
- Orbits of the satellites could be disturbed.
- Shortwave radio communication of the aircraft flying over polar regions could be interrupted.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, 4 and 5 only
- 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 only
- 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
Q.2) Which one of the following is a reason why astronomical distances are measured in light-years? (2021)
- Distance among stellar bodies do not change
- Gravity of stellar bodies does not change
- Light always travels in straight line
- Speed of light is always same











