Environment & Ecology
Context: A recent study conducted on Tibetan plateau showed that increase in South Asian black Carbon aerosols is increasing loss of glaciers from Tibetan Plateau.
Key highlights of the study:
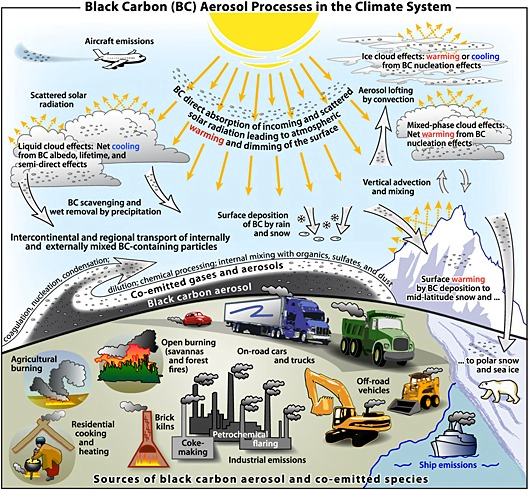
- Black carbon deposition in snow reduces the albedo of surfaces which accelerate melting of glaciers and snow cover and changes hydrological process and water resources in the region.
- Albedo is ability to reflect back Sun’s radiations.
- Black carbon aerosols in South Asia heat up the middle and upper atmosphere and increases North South temperature gradient.
- This increases convective activity in South Asia which causes convergence of water vapour in South Asia.
- Black carbon also increases the number of cloud condensation nuclei in the atmosphere.
About Black Carbon:

- Black carbon is the sooty black material emitted from gas and diesel engines, coal-fired power plants, and other sources that burn fossil fuel.
- It comprises a significant portion of particulate matter or PM, which is an air pollutant.
Impact of black carbon:
- Climate impacts: It has a warming impact that is 460-1,500 times stronger than CO2 on climate.
- It converts incoming solar radiation to heat.
- It influences cloud formation and impacts regional circulation and rainfall patterns.
- Health impacts- With size of 2.5 micrometres (PM2.5) or smaller, it can penetrate into lungs and facilitate transport of toxic compounds into the bloodstream.
- 5 can cause premature death and cause heart and lung disease, strokes, heart attacks, chronic respiratory disease like bronchitis, asthma and pneumonia.
- Impacts on ecosystem and vegetation- if deposited on plant leaves it will decrease its capability of photosynthesis and thus reduce food production.
- It can reduce sunlight that reaches the earth and modify rainfall patterns.
About Black Carbon aerosols:
- It is produced by the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels and biomass.
- It has strong absorption of solar radiation like- visible and infrared radiation.
- It is also called soot and is part of particulate matter above PM2.5.
- Thus, it contributes to pollution and Global warming.
- It can increase the temperature of atmosphere and darken surfaces, specifically snow and ice.
- It has short lifetime in atmosphere and gets removed in 1-2 weeks, so its impacts tend to be more regional rather than global.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Among the following crops, which one is the most important anthropogenic source of both methane and nitrous oxide ? (2022)
- Cotton
- Rice
- Sugarcane
- Wheat
Q.2) In the Guidelines, statements: context of WHO consider the Air Quality following
- The 24-hour mean of PM2.5 should not exceed 15 ug/m³ and annual mean of PM 2.5 should not exceed 5 µg/m³.
- In a year, the highest levels of ozone pollution occur during the periods of inclement weather.
- PM10 can penetrate the lung barrier and enter the bloodstream.
- Excessive ozone in the air can trigger asthma.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1 and 4 only
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1 and 2 only











