IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Recently the Government of India has approved a proposal for the sale of 30 Lakh Metric Tonnes of wheat under the Open Market Sale Scheme.
About the Open Market Scheme:
- It refers to selling of foodgrains by Government / Government agencies at predetermined prices in the open market from time to time.
- It aims to enhance the supply of grains especially during the lean season and thereby to moderate the general open market prices especially in the deficit regions.
- In addition to maintaining buffer stocks and making a provision for meeting the requirement of the Targeted Public Distribution Scheme and Other Welfare Schemes (OWS), Food Corporation of India (FCI) on the instructions from the Government, sells wheat and rice in the open market from time to time.
- For transparency in operations, the FCI has switched over to e- auction for sale under Open Market Sale Scheme (Domestic).
- The FCI conducts a weekly auction to conduct this scheme in the open market using the platform of commodity exchange NCDEX (National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange Limited).
- The State Governments/ Union Territory Administrations are also allowed to participate in the e-auction, if they require wheat and rice outside TPDS and OWS.
The present form of OMSS comprises 3 schemes as under:
- Sale of wheat to bulk consumers/private traders through e-auction.
- Sale of wheat to bulk consumers/private traders through e-auction by dedicated movement.
- Sale of Raw Rice Grade ‘A’ to bulk consumers/private traders through e-auction.
About Food Corporation of India:
- Food Corporation of India (FCI) is a Public Sector Undertaking, under the Department of Food and Public Distribution, Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution.
- FCI is a statutory body set up in 1965 under the Food Corporations Act 1964.
- It was established against the backdrop of major shortage of grains, especially wheat.
- Simultaneously, Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) was created in 1965 to recommend remunerative prices to farmers.
- It has primary duty to undertake purchase, store, move/transport, distribute and sell food grains and other foodstuffs.
- FCI coordinates its functions through a country-wide network of offices with Headquarters at New Delhi with five Zonal Offices, twenty-five Regional Offices and 170 District Offices under its control.
Source: NewsOnAir
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: The Supreme Court has relaxed the guidelines for ‘advance medical directive’ that it issued in its 2018 judgment by which it had legalised passive euthanasia under certain circumstances. There is a long legal history to the matter.
About Euthanasia:
- Greek words: The term Euthanasia comes from two Ancient Greek words: ‘Eu’ means ‘Good’, and ‘thantos’ means ‘death’, so Euthanasia means good death.
- Euthanasia can be also divided into two types according to means of death.
- Active Euthanasia: It is also known as ‘Positive Euthanasia’ or ‘Aggressive Euthanasia’.
- It refers to causing intentional death of a human being by direct intervention.
- For example, by giving lethal doses of a drug or by giving a lethal injection.
- Active euthanasia is usually a quicker means of causing death and all forms of active euthanasia are illegal.
- Passive Euthanasia: It is also known as ‘Negative Euthanasia’ or ‘Non-Aggressive Euthanasia’.
- It is intentionally causing death by not providing essential, necessary and ordinary care or food and water.
- It implies discontinuing, withdrawing or removing artificial life support systems.
- Passive euthanasia is usually slower and more uncomfortable than active.
- Most forms of voluntary, passive and some instances of non-voluntary, passive euthanasia are legal.
New guidelines:
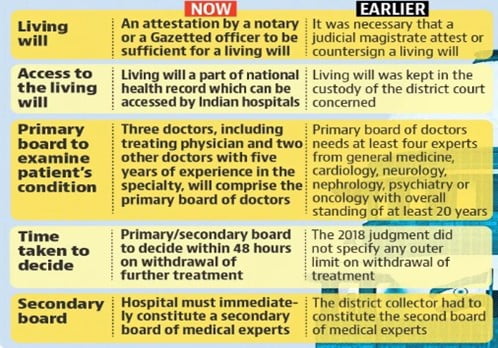
- Living will:
- 2018 guideline: It will be in the custody of the district court concerned.
- New guideline: It will be a part of the national health digital record which can be accessed by hospitals and doctors from any part of the country.
- Primary board:
- 2018 guideline: The primary board should comprise at least four experts from the fields of general medicine, cardiology, neurology, nephrology, psychiatry or oncology — with overall standing in the profession for at least 20 years.
- New guideline: Team of three doctors, including the treating physician and two other doctors with five years of experience in the concerned specialty will comprise the primary board.
- Time limit for Primary board:
- 2018 guideline: No time limit specified.
- New guideline: Board will preferably decide within 48 hours on the withdrawal of further treatment.
- Secondary medical board:
- 2018 guideline: The district collector concerned had to constitute the second board of medical experts.
- New guideline: If the primary medical board certifies that the treatment should be withdrawn in terms of the instructions contained in the living will, the hospital shall immediately constitute a secondary medical board.
- It comprising of a doctor nominated by the chief medical officer of the district concerned and two subject experts of the relevant specialty with minimum five years’ standing who were not part of the primary board.
- Time limit for Secondary medical board:
- 2018 guideline: There was no timeline specified secondary medical board in the 2018 judgment
- New guideline: Board will also decide preferably within 48 hours. They may also need to reflect on the conditions or consult others.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) What is the importance of using Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines in India? (2020)
- These vaccines are effective against pneumonia as well as meningitis and sepsis.
- Dependence on antibiotics that are not effective against drug-resistant bacteria can be reduced.
- These vaccines have no side effects and cause no allergic reactions.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Developed by an IIT Madras-incubated startup, BharOS is being pitched as India’s answer to the Google-owned Android and Apple’s iOS, the two most dominant mobile operating systems in the world.
About BharOS:

- BharOS is an Android Open Source Project and was developed by JandK Operations Private Limited (JandKops), a non-profit organisation incubated at IIT Madras.
- The project aims to reduce the dependence on foreign OS in smartphones and promote the use of locally developed technology.
- Funded by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), the indigenous mobile operating system wants to cater to the approximately 100 crore mobile phone users in India.
- Union Education and Skill Development and Entrepreneurship Minister along with Minister for Railways, Communications, Electronics and Information Technology successfully tested the ‘BharOS’, a Made In India mobile operating system developed by IIT Madras.
- What sets BharOS apart from Android, is that it is free from Google Services and Apps.
- Google has used its preinstalled apps and services to collect data, sometimes without explicitly asking a user.
- Similarly, other apps from Google’s Play Store share data with third-party services.
- BharOS does not come with any such preinstalled services or apps, and hence, is deemed to be more secure.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to Web 3.0, consider the following statements:
- Web 3.0 technology enables people to control their own data.
- In Web 3.0 world, there can be blockchain based social networks.
- Web 3.0 is operated by users collectively rather than a corporation
Which of the following given above are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to “Software as a Service (SaaS)”, consider the following statements:
- SaaS buyers can customise the user interface and can change data fields.
- SaaS users can access their data through their mobile devices.
- Outlook, Hotmail and Yahoo! Mail are forms of SaaS.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Chairman, Khadi and Village Industries Commission recently released margin money grant of Rs 100.29 crore to 3223 beneficiaries of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Uttarakhand under the Prime Minister Employment Generation Program (PMEGP) implemented by KVIC in Varanasi.
About Prime Minister Employment Generation Program (PMEGP):
- The Government of India approved the introduction of a credit linked subsidy programme called Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP) in 2008 for generation of employment opportunities through establishment of micro enterprises in rural as well as urban areas.
- It allows entrepreneurs to set up factories or units.
- It is a central sector scheme being administered by the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MoMSME).
- Implementing Agency at the National Level: Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) – a statutory organization under the administrative control of the Ministry of MSME.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Any individual, above 18 years of age.
- Only new projects/units are considered for sanction of loans.
- Self-help groups that have not availed benefits under any other public scheme, societies, production co-operative societies, and charitable trusts.
- Maximum Cost of Project/Unit Admissible:
- Manufacturing Sector: 50 lakh
- Service Sector: 20 lakh
- Government Subsidy:
- Rural Areas: 25% for general category and 35% for special category, which includes SC/ST/OBC/Minorities, NER, Hill and Border Areas, transgender, physically disabled, north eastern region, aspirational and border district applicants.
- Urban Areas: 15% for general category and 25% for special category.
- Loans are provided by Public Sector Banks, Regional Rural Banks, Co-operative Banks and Private Scheduled Commercial Banks approved by respective State Task Force Committee.
About Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC):
- The Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) is a statutory body formed in April 1957 (During 2nd Five Year plan) by the Government of India, under the ‘Khadi and Village Industries Commission Act of 1956’.
- It is an apex organization under the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, about khadi and village industries within India.
- The commission has three main objectives:
- The Social Objective – Employing in rural areas
- The Economic Objective – Providing saleable articles
- The Wider Objective – Creating self-reliance amongst people and building up a strong rural community spirit.
- KVIC implements the following schemes:
- Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP).
- Interest Subsidy Eligibility Certificate (ISEC) Scheme.
Source: PIB
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to Urban Cooperative Banks in India, consider the following statements:
- They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments.
- They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
- They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1996
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2021)
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Maternity Benefit Amendment Act, 2017? (2019)
- Pregnant women are entitled for three months pre-delivery and three months post-delivery paid leave.
- Enterprises with creches must allow the mother minimum six creche visits daily.
- Women with two children get reduced entitlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Over the years, scientists have realised that imprinting acts as a database for the immune system, helping it put up a better response to repeat infections.
About Immune Imprinting:
- Immune imprinting is a tendency of the body to repeat its immune response based on the first variant it encountered through infection or vaccination — when it comes across a newer or slightly different variant of the same pathogen.
- The phenomenon was first observed in 1947, when scientists noted that “People who had previously had flu, and were then vaccinated against the current circulating strain, produced antibodies against the first strain they had encountered”, according to a report published in the journal Nature.
- At the time, it was termed the ‘original antigenic sin’ but today, it’s commonly known as imprinting.
- Working : After our body is exposed to a virus for the first time, it produces memory B cells that circulate in the bloodstream and quickly produce antibodies whenever the same strain of the virus infects again.
Issue associated with Imprinting:
- The problem occurs when a similar, not identical, variant of the virus is encountered by the body.
- In such cases, the immune system, rather than generating new B cells, activates memory B cells, which in turn produce antibodies that bind to features found in both the old and new strains, known as cross-reactive antibodies.
- Although these cross-reactive antibodies do offer some protection against the new strain, they aren’t as effective as the ones produced by the B cells when the body first came across the original virus.
Ways to deal with Immune Imprinting:
- Nasal vaccines: Some scientists have said nasal vaccines might be better at preventing infections than injected ones.
- They believe the mucous membranes would create stronger protection, despite carrying some imprint of past exposure.
- Spacing vaccine shots: Researchers are also trying to find if spacing out coronavirus vaccine shots on an annual basis, could help with the problem of imprinting.
- Pan-sarbecovirus vaccines: There’s also considerable effort directed toward developing what’s called pan-sarbecovirus vaccines that will protect against all COVID-causing variants and maybe even protect against other SARS and related viruses.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body ? (2022)
- They protect the body from environmental allergens.
- They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
- They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
- They protect the body from the diseases caused by pathogens.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography and Environment
Context: Recently, Steering Committee of the Ken-Betwa Link Project (KBLP) held its third meeting in New Delhi.
About the project:
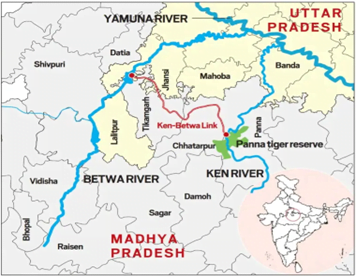
- The link will be in the form of a canal that will be fed by the new Daudhan Dam on the Ken, to be built within the Panna Tiger Reserve.
- The dam will generate 103MW of hydroelectric power.
- In phase-I, the Daudhan Dam complex and its subsidiary units such as the Low-Level Tunnel, High-Level Tunnel, Ken-Betwa Link Canal, and powerhouses will be completed.
- Construction of the Lower Orr Dam, Bina Complex Project, and Kotha Barrage will be progressed in phase II of the project.
Significance of the Project:
- With this project, the government aims to benefit the water-starved Bundelkhand region, spread to several other districts of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
- The project is expected to boost socio-economic prosperity in the backward region of Bundelkhand, on account of increased agricultural activities and employment.
Concern about the project:
- May incur an estimated loss of 58.03 square kilometres (10.07 per cent) of critical tiger habitat (CTH) in the reserve.
- An indirect loss of 105.23 sq km of CTH because of habitat fragmentation and loss of connectivity due to submergence.
- High reservoir-dam on the Ken River in the Panna National Park will impact ecology of important tiger reserve and its habitat.
- It has high chances of getting drowned if project gets completed.
- On the downstream of Panna national park lies the Ken Gharial Sanctuary which will severely impact critically endangered Gangetic gharial (Gavialis gangeticus).
- Standing Committee of the NBWL has not considered the impact of the project on the gharial sanctuary.
- Project has not received full forest clearance and its environment approval is pending before the National Green Tribunal (NGT).
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Gandikota canyon of South India was created by which one of the following rivers ? (2022)
- Cauvery
- Manjira
- Pennar
- Tungabhadra
Q.2) Consider the following pairs:
Reservoirs : States
- Ghataprabha : Telangana
- Gandhi Sagar : Madhya Pradesh
- Indira Sagar : Andhra Pradesh
- Maithon : Chhattisgarh
How many pairs given above are not correctly matched? (2022)
- Only one pair only
- Only two pairs only
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Syllabus
- Prelims – History and Art and Culture
Context: In the recent excavations, the Structural Complex of the Buddhist Monastery was found in the continuation of large Stupa, Black and Red ware pottery, and Sculptures discovered from excavation done 50 years ago at the same site in West Bengal.
About Buddhist Monastery:
- A monastery is a community of men or women (monks or nuns), who have chosen to withdraw from society, forming a new community devoted to religious practice.
- The word monk comes from the Greek word monos, which means alone.
- Buddhism, the first Indian religion to require large communal and monastic spaces, inspired three types of architecture.
- Stupa, vihara and chaitya are part of Buddhist and Jaina monastic complexes but the largest number belongs to the Buddhist religion.
Significance of the excavations:
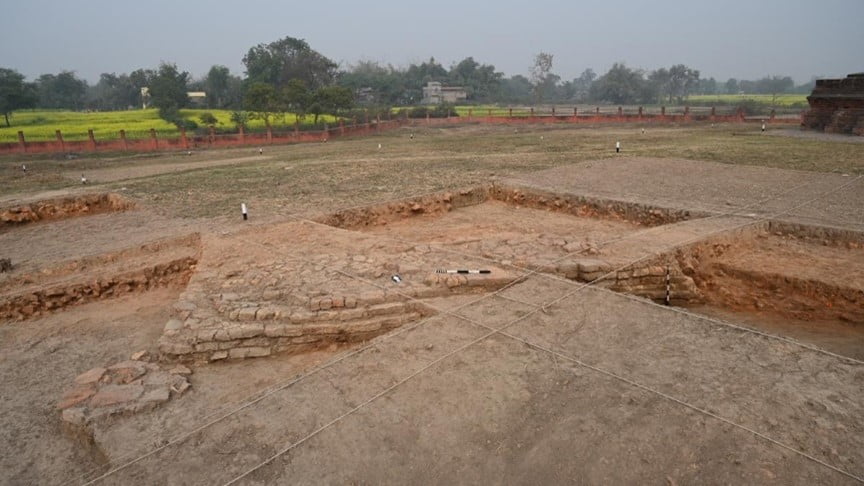

- The site was initially excavated fifty years ago between 1972 and 1975 when archaeologists from ASI found a Buddhist Stupa at the site.
- Excavations can help in finding the spread of Buddhism in the South West Bengal region.
- The discovery is also significant since black and red ware pottery from the chalcolithic age makes the village settlement on river Damodar possible.
- The complex makes the site religious while the settlement makes the site secular in nature.
- The stupa found is large compared to stupas found from other Buddhist sites in the state like Karnasubarna in Murshidabad, Moghalamari in Paschim Medinipur, and Jagjivanpur in Malda where smaller votive stupas were found.
Viharas:
- It was the ancient Indian term for a Buddhist monastery.
- Originally, viharas were dwelling places used by wandering monks during the rainy season but eventually they evolved into centers of learning and Buddhist architecture through the donations of wealthy lay Buddhists.
- Life in “Viharas” was codified early on.
- It is the object of a part of the Pali canon, the Vinaya Pitaka or “basket of monastic discipline.”
- Typical large sites such as the Ajanta Caves, Aurangabad Caves, Karli Caves, and Kanheri Caves contain several viharas.
- A rock-cut viharas at Ellora is an example of vihara.
Chaityas:
- It refers to a shrine, sanctuary, temple or prayer hall in Indian religions.
- Most early examples of chaitya that survive are Indian rock-cut architecture
- Chaityas have a gigantic hall with high vaulted roof, with a lot of sculpture work on the pillars and the entrance
- The largest Chaitya-Griha among all Buddhist monuments in India is the Karle caves.
- Many Chaityas show a stupa at the back.
- Chaityas were carved either as rectangular halls or apsidal vault-roof or apsidal vault pillarless halls.
Stupa Architecture :
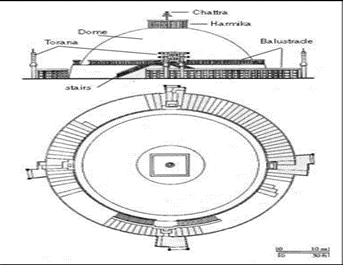
- The central structure consists of a hemispherical dome on a base, with a relic chamber deep within. The dome symbolizes, among other things, the dome of heaven enclosing the earth.
- It is surmounted by a squared railing (harmika) that can be said to represent the world mountain.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to Indian history, consider the following pairs:
Historical person Known as
- Aryadeva Jaina scholar
- Dignaga Buddhist scholar
- Nathamuni Vaishnava scholar
How many pairs given above are correctly matched ?
- None of the pairs
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- All three pairs
Q.2) Which one of the following ancient towns is well known for its elaborate system of water harvesting and management by building a series of dams and channelising water into connected reservoirs? (2021)
- Dholavira
- Kalibangan
- Rakhigarhi
- Ropar
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently during the Second National Conference of Chief Secretaries, the Prime Minister launched the Aspirational Blocks Programme (ABP).
- This transformational programme focuses on improving governance to enhance the quality of life of citizens in the most difficult and underdeveloped blocks of India by converging existing schemes, defining outcomes, and monitoring them on a constant basis.
About Aspirational Blocks Programme:
- An inter-ministerial committee in consultation with states had identified 500 blocks from across 28 states and four Union territories.
- In each of them, the ABP will focus on monitoring 15 key socio-economic indicators (KSIs) categorised under major sectors namely:-
- Health and nutrition
- Education
- Agriculture and water resources,
- Financial inclusion and skill development
- Basic infrastructure
- Social development.
- These themes were selected for facilitating holistic development of every block with states having the flexibility to include additional state-specific KSIs to address local challenges.
- The KSIs will be tracked on a real-time basis and periodic rankings will be released across key thematic areas to foster a healthy and dynamic competition among the blocks to encourage data-driven governance.
Objectives of Programme:
- The ABP aims to address the inequalities by improving governance and last mile service delivery at the block level.
- As key drivers of this initiative, states are expected to guide, support, review and build capacity of relevant officers to drive progress under this programme.
- Under the leadership of the district administration, the officers at the block level will improve critical last mile service delivery.
- They will focus on improving the infrastructure at the block level to aid social welfare development.
- Several departments of the block administration will converge and work in union to bridge critical administrative gaps and sustain these developments and improvements for a long period of time.
- It also provides a common platform for all block administrations to showcase their best practices and learnings.
- The ABP is built on the success of the government’s flagship Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP) launched in 2018 across 112 under-developed districts of India.
Significance of Blocks or Development Blocks:
- The focus on blocks echoes the historic importance of blocks or development blocks introduced in 1952 to provide for a substantial increase in the country’s agricultural programme, and for improvements in systems of communication, in rural health and hygiene, and in rural education.
- Development blocks ensure that a larger than proportionate share of development reaches the marginalised and vulnerable sections of the population by building social and economic infrastructure.
- As an administrative and monitoring unit, the block ensures that a “one-size-fits-all” approach is not applied to every part of the country.
- Instead, the block administration can adopt customised approaches towards improving socioeconomic indicators based on the context of the region and the most emergent needs.
Case study:
- For example, Paschimi Singbhum, a district in Jharkhand and a left-wing extremism-affected area, has raised registration of pregnant women within the first trimester from just 39 per cent in 2018 to 91 per cent in 2022.
- Districts such as Gumla in Jharkhand, Karauli in Rajasthan, Namsai in Arunachal Pradesh, and Dhalai in Tripura have increased the percentage of institutional deliveries from around 40 per cent to more than 90 per cent.
- Kupwara in Jammu and Kashmir has increased the percentage of secondary schools with functional electricity from less than 50 percent in 2018 to more than 95 per cent in 2022.
- Districts like Dhenkanal in Odisha, where less than 50 per cent children were immunised up until 2018, have now gone beyond the 90 per cent immunisation rate.
- The Finance Minister in her Union Budget speech of 2022 mentioned that 95 per cent of 112 aspirational districts have made significant progress in major indicators such as health, nutrition, financial inclusion, and skill development.
However, she also highlighted that some blocks continue to under-perform. The reasons for this can be multi-layered i.e. difficult terrain, lack of resources, historical injustice, social marginalisation and community vulnerability, among others.
Way Forward:
ABP will aid the achievement of critical targets identified under the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and enable the blocks to contribute to India’s GDP. The programme strives to protect the rights and uphold the dignity of every single citizen by increasing their awareness and enhancing access to government schemes. A “viksit” block is the foundation for a “viksit” Bharat. This forward-looking programme will leverage the three Cs of convergence, collaboration, and competition to achieve this vision.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding Open Market Sale Scheme:
- It refers to selling of foodgrains by Government / Government agencies at predetermined prices in the open market from time to time.
- For transparency in operations, the FCI has switched over to e- auction for sale under Open Market Sale Scheme (Domestic).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements regarding Food Corporation of India:
- FCI is a statutory body set up in 1965 under the Food Corporations Act 1964.
- It is a Public Sector Undertaking, under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- FCI coordinates its functions through a country-wide network of offices with Headquarters at Mumbai.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
Q.3) The Prime Minister Employment Generation Programme is being administered under
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
- Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
- Ministry of Finance
- Prime Minister’s Office
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 25th January 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 24th January – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – c











