Science and Technology
Context: The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) recently announced that the James Webb Space Telescope has discovered its first new exoplanet.
- Researchers have labelled the planet as LHS 475 b, and it’s roughly the same size as Earth.
About Exoplanets:
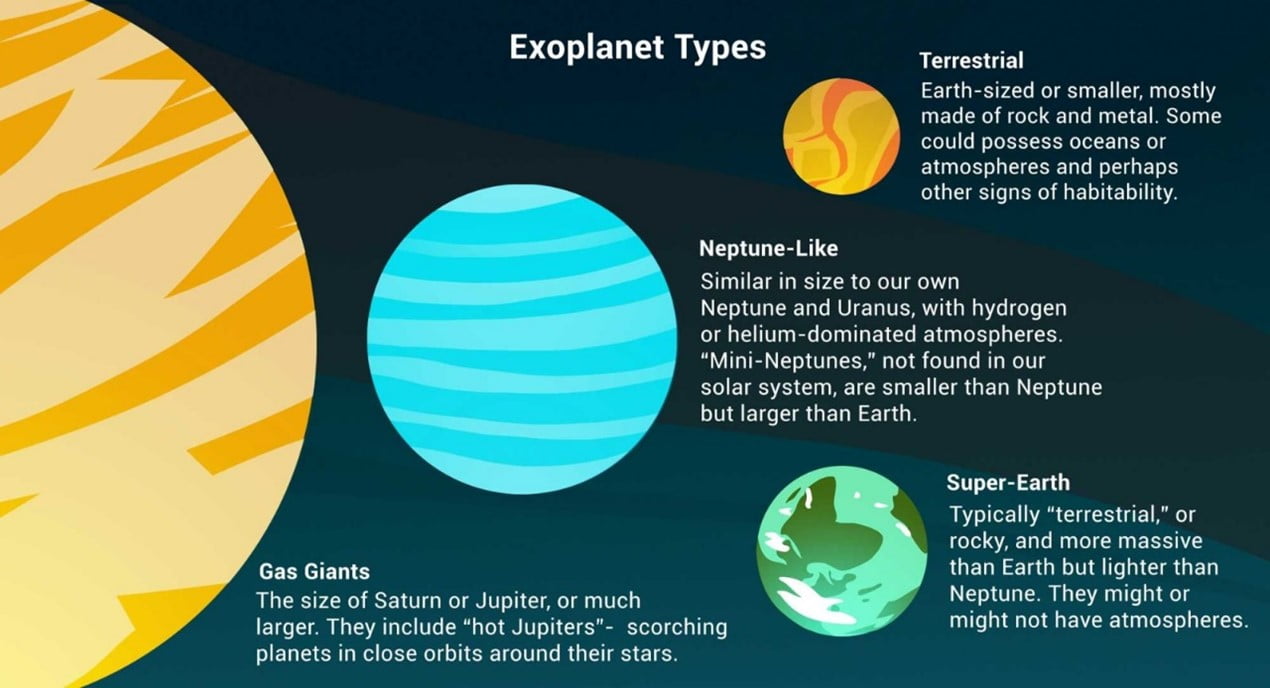
- An exoplanet is any planet beyond our solar system.
- Most orbit other stars, but free-floating exoplanets, called rogue planets, orbit the galactic centre and are untethered to any star.
- They can be gas giants bigger than Jupiter or as small and rocky as Earth.
- They are also known to have different kinds of temperatures — boiling hot to freezing cold.
- Scientists rely on indirect methods for discovering exoplanets, such as the transit method, which is measuring the dimming of a star that happens to have a planet pass in front of it.
About red dwarf stars:
- Such types of stars are the most common and smallest in the universe.
- As they don’t radiate much light, it’s very tough to detect them with the naked eye from Earth.
- However, as red dwarfs are dimmer than other stars, it is easier to find exoplanets that surround them.
- Therefore, red dwarfs are a popular target for planet hunting.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best reflects the idea behind the “Fractional Orbital Bombardment System” often talked about in media?
- A hypersonic missile is launched into space to counter the asteroid approaching the Earth and explode it in space.
- A spacecraft lands on another planet after making several orbital motions.
- A missile is put into a stable orbit around the Earth and deorbits over a target on the Earth.
- A spacecraft moves along a comet with the same speed and places a probe on its surface.
















