History and Art and Culture
Context: A recent excavation at Juna Khatiya village of Kutch district Gujarat has revealed some new findings on burial practice of Harrapan and early Harrapan times.
- Juna Khatiya village is a biggest cemetery of Harappan era. It has around 500 graves from 3,200 BCE to 2,600 BCE era.
Important findings from the Juna Khatiya village:
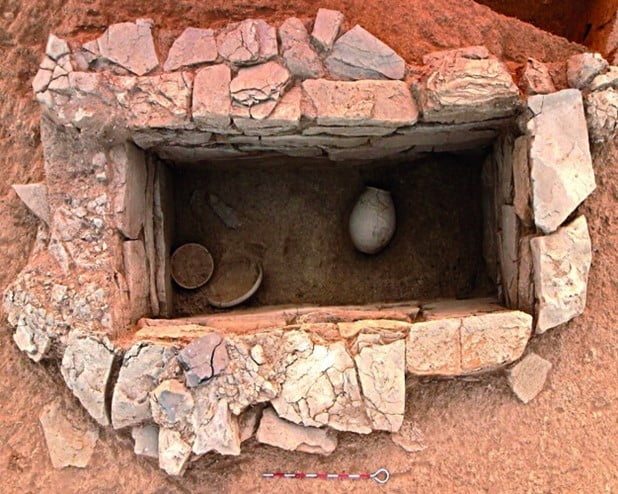

- Burial structures, secondary memorials, cremation sites and pot burials.
- Burial structures shapes vary from rectangular to oval or circular.
- Rows of graves with- skeletal remains, ceramic pots, plates and vases, beaded jewellery, and animal bones that piqued their interest.
- Region demonstrates transition from earth-mound burials to stone graves.
- Pottery have features and style similar to early Harappan sites in Sindh and Baluchistan.
- Rectangular graves were made of shale and sandstone, common rocks in the region.
- They were cut into natural soil without stone facings.
- Construction of cemetery: Pebbles of local rock, basalt, soil, sand, etc were used and clay was used to bind them together.
- Items like clay bowls and dishes, prized possessions like beads and bangles of terracotta, seashells, and lapis lazuli were placed with dead.
- Majority of burial pits had five to six pots.
- There is no metal artefact found.
- Some of burial structures have boulders of basalt as coverings.
- In few cemeteries bases of the pits have stone paving too.
- Bases of some pits are lined with soil that is different in colour and texture from other layers.
- Burials were oriented in different directions – some are along east-west axis, some along north- south orientation.
Significance of findings in Juna Khatiya village:
- Juna Khatiya can help in understanding cultural exchange between the Sindh and Gujarat regions in Early Harappan period due to the similar artefacts and customs.
Burial practices of Harappan/Indus Valley Civilization:
- Specific individuals, communities, and societies had their own methods of burial which suggests religious and cultural diversity.
Three types of burial customs:
- Complete burial of intact bodies.
- Full cremation with burial of bones or ashes- most common.
- Partial burials containing only the bones of the deceased.
- Mohenjo-daro: Most cremation urns did not contain human bone remains, but ornaments possessed during life, animal bones, ash and charcoal were found.
- Majority of corpses were mummified in the act of death, as opposed to being disposed of later.
- Only few populations were buried formally in ground, which means those people enjoyed some important status in society.
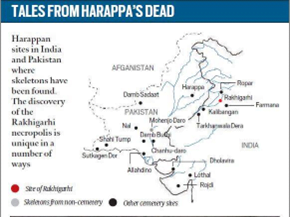
- Rakhigarhi (Haryana): Most of the burial pits were rectangular in shape, with vertically cut sides and flat bottoms.
- They were generally arranged on the north-south axis with the head to the north.
- Graves were humble in nature with exotic items like- inscribed seals or ritual objects.
- High ranking individuals, including women were buried wherein the soil had been built up with pots upon which the body was laid.
- These graves tended to be laid with bricks.
- Many votive pots in male graves indicates women were not considered equal to male citizens.
Source: Times of India
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) According to Kautilya’s Arthashastra, which of the following are correct?
- A person could be a slave as a result of a judicial punishment.
- If a female slave bore her master a son, she was legally free.
- If a son born to a female slave was fathered by her master, the son was entitled to the legal status of the master’s son.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which one of the following ancient towns is well known for its elaborate system of water harvesting and management by building a series of dams and channelising water into connected reservoirs? (2021)
- Dholavira
- Kalibangan
- Rakhigarhi
- Ropar











