Science and Technology
Context: Scientists from South Korea have developed a new water purification system that can quickly and efficiently filter out microplastics. Crucially, the polymer used is relatively inexpensive with excellent adsorption performance and good photothermal properties.
About Microplastics:
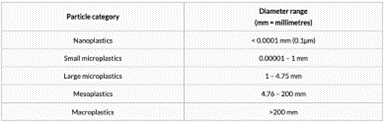
- Microplastics are those particles with less than 5 millimeters (0.2 inches).
- There are two types:
- primary microplastics and
- secondary microplastics.

- Primary microplastics are directly designed for commercial purposes:
- Nurdles: small pellets that put together, melted and molded to make larger plastic shapes;
- Microbeads: which are used in personal care products to help scrub off dead skin;
- Fibers: many clothes today are made of synthetic plastic fibres like nylon and polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
- Secondary microplastics are formed as large, original plastic pieces break down into millions of smaller pieces.
Major sources of Microplastics:
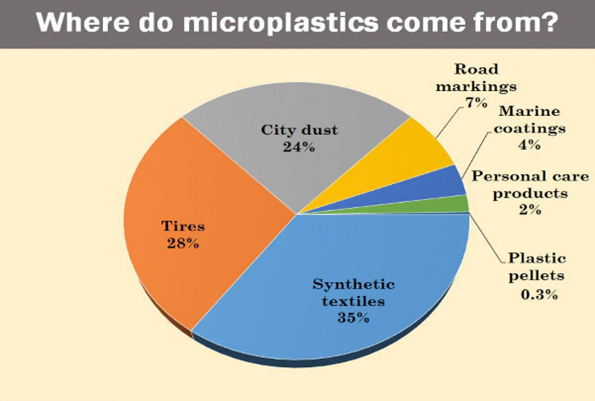
- Plastic materials are either originated at land or at the ocean.
- Around 70-80% of ocean plastics have land-based sources, while 20-30% of plastics come from marine sources.
- Of the plastic materials coming from marine sources, half is estimated to be caused by fishing fleets that leave behind fishing nets, lines, ropes, and sometimes abandoned vessels.
- Regarding land waste, discarded plastic materials enter the marine environment as trash, industrial discharge, or litter via inland waterways, wastewater outflows, and wind transport.
- While 25% of land-based discharges come from within the waste management system, the largest slice, 75% is uncollected waste.
Effects of microplastics on human health:
- A case of the World Health Organization (WHO) claims with respect to drinking water, that “microplastics are increasingly found in drinking water, but there is no evidence so far that this poses a risk to humans.”
- It is also known that the human body’s excretory system eliminates microplastics, likely disposing of > 90% of ingested micro- and nano plastic via faeces.
- However, other studies suggest microplastics with particular characteristics can move across living cells and impact the immune system and cell health.
- Ingested microplastics may cause inflammation in tissue, cellular proliferation, and necrosis and may compromise immune cells.
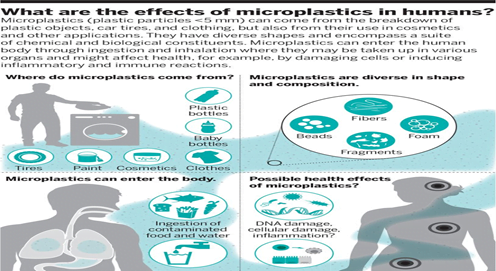
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements:
- Other than those made by humans, nanoparticles do not exist in nature.
- Nanoparticles of some metallic oxides are used in the manufacture of some cosmetics.
- Nanoparticles of some commercial products which enter the environment are unsafe for humans.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2022)
- 1 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
Q.2) “Triclosan” considered harmful when exposed to high levels for a long time, is most likely present in which of the following? (2022)
- Food preservatives
- Fruit ripening substances
- reused plastic containers
- Toiletries











