History and Art and Culture
Context: Recently, actor Naseeruddin Shah was in news for praising Akbar’s ‘broad-mindedness and tolerance of all faiths.’
About Akbar :
- Dynasty:Timurid; Mughal
- Predecessor:Humayun
- Successor:Jahangir
- Biography:Akbarnama; Ain-i-Akbari
- Mausoleum:Sikandra, Agra
- He was the son of Nasiruddin Humayun and succeeded him as the emperor in the year 1556.
- He was born in Umarkot (which is now in Sindh province, Pakistan), and died, in Agra, India.
- He extended Mughal power over most of the Indian subcontinent and he reigned from 1556 to 1605.
- He established a centralized system of administration and adopted a policy of marriage alliance and diplomacy.
- Biography by : Abul Fazal
Administration
- The Emperor himself was the supreme governor of the empire.
- He retained ultimate judicial, legislative, and administrative power above anyone else.
- He introduced the Mansabdari system to effectively organize the Military.
- He was assisted inefficient governance by several ministers –
- Vakil-chief adviser to the King over all matters
- Diwan-minister in charge of finance
- Sadar-i-sadur– religious advisor to the King
- Mir Bakshi-the one who maintained all records
- Daroga-i-Dak Chowki – to oversee proper enforcement of law
- Muhtasib– to oversee the postal department.
Revenue System:
- The land was divided into four classes according to their productivity – Polaj, Parauti, Chachar, and Banjar.
- Polaj – Throughout the empire, Polaj was the ideal and best type of land. This land was always cultivated and was never left fallow.
- Parauti – This was the land that was temporarily kept out of cultivation in order to regain its fertility.
- Chachar – Chachar was a type of land that was allowed to lie fallow for three or four years before being cultivated again.
- Banjar – Banjar was the worst type of land that had been left uncultivated for five years or more.
- Bigha was the unit of land measurement.
- Land revenue was paid either in cash or in kind.
- Dahsala system of land taxation was introduced under the reign of Akbar.
Judicial Reforms:
- Hindu customs and laws were referred to in the case of Hindu subjects for the first time during Akbar’s reign.
- The Emperor was the highest authority in Law and the power to give capital punishment rested solely with him.
- The major social reform introduced by Akbar was the abolition of the Pilgrimage Tax for Hindus in 1563 as well as the Jazia tax.
- He discouraged child marriage and encouraged widow remarriage.
- He craved religious unity for his people and with that vision founded the sect Din-i-Ilahi (Faith of the Divine).
Architecture and Culture
- Among the architectural marvels commissioned during his rule are the Agra Fort (1565–1574), the town of Fatehpur Sikri (1569–1574) with its beautiful Jami Masjid and Buland Darwaza, Humayun’s Tomb (1565-1572), Ajmer Fort (1563-1573), Lahore Fort (1586-1618) and Allahabad Fort (1583-1584).
- Akbar’s Nava Ratnas or the Nine Gems : Abul Fazel, Faizi, Mian Tansen, Birbal, Raja Todar Mal, Raja Man Singh, Abdul Rahim Khan-I-Khana , Fakir Aziao-Din and Mullah Do Piaza.
Important Conquests:
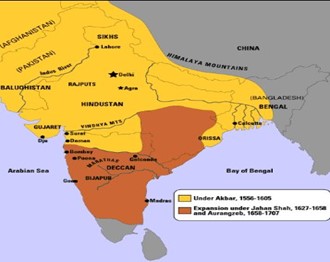
- He defeated Hemu in the second battle of Panipat in 1556.
He consolidated his supremacy over most of north and central India and then over Rajputana by 1576 with the Battle of Haldighati. - Akbar brought in Gujarat (1584), Kabul (1585), Kashmir (1586-87), Sindh (1591), Bengal (1592), and Kandahar (1595) within the Mughal territory.
- The Mughal army led by General Mir Mausam also conquered parts of Baluchistan around Quetta and Makran by 1595.
- By 1600, Akbar had captured Burhanpur, Asirgarh Fort, and Khandesh in Deccan.
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to the cultural history of India, consider the following statements (2018)
- White marble was used in making Buland Darwaza and Khankah at Fatehpur Sikri
- Red sandstone and marble were used in making Bara Imambara and Rumi Darwaza at Lucknow
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Ibadat Khana at Fatehpur Sikri was (2014)
- the mosque for the use of Royal Family
- Akbar’s private chamber prayer
- the hall in which Akbar held discussions with scholars of various religions.
- the room in which the nobles belonging to different religions gathered to discuss religious affairs
Q3) Who among the following Mughal Emperors shifted emphasis from illustrated manuscripts to the album and individual portrait?(2019)
- Humayun
- Akbar
- Jahangir
- Shah Jahan











