IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims -Economy
Context: Cabinet Approves revision in Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) rates for RABI Season, 2022-23 and for KHARIF Season, 2023 on Phosphatic and Potassic (P&K) fertilizers
About Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) Scheme
- The Nutrient Based Subsidy Scheme provides subsidies for all non-urea-based fertilizers. Under the NBS regime – fertilizers are provided to the farmers at the subsidized rates based on the nutrients (N, P, K & S) contained in these fertilizers.
- Also, the fertilizers which are fortified with secondary and micronutrients such as molybdenum (Mo) and zinc are given additional subsidy.
- The subsidy on P&K fertilizers is announced by the Government on an annual basis for each nutrient on a per kg basis for Rabi and Kharif seasons.
- The subsidy on P&K fertilizers is being governed by NBS Scheme since 2010.
- It is being implemented by the Department of Fertilizers, Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers.
Significance of the NBS Scheme
- It will have the the two-fold benefit of ensuring availability of DAP and other P&K fertilizers to farmers at subsidized, affordable and reasonable prices and will also ensure rationalization of subsidy on P&K fertilizers .
- Balanced nutrient availability will improve soil health which in turn enhances yield of crops resulting in increased income to the farmers.
Concerns Related with NBS Scheme
- Imbalanced Price and Deteriorating Soil Health: All Non-Urea based fertilisers are regulated under NBS Scheme however on the other hand the prices of other on regulated fertilizers have gone up. This led to the more application of subsidised urea fertilizers on soil lead to soil nutrient imbalance.
- Costs of Subsidies: Fertilizer subsidies are the second-largest subsidy after food subsidies. Thus it leads to fiscal imbalances of budgets
- Diversion: Subsidized urea is being diverted to large purchasers, traders, or even non-agricultural consumers like plywood manufacturers and producers of animal feed. The government loses around Rs 6,000 crore annually due to illegal diversion of highly subsidised urea for industrial use.
- It has also been diverted to neighbouring countries like Bangladesh and Nepalthat leads to enhenaced border related crimes such as black marketing.
- Environmental Pollution: The compounded harmful effects of imbalanced fertilizer use are not only intensifying soil and atmospheric pollution but also impacting water bodies (eutrophication) and causing threat to biodiversity and human health.
MUST READ: Soil Health https://iasbaba.com/2022/12/soil-health/
SOURCE: PIB https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1924767
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to chemical fertilizers in India, consider the following statements: (2020)
- At present, the retail price of chemical fertilizers is market-driven and not administered by the Government.
- Ammonia, which is an input of urea, is produced from natural gas.
- Sulphur, which is a raw material for phosphoric acid fertilizer, is a by-product of oil refineries.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1only
- 2 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) The Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane is approved by the (2015)
- Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs
- Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices
- Directorate of Marketing and Inspection, Ministry of Agriculture.
- Agricultural Produce Market Committee
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: An undersea UAE-Gujarat gas pipeline proposed that connects Middle East with India.
About the Gas Pipeline Project
- A $5-billion, undersea UAE-Gujarat gas pipeline proposed, 2,000-km-long energy corridor connecting Middle East and India, a $5 billion project, can lead to an annual saving of about `7,000 crore in comparison with similar quantity of liquefied natural gas (LNG) import.
- South Asia Gas Enterprise (SAGE), an international consortium of companies in deepwater pipeline projects, has sought the support of ministry of petroleum and others to develop an undersea gas pipeline from Gulf to India.
- The proposed 2,000-km-long energy corridor connecting Middle East and India, a $5 billion project, can lead to an annual saving of about `7,000 crore in comparison with similar quantity of liquefied natural gas (LNG) import.
About SAGE
- South Asia Gas Enterprise Private Limited is a Private incorporated on 21 November 2005. It is classified as Non-govt company and is registered at Registrar of Companies, Delhi. It is promoted by the New Delhi based Siddho Mal Group, in Joint Venture with a UK-based Deepwater Technology Company.
- SAGE is working with a Global Consortium of some of the most reputed companies in the field of Deepwater Pipelines, to create a Multi-Billion Dollar “Energy Corridor” that can transport gas from the Middle East to India, bypassing the land route through Pakistan.
Significance of the project
- The proposed 2,000-km energy corridor connecting the Middle East and India will lead to an annual saving of about Rs 70 billion ($849.60 million).
- The route will run via Oman and UAE through the Arabian Sea, allowing import from Oman, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Turkmenistan and Qatar, a region with 2,500 trillion cubic feet of gas reserves.
- Qatar, Iran, Iraq and Turkmenistan together have enormous Natural Gas reserves to the tune of 2,000 trillion cubic feet (TCF) and SAGE plans to transport some of this to India through its Deepwater Pipeline Infrastructure. Dialogue and discussions with the above-mentioned countries are on at the Highest Levels. The option of Gas Swaps between these nations is also being explored.
- In addition, SAGE also plans to supply Natural Gas to Oman/ UAE on its Pipeline Route to India, and seeks to further build Cooperative Relations with the friendly Gulf and Middle East countries.
MUST READ: TAPI Gas Pipeline Project https://iasbaba.com/2022/01/india-central-asia-summit/
SOURCE: The Financial Express https://www.financialexpress.com/industry/5-billion-undersea-uae-gujarat-gas-pipeline-proposed/3089046/
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Snow Leopards spotted in Jammu & Kashmir’s Kishtwar National Park.
- The presence of the elusive snow leopards in Jammu and Kashmir’s Kishtwar High Altitude National Park has been confirmed by a research team of Department of Wildlife Protection through camera trap.
- Attributed as one of the seven snow leopard reserves under a project launched by Central Government, the Kishtwar High Altitude National Park lies in Doda District, about 40km north-east of Kishtwar Town.
- The park was established to conserve the snow leopard species, its prey populations and its fragile mountain habitat.
- Spread over an area of 400 sq km the park was declared a national park on 4 February 1981.
- With Rinnay River in the north, KibarNala catchment in the south, the Great Himalayas in the east and Marwa River in the west, the area lies in the Central Crystalline belt of the Great Himalayas. The altitude of the park ranges from 1700m to 4800m.
Snow leopards in India
- Snow leopards are distributed across the 100,146 sq. km of snowy forests in five Himalayan states – Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim & Arunachal Pradesh.
- Hemis National Park, Gangotri National Park, Khangchendzonga National park and Great Himalayan National Park are some protected areas where snow leopards are known to be found.
- It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List because the global population is estimated to number fewer than 10,000 mature individuals and is expected to decline about 10% by 2040.
MUST READ: India’s High Altitude National Parks
SOURCE: The Indian Express
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2013)
- Nokrek Biosphere Reserve : Garo Hills
- Logtak (Loktak) Lake : Barail Range
- Namdapha National Park : Dafla Hills
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- None
Q.2) Which one of the following National Parks lies completely in the temperate alpine zone? (2019)
- Manas National Park
- Namdapha National Park
- Neora Valley National Park
- Valley of Flowers National Park
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: The National Medical Commission (NMC) issued a notification that obliges doctors to seek a transfer of their practice license when they move to another state.
About National Medical Commission
- The National Medical Commission Act of 2019 establishes the National Medical Commission (NMC), which is responsible for the creation and regulation of all elements of medical education, practice, and institutions.
- National Medical Commission consists of 25 members including
- The Chairperson, Presidents of Postgraduate Medical Education Boards, and Presidents of Undergraduate Medical Education Boards
- Director General of Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)
- Director General of Health Services.
- There are four boards in the National Medical Commission
- Under-Graduate Medical Education Board (UGMEB)- sets norms for undergraduate courses
- Post-Graduate Medical Education Board (PGMEB)- sets norms for post-graduate courses
- Medical Assessment and Rating Board– inspects and rates the medical education institutes
- Ethics and Medical Registration Board– regulates professional conduct of the doctors and registers them
- The draft National Medical Commission (NMC) bill 2022seeks to introduce a fifth autonomous body under the country’s apex medical education regulator to conduct the National Exit Test (NExT)
SOURCE: The New Indian Express https://www.newindianexpress.com/nation/2023/may/18/doctors-peeved-at-nmc-notificationon-licence-transfer-2576217.html
Syllabus
- Prelims – Schemes in news
Context: The Union Government launched Production Linked Incentive Scheme for IT hardware with Rs. 17,000 crore
About Production Linked Incentive Scheme for IT Hardware
- An updated production linked incentive (PLI) scheme for IT hardware, nearly doubling the overall outlay for the scheme to around Rs 17,000 crore. The tenure of the programme will be applicable for six years and the government expects investments worth Rs 2,430 crore in the scheme.
- The first version of the scheme was a laggard with only two companies – Dell and Bhagwati. PLI 2.0 scheme for the IT hardware sector that aims to boost domestic manufacturing and attract large investments and jobs over the coming years.
About Production Linked Incentive Scheme
- Objective: The objective is tomake domestic manufacturing globally competitive and to create global Champions in manufacturing.
- The strategy behind scheme is to offer companies incentives on incremental sales from products manufactured in India, over the base year. They have been specifically designed to
- boost domestic manufacturing in sunrise and strategic sectors
- curb cheaper imports and reduce import bills,
- improve cost competitivenessof domestically manufactured goods, and
- enhance domestic capacity and exports.
- The Union Budget 2021-22 announced an outlay of INR 1.97 Lakh Crores for the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes for 13 key sectors, to create national manufacturing champions and generate employment opportunities for the country’s youth.
- It was launched in April 2020, for the Large Scale Electronics Manufacturing sector, but later towards the end of 2020 was introduced for 10 other sectors. This scheme was introduced in line with India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat Campaign
SOURCE: The Indian Express https://indianexpress.com/article/india/cabinet-rs-17000-cr-it-hardware-pli-scheme-2-0-8614534/
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following is a purpose of ‘UDAY’, a scheme of the Government?
- Providing technical and financial assistance to start-up entrepreneurs in the field of renewable sources of energy
- Providing electricity to every household in the country by 2018
- Replacing the coal-based power plants with natural gas, nuclear, solar, wind and tidal power plants over a period of time
- Providing for financial turnaround and revival of power distribution companies
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) launched TAFCOP (Telecom Analytics for Fraud Management and Consumer Protection)module facilitates a mobile subscriber to check the number of mobile connections taken in his/her name
About TAFCOP Portal
- Tafcop portal gov.in has been developed by The Indian Government For Telecom Analytics For Fraud Management And Consumer Protection.
- It has been developed to help subscribers and consumers, to check the number of mobile connections working in their name and to take the appropriate action to regularize any additional mobile connections they may have.
About Sanchar Saathi Portal
- The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) launched the Sanchar Saathi portal, which enables people across India to track and block their lost or stolen mobile phones.
- Through this portal, people can also verify the authenticity of used devices before making a purchase, and track how many numbers are associated with their identity without their knowledge.
- Key sections of the portal include the Central Equipment Identity Register (CEIR) regarding blocking and tracking of phones, ‘Know Your Mobile’ feature that allows users to verify the authenticity of second-hand mobile phones, and the TAFCOP (Telecom Analytics for Fraud Management and Consumer Protection) facility to check numbers associated with an identity.
SOURCE: The Financial Express https://www.financialexpress.com/industry/lost-your-phone-a-portal-to-help-track-your-device/3090403/
Syllabus
- Prelims – Georaphy
Context: Militant activity has claimed more casualties in the Pir Panjal valley than in the Kashmir valley this year
About Important Himalayan Ranges
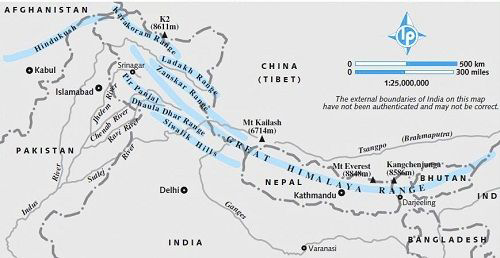
Image Link: https://i.pinimg.com/564x/6c/42/35/6c4235ccbc7753298bb77477d186215f.jpg
- The Himalayas, or Himalaya is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The Himalayas abut or cross five countries: Bhutan, India, Nepal, China, and Pakistan.
- The Himalayan range is bordered on the northwest by the Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges, on the north by the Tibetan Plateau, and on the south by the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Some of the world’s major rivers, the Indus, the Ganges, and the Tsangpo–Brahmaputra, rise in the vicinity of the Himalayas.
- Characteristics of Himalayan ranges
- It is composed of a series of several parallel or converging ranges.
- The ranges are separated by gorges and deep valleys creating a highly dissected and hog back topography.The southern slopes have steep gradients and the northern slopes have comparatively gentler slopes.
- The ranges are dissected by several passes that provides the critical transportantation and communication links. Major are Banihal, Zoji La, Nathula la, Khardung La etc
- The important divisions of Himalayas include
- The Trans Himalayas – Tibetan Himalayas
- The Greater Himalayas
- Lesser or Middle Himalayas
- Shiwaliks or Outer Himlayas
- The Easter Hills- Purvanchal Himalatayas
The Trans Himalayas
- Trans-Himalayas, eastward continuation of the most northerly ranges of the Himalayas in the southern part of the Tibet Autonomous Region of China.
- The Trans-Himalayas, mainly composed of granites and volcanic rocks of Neogene and Paleogene ag
- It is bounded by the Kailas (southwest), Nganglong Kangri (north), and Nyainqentanglha (southeast) mountain ranges and by the Brahmaputra (Yarlung Zangbo) River (south).
- Northern slopes of the range are extremely rugged
- The southern slopes also are comparatively well watered, and the natural environment is clearly divided into vertical zones, rich in grasses and shrubs affording good mountain pastures.
- The southern slopes drain into the Yarlung Zangbo River, the name in China for the Brahmaputra
The Greater Himalayas
- It is the highest and northernmost section of the Himalayan mountain ranges.
- It extends southeastward across northern Pakistan, northern India, and Nepal before trending eastward across Sikkim state (India) and Bhutan and finally turning northeastward across northern Arunachal Pradesh state (India); throughout nearly all of its length it adjoins to the north the southern Tibet Autonomous Region of China.
- The range’s total length is some 1,400 miles (2,300 km), and it has an average elevation of more than 20,000 feet (6,100 metres).
- The Great Himalayas contain many of the world’s tallest peaks, including (from west to east) Nanga Parbat, Annapurna, Mount Everest, and Kanchenjunga
- Assam Himalayas, eastern section of the Great Himalayas, extending eastward across Sikkim state (India) and Bhutan, into northern Assam and Arunachal Pradesh states (India), and along the border with the Tibet Autonomous Region (China).
- The mountains run eastward for 450 miles (720 km) from the upper Tista River in the west to the great southward bend of the Brahmaputra River (there called the Tsangpo River) in the east.
Lesser Himalayas
- Lesser Himalayas, also called Inner Himalayas, Lower Himalayas, or Middle Himalayas, middle section of the vast Himalayan mountain system in south-central Asia.
- The Lesser Himalayas extend for some 1,550 miles (2,500 km) northwest-southeast across the northern limit of the Indian subcontinent. Areas include the disputed Kashmir region (Gilgit-Baltistan, administered by Pakistan, and Jammu and Kashmir union territory, administered by India), the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand, Nepal, the Indian state of Sikkim, and Bhutan.
- The range lies between the Great Himalayas to the northeast and the Siwalik Range (Outer Himalayas) to the southeast and has an average elevation of 12,000 to 15,000 feet (3,700 to 4,500 metres).
- It includes portions of the western (Punjab), Kumaun, Nepal, and Assam Himalayas ranges
Shiwaliks- or Outer Himalayas
- extends west-northwestward for more than 1,000 miles (1,600 km) from the Tista River in Sikkim state, northeastern India, through Nepal, across northwestern India, and into northern Pakistan.
- Nepal’s portion of the range is called the Churia Range.
- It rises abruptly from the plain of the Indus and Ganges (Ganga) rivers (south) and parallels the main range of the Himalayas (north), from which it is separated by valleys.
- Everywhere in this section the poor scrub forests have long since been removed, and the hills are subject to severe erosion. Seasonal torrents, called cos, sweep masses of sand and silt down into ever-changing great streambeds that are dry except after rains.
The Eastern Himalayas
- The Purvanchal Hills are a range of hills in northeastern India, located in the states of Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, and Nagaland. The name “Purvanchal” means “eastern mountains” in Hindi and refers to the region’s location to the east of the Ganges River.
- The Dafla Hills, Patkai Hills, and Mishmi Hills are some of the major ranges within the Purvanchal Hills.
Kashmir Valley
- It is an intermontane valley, western Jammu and Kashmir union territory, northern India.
- Lying wholly within the Indian-administered portion of the Kashmir region, it is flanked by the main range of the Himalayas on the northeast and the Pir Panjal Range on the southwest.
- The Vale of Kashmir is an ancient lake basin about 85 miles (135 km) long, 20 miles (32 km) wide, and 5,300 feet (1,620 metres) high that is drained by the upper Jhelum River.
- The population of the Kashmir region is concentrated in the valley, at the centre of which lies Srinagar, the summer capital of Jammu and Kashmir. The fertile alluvial soil yields rice, corn (maize), fruit, and vegetables, and the scenic mountains and lakes (notably Wular, Dal, and Nagin) attract many tourists.
SOURCE: The Hindu https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/with-militants-changing-tack-rajouri-poonch-sector-an-uphill-task-for-security-agencies/article66857787.ece
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: UN roadmap outlines solutions to cut global plastic pollution
About Circular Economy
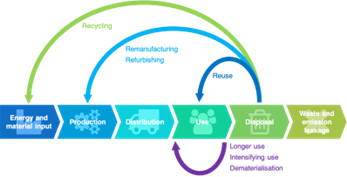
Image Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/8b/The_Circular_Economy_concept.png
- A circular economy reduces material use, redesigns materials, products, and services to be less resource intensive, and recaptures “waste” as a resource to manufacture new materials and products.
- A circular economy is based on three clear principles that bring multiple benefits, including benefits for our climate. These are:
- Eliminating waste and pollution, in turn reducing and avoiding emissions across the value chain.
- Circulating products and materials, in turn enabling embodied emissions to be retained.
- Regenerating nature, thereby also improving carbon sequestration.
Significance of Circular Economy
- Reduces waste generation: Practicing circular economic practices will reduce the daily waste generation associated with various consumption pattern.
- Enhances mindful consumption pattern: A more mindful consumption will change the attitude of users and will enhance reuse and reduce waste associated with daily life.
- Reduces carbon footprint: A circular economy will have lower carbon emissions than a linear economy. Producing new materials results in carbon emissions; circular economies minimize the need for producing new materials by maximizing the re-use of resources,
- Shifts use to durable products: A circular economy favours activities that preserve value in the form of energy, labour, and materials. This means designing for durability, reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling to keep products, components, and materials circulating in the economy.
India’s Efforts to promote Circular Economy
- Plastic Waste Management (Second Amendment) Rules, 2022: The Union Environment Ministry has launched this policy to mandate to increase in the thickness of plastic carry bags to over 120 microns starting on December 31, 2022, and the phase-out of some single-use plastic products starting on July 1, 2022.
- E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2022: No Entity shall carry out any business without registration and the registered entity shall not deal with any unregistered manufacturer, producer recycler and refurbisher. For registration, registration fee and annual maintenance charges shall be based on the capacity of e -waste generated, recycled or handled
- FAME India Scheme: The Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme was launched in April 2015 under the National Electric Mobility Mission, to encourage electric and hybrid vehicle purchase by providing financial support.
Challenges of Circular Economy:
- Consumer Convince: Industries and Shopping malls are using more plastic products due to single use and much convinces for producers for packaging and carrying and transportation for consumers
- Disruption of linear economy: Current economic model has produced industries and services based on linear economic model thus a shift to circular economic model eliminates some of the products and services which in turn leads to sudden disruptions.
- Lack of infrastructure and management for waste treatment: India is grossly inadequate in its infrastructure and services relating to waste management. Thus it will hamper the circular economic activities.
- Lack of recycling technology: There are materials that need higher recycling technology such as textile and the beverage cartons that we use to contain milk or juice. In order for the circular economy implementation to succeed, we need to make sure that the technologies needed to recycle the materials are enough to cover all the industries’ requirements – both in numbers and quality
- Poor Economic Models: The current economic models that proposes circular economy does not matches with the demand and supply of current economic forces in play.
Way Forward
The key to accelerating the change is by collaborating with other stakeholders. Better materials, a source of renewable energy, better connection to spread awareness, and Extended Producer Responsibility in waste management .Great collaborations could help us to be a step closer to the circular economy
MUST READ: Plastic Waste Management https://iasbaba.com/2021/10/plastic-waste-management/
Extended Producer Responsibility https://iasbaba.com/2023/02/extended-producer-responsibility/#:~:text=EPR%20responsibility%20makes%20it%20the,the%20amount%20of%20waste%20generated.
SOURCE: The Financial Express https://www.financialexpress.com/industry/how-circular-economy-is-revolutionising-plastics-packaging-industry/3092329/
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology)
Context: Recently, government approved the National Quantum Mission (NQM) at a total cost of Rs.6003.65 crore from 2023-24 to 2030-31, aiming to seed, nurture and scale up scientific and industrial R&D and create a vibrant & innovative ecosystem in Quantum Technology (QT).
About Quantum Technology:
- Quantum Technology is based on the principles of Quantum mechanics that was developed in the early 20th century to describe nature at the scale of atoms and elementary particles.
- The first phase of this revolutionary technology has provided the foundations of understanding of the physical world and led to ubiquitous inventions such as lasers and semiconductor transistors.
- The second revolution is currently underway with the goal of putting properties of quantum mechanics in the realms of computing.
Applications of Quantum Technologies:
- Electronics: Many modern electronic devices are designed using quantum mechanics. Examples include the laser, the transistor (and thus the microchip), the electron microscope, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Cryptography: Researchers are currently seeking robust methods of directly manipulating quantum states.
- Efforts are being made to develop quantum cryptography, which will theoretically allow guaranteed secure transmission of information.
- Quantum computing: Another goal is the development of quantum computers, which are expected to perform certain computational tasks exponentially faster than classical computers.
- Instead of using classical bits, quantum computers use qubits, which can be in superpositions of states.
- Quantum programmers can manipulate the superposition of qubits in order to solve problems that classical computing cannot do effectively, such as searching unsorted databases or integer factorization.
- Disaster Management: Tsunamis, drought, earthquakes and floods may become more predictable with quantum applications.
- Research: It can help in solving some of the fundamental questions in physics related to gravity, blackhole etc.
- Similarly, the quantum initiative could give a big boost to the Genome India project, a collaborative effort of 20 institutions to enable new efficiencies in life sciences, agriculture and medicine.
Issues and Challenges in Quantum domain:
- High precision: Controlling quantum superposition in a highly controlled manner. The qubits tend to be very fragile and lose their “quantumness” if not controlled properly.
- Expensive hardware: The quantum infrastructure like superconductors, non-linear optical crystals, ultra-fast transistors, etc are very expensive
- Still in the Budding Stage: On the theoretical front lies the challenge of creating the algorithms and applications for quantum computers.
- These projects will also place new demands on classical control hardware as well as software platforms.
- Further, Information technology-based security infrastructure would never be the same once quantum systems become a reality, given the ultra-fast speed of computing power.
- New Warfare and conflict strategies: Need to develop integrated war-theatre strategies factoring in quantum technologies.
- Lack of adequate skilled manpower
Quantum Technology and India:
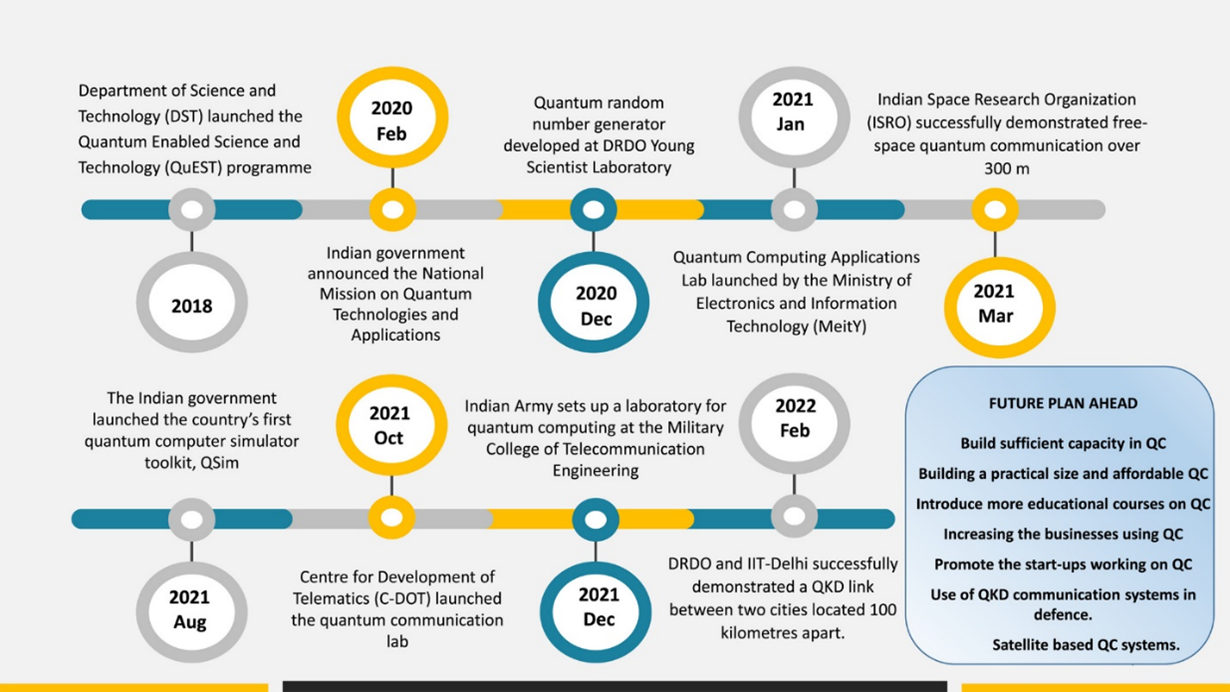
- Globally, research in this area is about two decades old, but in India, serious experimental work has been under way for only about five years.
- In 2018, the Department of Science & Technology unveiled a programme called Quantum-Enabled Science & Technology (QuEST) and committed to investing ₹80 crore over the next three years to accelerate research.
- The government in its budget 2020 has announced a National Mission on Quantum Technologies & Applications (NM-QTA) with a total budget outlay of Rs 8000 Crore for a period of five years to be implemented by the Department of Science & Technology (DST).
- The Indian government has launched the country’s first quantum computer simulator toolkit, called QSim, which will enable researchers and students to carry out cost-effective research in quantum computing.
Steps taken by the Government:
- In 2018, the government initiated serious discussions in quantum technologies and kick-started research projects across 51 organisations under QUEST – Quantum Enabled Science and Technology.
- Government of India declared quantum tech as a “mission of national importance” in 2019.
- About 100 government-funded projects on quantum and allied technologies have expanded various stages.
- In 2021, Department of Science and Technology and around 13 research groups from IISER Pune have established the I-HUB Quantum Technology Foundation (I-HUB QTF).
- In 2021, a Quantum Computing Applications Lab was launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) in collaboration with Amazon Web Services.
- In 2023, National Quantum Mission was launched with a plan of 8 years to develop key infrastructure and capabilities in the Quantum domain.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The Union Cabinet Wednesday cleared a revised production linked incentive (PLI) scheme for IT hardware with an outlay of Rs 17,000 crore, more than doubling the budget for the scheme that was first cleared in 2021.
About Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme:
- The PLI scheme was conceived to scale up domestic manufacturing capability, accompanied by higher import substitution and employment generation.
- The government has set aside Rs 1.97 lakh crore under the PLI schemes for various sectors and an additional allocation of Rs 19,500 crore was made towards PLI for solar PV modules in Budget 2022-23.
- Launched in March 2020, the scheme initially targeted three industries:
- Mobile and allied Component Manufacturing
- Electrical Component Manufacturing and
- Medical Devices
Sectors Under PLI Scheme:
- Mobile Manufacturing and Specified Electronic Components
- Critical Key Starting materials/Drug Intermediaries and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
- Manufacturing of Medical Devices
- Automobiles and Auto Components
- Pharmaceuticals Drugs
- Specialty Steel
- Telecom and Networking Products
- Electronic/Technology Products
- White Goods (ACs and LEDs)
- Food Products
- Textile Products: MMF segment and technical textiles
- High-efficiency solar PV modules
- Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery
- Drones and Drone Components
Advantages:
- It helps to boost domestic manufacturing and reduce the reliance on imports.
- It encourages foreign companies to set up their production units in India.
- More employment opportunities are generated in the manufacturing sector.
- It will boost the growth in GDP and will make it easier for India to effectively penetrate into the global supply chains.
- It will help achieve the aim of ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’.
- Integrates India with global markets and boosts exports.
- Gain strategic upper hand by focusing on crucial sectors.
Challenges faced by PLI Scheme
- As per a report, out of the 14 eligible sectors, only two or three were likely to meet their first-year targets under the PLI scheme.
- There is no common set of parameters to understand the value added by companies that have received or are likely to receive incentives under the scheme.
- According to the research, the industries think that further incentives are required to make India more appealing than China and Vietnam.
- The companies need more incentives to run the scheme properly and boost exports.
Way Forward:
The bottlenecks in the PLI scheme are needed to be removed as soon as possible to make India a manufacturing hub and reduce its reliance on China and other nations globally. The government is proactively engaging with all the stakeholders to regularly tweak and update the PLI scheme.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements
- Nutrient Based Subsidy Scheme is available to all fertilizers sold in India.
- The aim of Nutrient Based Subsidy Policy is to increase the consumption of P & K fertilizers so that an optimum balance of N:P:K = 4:2:1 can be achieved
- Nutrient Based Subsidy Scheme has led to unscientific fertilizer applications to Indian crops.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which one of the following is the correct sequence of Purvachal ranges from North to South?
- Mishmi Hills
- Patkai Bum
- Naga Hills
- Manipur Hills
- Mizo Hills
Select the correct answer using the code given below
- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5
- 2- 1- 3- 4- 5
- 2- 1- 3- 5- 4
- 2- 3- 4- 5- 1
Q.3) Which among the following portals enables people across India to track and block their lost or stolen mobile phones?
- NAMASTE Portal
- SAGE Portal
- Sanchar Saathi Portal
- E- Amrit Portal
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 18th May 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 17th May – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – a













