IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current event
Context: OpenAI, the creator of the revolutionary chatbot ChatGPT, has unveiled a new generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) model that can convert a text prompt into video called Sora.
Background:-
- Generative artificial intelligence (AI) describes algorithms (such as ChatGPT) that can be used to create new content, including audio, code, images, text, simulations, and videos.The recent buzz around generative AI has been driven by the simplicity of new user interfaces for creating high-quality text, graphics and videos in a matter of seconds.
About Sora:-
- Sora is a generative AI model designed by Open AI (makers of chatGPT) that can convert a text prompt into video.
- Sora can generate videos up to a minute long while maintaining visual quality and adherence to the user’s prompt.
- While generation of images and textual responses to prompts on GenAI platforms have become significantly better in the last few years, text-to-video was an area that had largely lagged, owing to its added complexity of analysing moving objects in a three-dimensional space.
- Other companies apart from Open AI too have ventured into the text-to-video space. Google’s Lumiere, which was announced last month, can create five-second videos on a given prompt, both text- and image-based.
- Other companies like Runway and Pika have also shown impressive text-to-video models of their own.
- Open AI has said that it will take some “safety steps” ahead of making Sora available in OpenAI’s products, and will work with red teamers — domain experts in areas like misinformation, hateful content, and bias — who will be “adversarially” testing the model.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS3
Context: Thousands of farmers amassed at the Punjab and Haryana border are protesting for legal guarantee to minimum support prices
Background:
- The farmer’s unions assert that the Centre has failed to fulfill its promise of providing a legal guarantee for MSP, as agreed upon at the conclusion of the massive protests in 2021.
About MSP:
- MSP is the minimum rate at which the government procurement agencies purchase agricultural commodities from farmers.
- It serves as a safety net for farmers, ensuring them a minimum income for their produce, particularly during times of market fluctuations or distress.
- The Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) is tasked with recommending MSPs for various crops.
- Operating as an attached office of the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, the CACP has been functioning since January 1965.
How is the MSP Calculated?
- When determining the MSP, farmers’ incurred costs, both implicit and explicit, are carefully considered. Implicit costs, such as family labour and rent paid by farmers, are factored into the calculation alongside explicit costs. These variables are represented by A2, FL, and C2.
- A2: This includes expenses incurred by farmers for purchasing chemicals, fertilisers, seeds, and hiring labour for crop growth, production, and maintenance.
- A2 + FL: This includes actual costs along with implicit costs in the form of family labour.
- C2: This includes A2 + FL along with fixed capital assets and rent paid by farmers.
- Additionally, the CACP considers several other factors when deciding the MSP like market prices of concerned crops and any fluctuations, information on produce supply, including area, yield, production, imports, exports, and stocks with public agencies or industries, demand information across regions, including total and per capita consumption, processing industry trends, and capacity etc
- Once the CACP submits its recommendations, the final decision regarding the MSP levels is taken by the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), chaired by Prime Minister of India.
Key Benefits of the MSP for farmers
- Income Security: MSP gives farmers with a guaranteed minimum price for their crops, ensuring a stable and predictable income, especially during times of market volatility.
- Price Stability: By setting a floor price for agricultural commodities, MSP helps stabilise market prices, preventing sharp fluctuations that could negatively impact both farmers and consumers.
- Boosts Production: MSP serves as an incentive for farmers to raise production of crops covered under the MSP regime, as they are assured of receiving a remunerative price for their efforts.
- Food Security: MSP plays a vital role in ensuring food security by incentivising farmers to cultivate essential food crops. This helps maintain a steady supply of food grains in the market, cutting the dependence on imports and enhancing domestic food security.
Source: Money Control
Syllabus
- Prelims : Economy
Context: India initiates anti-dumping probe into imports of solar glass from China, Vietnam.
Background:
- Solar glass is used to make solar panels and modules for renewable energy generation. India is one of the largest markets for solar power, and has set a target of installing 450 gigawatts of renewable energy capacity by 2030.
About Anti Dumping Duty:
- Anti-dumping duty is a tariff imposed by a government on imported goods that are sold at a price lower than their normal value in the exporting country.
- The purpose of anti-dumping duty is to protect the domestic industry from unfair competition and trade distortion caused by dumping.
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) regulates dumping practices through the Anti-Dumping Agreement, which sets forth the rules and procedures for the investigation, determination, and application of anti-dumping measures by WTO members.
- According to the Anti-Dumping Agreement, a WTO member can impose anti-dumping measures if it can prove that:
- The imports are being sold at a price below their normal value in the exporting country.
- The dumping is causing material injury to the domestic industry producing similar goods.
- There is a causal link between the two.
Authority to impose anti- dumping duty in India
- The Ministry of Finance has the final authority to impose anti-dumping duty on the imports that are found to be dumped and causing injury to the domestic industry.
- The Ministry of Finance acts on the basis of the recommendations of the Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR), which conducts the investigation and determines the existence and extent of dumping and injury.
- The Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR), is a part of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, which is responsible for formulating and implementing the foreign trade policy and dealing with multilateral and bilateral trade relations.
Source: Economic Times
Syllabus
- Prelims -Current Event
Context: Terai Arc Landscape recognized as UN World Restoration Flagship as a part of the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration.
Background:
- The UN World Restoration Flagship is a global recognition and support program for the large-scale ecosystem restoration.
- The Terai region is a lowland area that lies south of the Himalayas and north of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, in parts of northern India and southern Nepal. It is characterized by tall grasslands, scrub savannah, sal forests, and clay-rich swamps. It is also home to diverse and endangered wildlife, such as tigers, rhinos, elephants, and dolphins.
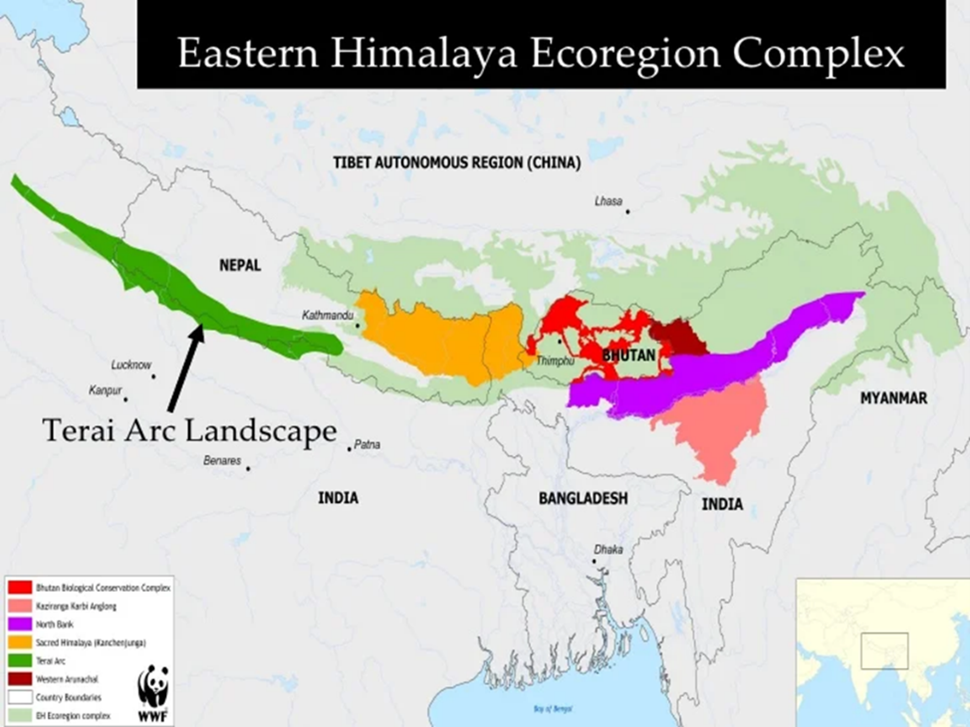
About The Terai Arc Landscape (TAL) initiative
- The Terai Arc Landscape (TAL) initiative is a joint effort by Nepal and India to conserve and restore the biodiversity and ecosystems of the Terai region, which is home to many endangered species such as tigers, rhinos, elephants, and gharials.
- The initiative has been recognized by the U.N. as one of the World Restoration Flagships, which are exemplary projects that demonstrate the benefits of ecosystem restoration for people and nature.
- The Terai Arc Landscape (TAL) is a transboundary region that spans across India and Nepal, covering 14 protected areas.
- The protected areas included in the Terai Arc Landscape:
- Parsa National Park, Nepal
- Chitwan National Park, Nepal
- Banke National Park, Nepal
- Bardia National Park, Nepal
- Blackbuck Conservation Area, Nepal
- Shuklaphanta Wildlife Reserve, Nepal
- Valmiki National Park, India
- Sohelwa Wildlife Sanctuary, India
- Katarniaghat Wildlife Sanctuary, India
- Dudhwa National Park, India
- Kishanpur Wildlife Sanctuary, India
- Corbett National Park, India
- Rajaji National Park, India
- Pilibhit Tiger Reserve, India
Source: Mongabay
Syllabus
- Prelims and Mains – Environment
Context: As 2023 was regarded as one of the worst in terms of environmental damages, multiple associated issues have come to discussion.
Background:
- Acid Rain is a complex environmental issue with multiple causes and widespread consequences, and it has its origins in fossil fuels.
About Acid Rain:
- Acid rain or acid deposition is a broad term that includes any form of precipitation with acidic components, such as sulfuric or nitric acid that fall to the ground from the atmosphere in wet or dry forms. This can include rain, snow, fog, hail, or even dust that is acidic.
Formation of acid rain:
- When SO2 (Sulphur Dioxide) and NOx (Nitrogen Oxide) combine with water and oxygen in the atmosphere, they form sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and nitric acid (HNO3), respectively.
- These acids then dissolve in water droplets, leading to the creation of acid rain, snow, or fog.
Causes of acid rain:
- Burning of fossil fuels, particularly those containing sulfur, releases sulfur dioxide (SO2) and, at higher temperatures, nitrogen oxides (NOx).
- Fossil fuel combustion is prevalent in vehicles such as automobiles and the combustion of coal in power plants and industrial processes.
- Volcanic eruptions and lightning contribute to the presence of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides in the atmosphere.
- In the atmosphere, the pollutants SO2 and NOx undergo chemical reactions, forming sulfuric and nitric acids. When combined with water vapor, they create acid rain during precipitation.
Consequences/impacts of acid rain:
- Acid rain can make water bodies, such as rivers and lakes, inhospitable to certain species of aquatic life as the increased acidity disrupts their reproductive patterns and can lead to fish population decline in affected rivers and lakes.
- The increased acidity alters the pH of marine environments, adversely impacting the distribution and survival of various organisms.
- Shell-forming marine species, like molluscs and certain types of plankton, face particular challenges as acidification interferes with their ability to build and maintain protective shells.
- Acid rain poses substantial threats to physical structures and monuments, causing deterioration and discoloration. Notable examples include the Taj Mahal, whose iconic white marble has been affected, exhibiting a yellowish hue due to sulfuric acid reactions.
Source: EPA
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: The Indian government has announced a slight increase in the windfall tax on domestically produced crude oil and diesel, effective from February 16.
Background:
- The tax is levied in the form of a Special Additional Excise Duty (SAED).
About windfall tax
- A windfall tax is a higher tax rate levied by governments on certain industries or sectors that experience significantly above-average profits due to unexpected events or market conditions.
- A windfall tax is different from a regular income tax, as it is applied only to the profits that exceed a certain threshold or percentage, and only for a limited period of time.
- India first imposed windfall profit taxes on July 1, 2022, joining a host of nations that tax supernormal profits of energy companies.
- This is part of the government’s strategy to capitalise on energy sector profits amid global uncertainties.
- The tax rates are reviewed every fortnight based on average oil prices in the previous two weeks.
Rationale behind the imposition of windfall tax
- Redistribution of unexpected gains, when high prices benefit producers at the expense of consumers.
- Funding social welfare schemes or public goods, such as health, education, or infrastructure.
- Providing a supplementary revenue stream for the government, especially during fiscal deficits or crises.
- Encouraging more efficient use of resources or reducing negative externalities, such as pollution or overexploitation.
- Narrowing the country’s widened trade deficit.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1.) With reference to Windfall tax, consider the following statements:
- It is a higher tax rate levied by governments on certain industries or sectors that experience significantly above-average profits due to unexpected market conditions.
- India hasn’t imposed any form of windfall taxes on any sector/industry yet.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q2.) The Terai Arc Landscape is one among the World Restoration Flagships selected as part of the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration. Which of the following protected area is not a part of it?
- Valmiki National Park
- Dudhwa National Park
- Corbett National Park
- Mukundhara National Park
Q3.) Consider the following statements:
- Anti-dumping duty is a tariff imposed by a government on imported goods that are sold at a price lower than their normal value in the exporting country.
- The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) regulates dumping practices through the Anti-Dumping Agreement.
- Ministry of Commerce and Industry has the final authority to impose anti-dumping duty in India.
How many statements given above are not correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 17th February 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 16th February – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – a











