IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: Palestine accuses Israel of apartheid at ICJ
Background:-
- The International Court of Justice is holding hearings on the legal implications of occupation of territories by Israel.
About International Court of Justice :-
- The ICJ is the principal judicial organ of the United Nations (UN).
- It was established in June 1945 by the Charter of the United Nations and began work in April 1946.
- The court is the successor to the Permanent Court of International Justice (PCIJ), which was brought into being through, and by, the League of Nations, 1922.
- Like the PCIJ, the ICJ is based at the Peace Palace in The Hague.
- It is the only one of the six principal organs of the UN that is not located in New York City. (The other five organs are the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council, the Trusteeship Council, and the Secretariat.)
- According to the ICJ’s own description, its role is “to settle, in accordance with international law, legal disputes submitted to it by States and to give advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by authorized United Nations organs and specialized agencies”. The court “as a whole must represent the main forms of civilization and the principal legal systems of the world”.
- English and French are the ICJ’s official languages.
- All members of the UN are automatically parties to the ICJ statute, but this does not automatically give the ICJ jurisdiction over disputes involving them. The ICJ gets jurisdiction only if both parties consent to it.
- The judgment of the ICJ is final and technically binding on the parties to a case. There is no provision of appeal; it can at the most, be subject to interpretation or, upon the discovery of a new fact, revision.
- However, the ICJ has no way to ensure compliance of its orders, and its authority is derived from the willingness of countries to abide by them.
- The ICJ has 15 judges who are elected to nine-year terms by the UN General Assembly and Security Council, which vote simultaneously but separately.
- To be elected, a candidate must receive a majority of the votes in both bodies.
- A third of the court is elected every three years.
- Four Indians have been members of the ICJ so far.
Source: The Guardian
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – Environment
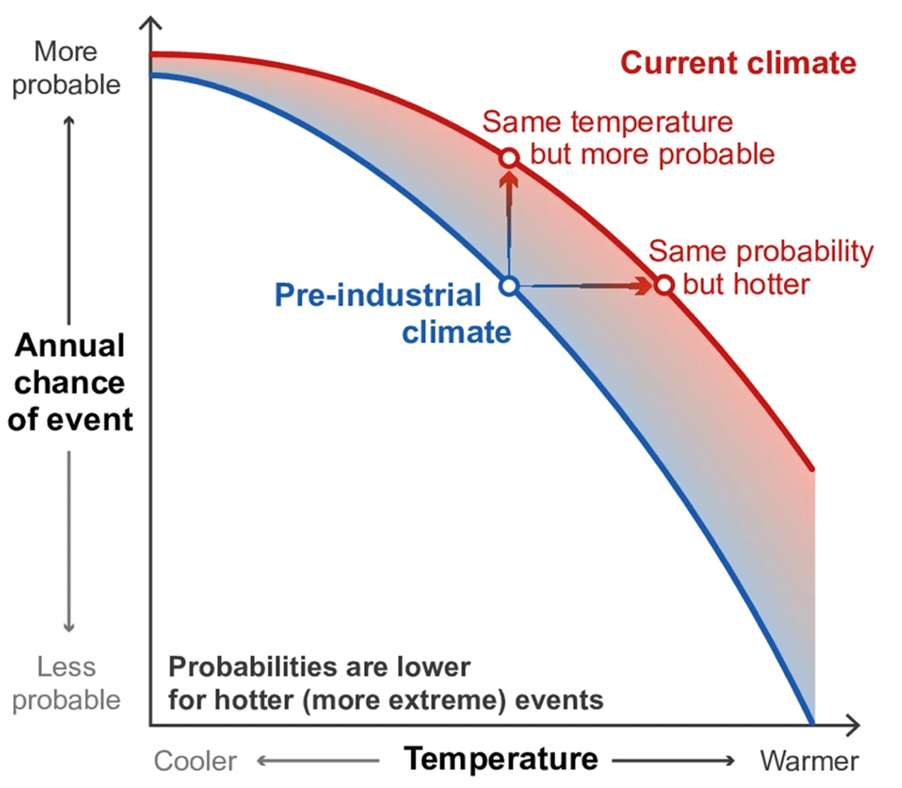
Context: The year 2023 has been confirmed as the hottest year in global temperature records going back to 1850 triggering debates about extreme weather events in the near future.
Background:
- The average global temperature on Earth has increased by at least 1.1 degree Celsius since 1850, primarily due to human activities that have released unprecedented levels of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.The spike in the temperatures has resulted in more frequent and more intense extreme weather events across the world. These events include heat waves, droughts, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires.
About the interconnection between climate change and extreme weather events:
- Extreme heat creates conditions more prone to wildfire and a longer wildfire season by evaporating more moisture from land. According to a 2023 report by Weather Attribution (WWA), climate change more than doubled the likelihood of extreme “fire weather” conditions in Eastern Canada.
- Warmer air can suck moisture out of the soil, amplifying droughts.
- Higher temperatures cause evaporation of water not only from land but also oceans and other water bodies, meaning a warmer atmosphere holds more moisture.
- For every 1 degree Celsius rise in average temperature, the atmosphere can hold about 7% more moisture. This makes storms more dangerous as it leads to an increase in precipitation intensity, duration and/or frequency, which ultimately can cause severe flooding.
- Oceans have absorbed 90% of the additional heat generated by the greenhouse gas emissions in recent years. Due to this, global mean sea surface temperature has gone up by close to 0.9 degree Celsius since 1850.
- Higher sea surface temperatures cause marine heat waves, an extreme weather event, which, in turn, makes storms like hurricanes and tropical cyclones more intense. When storms travel across hot oceans, they gather more water vapour and heat. This results in stronger winds, heavier rainfall, and more flooding when storms reach the land.
Source: The Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims -Current Event
Context: Prime Minister Modi will inaugurate the Chenab Bridge, the worlds highest single arch railway Bridge.
Background:
- Approved in 2003 and contracted in 2008, after much worries over its safety and stability, the single-arch bridge over River Chenab in J&K passed all its mandatory tests and is set to mark India on the railroad history after two decades of waiting.
About Chenab bridge
- The Bridge spans the Chenab River and has a total length of 1315 m
- The arch bridge runs between Bakkal and Kauri in the Reasi district of Jammu and Kashmir, and forms a crucial link from Katra to Banihal.
- It stands at the height of 1,178 feet above the riverbed, making it 35 metres taller than Paris’ tourist icon, the Eiffel Tower.
- The bridge is part of the Rs 35000 crore Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Railway Link (USBRL) project which aims to boost connectivity in Jammu and Kashmir by providing connectivity in complex topography and weather conditions.
- The bridge is expected to have a shelf life of around 120 years.
- It will also be able to withstand winds with speeds up to 260 km/per hour.
Source: The Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims- Environment
Context: An adult male tiger was recently recorded on a camera trap in Buxa Tiger Reserve in north Bengal after 23 years.
Background:
- There was no direct evidence confirming tiger presence in the reserve since 1998. Ecosystem restoration activities in the Buxa Tiger Reserve, including grassland management, helped bring the tiger back to the protected area, experts say.
About Buxa Tiger Reserve:
- Tiger reserves are protected areas in India that are dedicated to the conservation of tigers and their habitats.
- They are governed by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) under the Project Tiger scheme, which was launched in 1973.
- Buxa Tiger Reserve is a tiger reserve and national park in northern West Bengal, India.
- It is home to a rich diversity of flora and fauna, including tigers, elephants, leopards, gaurs, and many bird species.
- Buxa Tiger Reserve was created in 1983 as the 15th tiger reserve in India.
- It is named after the historic Buxa Fort, which was used as a prison and detention camp by the British during the Indian freedom movement.
- Buxa Tiger Reserve is part of the Terai eco-system, which is a fragile and biodiverse region along the foothills of the Himalayas.
- It also serves as an international corridor for elephant migration between India and Bhutan.
Source: Mongabay
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
Context: The Fourteenth Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS COP 14) adopted the Initiative for the Central Asian Flyway introduced by India on February 17, 2024.
Background:
- The CMS holds a Conference of the Parties (COP) every three years, where the member states review the progress and adopt new measures for the conservation of migratory species. The 14th COP was held in Samarkand, Uzbekistan, in February 2024, and it was the first UN wildlife meeting in Central Asia.
About Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
- The Central Asian Flyway (CAF) initiative is a conservation project led by India under the umbrella of the Convention on Migratory Species (CMS), which is an international treaty that aims to protect and conserve migratory animals and their habitats.
- The initiative aims to promote the conservation and sustainable use of migratory waterbirds and their habitats, as well as to enhance cooperation and coordination among the range states and other stakeholders.
- The Central Asian Flyway (CAF) is a flyway covering a large continental area of Eurasia between the Arctic Ocean and the Indian Ocean and the associated island chains.
- A flyway is a geographical region within which a single or group of migratory species completes its annual cycle of breeding, moulting, staging and non-breeding.
- The CAF comprises several important migration routes of waterbirds, most of which extend from the northernmost breeding grounds in Siberia to the southernmost non-breeding wintering grounds in West Asia, India, the Maldives and the British Indian Ocean Territory.
- The CAF covers 30 countries and at least 279 migratory waterbird populations of 182 species, including 29 globally threatened or near-threatened species.
- The Central Asian Flyway consists of the following countries: Afghanistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, Georgia, India, Iran, Iraq, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, the Maldives, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Pakistan, Qatar, Russian Federation, Saudi Arabia, Sri Lanka, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom (British Indian Ocean Territory), Uzbekistan and Yemen.
Source: Down to Earth
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 and 3
Context: A new study has been published in the journal Nature Communications titled- ‘Arctic marine heatwaves forced by greenhouse gases and triggered by abrupt sea-ice melt’, which shows that since 2007, unprecedented Marine Heatwave (MHW) events have occurred over the Arctic Ocean.
Background:
- A A MHW is an extreme weather event. It occurs when the surface temperature of a particular region of the sea rises to 3 or 4 degrees Celsius above the average temperature for at least five days.According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), MHWs can last for weeks, months, or even years.
Key findings/highlights of the study:
- There have been 11 Marine Heatwaves (MHWs) events in the Arctic from 2007 to 2021, characterized by prolongedhigh Sea Surface Temperatures (SST). These events coincide with record declines in Arctic Sea ice. In 2022, the Arctic saw severe and extreme marine heatwaves in the Laptev and Beaufort seas from spring to autumn, according to the State of the Global Climate 2022 Report.
- The perennial sea ice cover over the Arctic Ocean, known to reflect solar radiation, has seen a marked decrease in both summer and winter since the mid-1990s. Since 2007, there has been apronounced regime shift from a thicker and deformed ice cover to a thinner and more uniform one. The thin ice is less durable and melts more quickly, allowing incoming solar radiation to warm the water’s surface.
- Arctic MHWs primarily occur over marginal seas, including theKara, Laptev, East Siberian, and Chukchi seas. These regions are characterized by shallow mixed-layer depths and predominantly first-year ice cover, creating conditions conducive to MHW development.
- Without GHGs, marine heatwaves exceeding5°C couldn’t happen. GHGs are a sufficient cause for moderate marine heatwaves, with a 66-99% probability.
- There is a pronouncedlong-term warming trend in the Arctic, with SST increasing at a rate of 1.2°C per decade from 1996 to 2021. Over the last two decades, there has been an increase in the frequency of extreme SST events in the eastern Arctic marginal seas.
Sources : Down To Earth
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Consider the following statements about international Court of Justice:
- The ICJ is the principal judicial organ of the United Nations (UN).
- It is the only one of the six principal organs of the UN that is not located in New York City.
- Four Indians have been members of the ICJ so far.
How many statements given above is/ are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- All the above
- None of the above
Q2.) With reference to Central Asian Flyway (CAF) initiative, consider the following statements:
- Central Asian Flyway (CAF) initiative is a conservation project led by India under the umbrella of G20 Summit.
- The CAF comprises several important migration routes of waterbirds extending from the northernmost breeding grounds in Siberia to the southernmost non-breeding wintering grounds in Australia.
How many statements given above is/ are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q3.) Consider the following tiger reserves in India:
- Ranthambore
- Sunderban
- Namdapha
- Buxa
How many of the above are located in West Bengal?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 20th February 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 19th February – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – a











