IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: Concerns have been raised about the misuse of Interpol’s notice system, especially the issuance of blue corner notices.
Background:-
- Although Interpol’s Constitution explicitly forbids any activities of a political character, activists have accused it of failing to enforce this rule. Much of this outrage is directed at Russia, which has repeatedly issued notices and diffusions for the arrest of Kremlin opponents.
About Interpol
- The International Criminal Police Organization (INTERPOL) is an intergovernmental organization that helps coordinate the police force of 196 member countries.
- Each of the member countries hosts an INTERPOL National Central Bureau (NCB).
- The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) is designated as the National Central Bureau of India.

- It is headquartered in Lyon, France
Types of Notice issued by Interpol
- INTERPOL Notices are international requests for cooperation or alerts allowing police in member countries to share critical crime-related information.
- Notices are issued by the General Secretariat at the request of a member country’s INTERPOL National Central Bureau
- Notices can also be issued at the request of International Criminal Tribunals and the International Criminal Court to seek persons wanted for committing crimes within their jurisdiction, notably genocide, war crimes, and crimes against humanity.
- They can also be issued at the request of the United Nations in relation to the implementation of sanctions imposed by the Security Council.
- Red Notice: To seek the location and arrest of persons wanted for prosecution or to serve a sentence.However, Interpol cannot compel law enforcement authorities in any country to arrest the subject of a red corner notice as the exercise of such powers is entirely discretionary.
- Yellow Notice: To help locate missing persons, often minors, or to help identify persons who are unable to identify themselves.
- Blue Notice: To collect additional information about a person’s identity, location or activities in relation to a criminal investigation.
- Black Notice: To seek information on unidentified bodies.
- Green Notice: To provide warning about a person’s criminal activities, where the person is considered to be a possible threat to public safety.
- Orange Notice: To warn of an event, a person, an object or a process representing a serious and imminent threat to public safety.
- Purple Notice: To seek or provide information on modus operandi, objects, devices and concealment methods used by criminals.
- INTERPOL–United Nations Security Council Special Notice: Issued for entities and individuals who are the targets of UN Security Council Sanctions Committees.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Culture
Context: The Telangana Governor extended her wishes to the tribal communities, lauding the Medaram Jatara as an unparalleled testament to indigenous culture and heritage.
Background:
- Lakhs of pilgrims poured into Medaram, which commemorates a revolt against the levy of taxes on the tribal populace during a period of drought by the Kakatiya rulers in the 12th century
About Medaram Jatara
- Sammakka Saralamma Jathara or Medaram Jathara is a tribal festival of honouring the goddesses celebrated in the state of Telangana, India. The Jathara begins at Medaram in Tadvai Mandal in Mulugu district.
- Medaram is a remote place in the Eturnagaram Wildlife Sanctuary, a part of Dandakaranya, the largest surviving forest belt in the Mulugu.
- It commemorates the fight of a mother and daughter, Sammakka and Saralamma, with the reigning rulers against an unjust law.
- The Medaram Jathara festival is held every two years.
- Sammakka Saralamma Jathara is the time for the largest tribal religious congregation in the world,with approximately ten million people converging on the place, over a period of four days.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
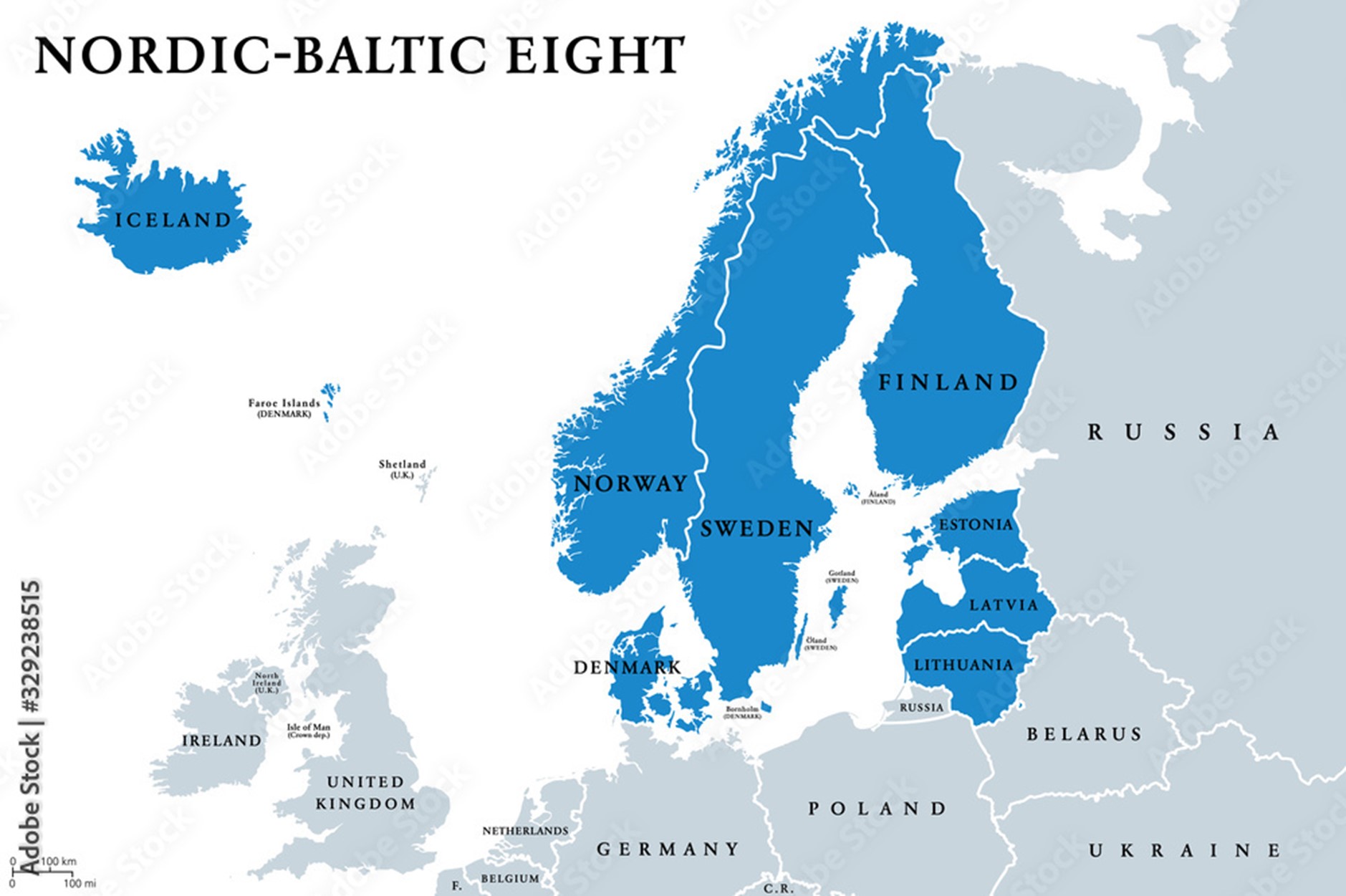
Context: In this year’s Raisina Dialogue in New Delhi, the eight Nordic-Baltic countries, are participating in it together as representatives of the Nordic-Baltic cooperation, the NB8.
Background:
- Participation of NB8 is significant as the Russia ukraine conflict continues.
About Nordic-Baltic Eight (NB8)
- Nordic-Baltic Eight (NB8) is a regional co-operation format that includes Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, and Sweden.
- Named as 5+3 in the beginning of cooperation (five Nordic countries plus three Baltic States), the format changed its name to NB8.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
Context: Union Minister for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change Bhupender Yadav has recently said that there is no need for any amendment in the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 to address human-wildlife conflict as the chief wildlife warden was empowered to trap, catch, and, if necessary, shoot wildlife according to the Section 11 of the Act.
Background:
- Recently, the Kerala Legislative Assembly passed a resolution that urged the Centre to make changes in some sections of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972. The urge to make these amendments is for the purpose of catering to the issue of increasing conflicts between humans and animals in Kerala.
About The Wildlife Protection Act:
- The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 is a significant legislation in India that provides a legal framework for the protection of various species of wild animals and plants, management of their habitats, and regulation and control of trade in wild animals, plants, and products derived from them.
- The Act provides for the establishment of wildlife advisory boards, regulations for hunting wild animals and birds, and the establishment of sanctuaries and national parks.
Wildlife (Protection) Amendment Act, 2022:
- The Act seeks to increase the species protected under the law and implement CITES (CITES is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals from the threats of international trade).
- The number of schedules has been reduced to four from six:
- Schedule I contains animal species enjoying the highest level of protection.
- Schedule II for animal species subject to a lesser degree of protection.
- Schedule III for protected plant species, and
- Schedule IV for scheduled specimens under CITES.
- The Act permits the use of elephants for ‘religious or any other purposes’.
- The penalties have also been increased for general and specially protected animals’ violations.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims– Economy
Context: The Enforcement Directorate (ED) issued showcause notices to Byju’s, a leading edtech startup, and its founder and CEO Byju Raveendran for allegedly violating Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) provisions to the tune of over Rs 9,362 crore.
Background:
- According to the ED, Byju’s and its founder violated FEMA by transferring funds to foreign entities without obtaining prior approval from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) or submitting the required documents. The ED also alleged that Byju’s did not disclose the source and purpose of the funds, and did not maintain proper records of the transactions.
About Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA)
- The Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) is a law that regulates the transactions involving foreign exchange in India.
- It was enacted in 1999 to replace the Foreign Exchange Regulation Act (FERA) of 1973.
- The new Act is in consonance with the frameworks of the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
- FEMA aims to facilitate external trade and payments, promote orderly development and maintenance of foreign exchange market, and prevent money laundering and other illegal activities.
- Main Features of FEMA
- It gives powers to the Central Government to regulate the flow of payments to and from a person situated outside the country.
- It requires all transactions involving foreign exchange or foreign securities to be carried out through authorized persons, such as banks, dealers, or agents.
- It allows the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to impose restrictions on transactions from current account or capital account, depending on the foreign exchange situation in the country.
- It permits Indians residing in India to hold or own foreign exchange, foreign securities, or immovable property abroad, subject to certain conditions and limits.
- It provides for penalties and enforcement actions for contravention of the provisions of the Act or the rules and regulations made under it.
- FEMA works in coordination with other laws and agencies, such as the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), the Income Tax Act, the Enforcement Directorate (ED), and the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU), to combat money laundering and related crimes.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS4
Context: According to Elon Musk, the first human received an implant from his computer-brain interface company Neuralink.
Background:
- Since its founding in 2016, Elon Musk’s neurotechnology company Neuralink has had the ambitious mission to build a next-generation brain implant with at least 100-times more brain connections than devices currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
What is a Brain-Computer Interface?
- A Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) is a technology that enables direct communication between the brain and external devices, such as computers or prosthetics, without using traditional neuromuscular pathways like nerves and muscles.
- BCI typically involves the use of sensors to detect brain activity, which is then translated into commands or actions, allowing individuals to control devices or interact with the external world using their thoughts.
Potential applications of Brain-Computer Interface:
- Monitoring and treating neurological conditions like epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and neurodegenerative disorders by directly interfacing with the brain.
- Assisting in motor function recovery and rehabilitation after a stroke.
- Enabling individuals with paralysis or motor impairments to control devices, such as prosthetics, wheelchairs, or robotic limbs, using their thoughts. Restoring communication for individuals with conditions like locked-in syndrome (paralyzed except for the muscles that control eye movement).
- Providing real-time data for monitoring and managing mental health conditions, such as depression or anxiety.
- Enhancing virtual and augmented reality experiences by allowing users to interact with digital environments using their thoughts.
Ethical considerations related to Brain-Computer Interface (BCI):
- BCIs can potentially decode thoughts and emotions. Unauthorized access to this information raises concerns about cognitive privacy. As with any technology that involves the collection and storage of sensitive data, there are risks of hacking and unauthorized access to brain data, which could lead to identity theft or other malicious uses.
- There is a risk that BCIs could be manipulated to unauthorized control or manipulation of a person’s thoughts or actions.
- Critics argue that BCIs could exacerbate existing social inequalities if only specific socioeconomic groups can afford the technology due to its high cost and may lead to a situation of cognitive divide.
- Distinguishing between therapeutic uses of BCIs and threats to normal cognitive function is subjective.
Sources : The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1.)Which among the following country is not a part of NB8?
- Finaland
- Iceland
- Sweden
- Germany
Q2.)With reference to Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), consider the following statements?
- The Act gives powers to the Central Government to regulate the flow of payments to and from a person situated outside the country.
- All financial transactions concerning foreign securities or exchange cannot be carried out without the approval of FEMA.
- The Act is in consonance with the frameworks of the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
How many statements given above is/are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q3.) Consider the following statements:
Statement-I:
The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 is a significant legislation in India that provides a legal framework for the protection of various species of wild animals and plants.
Statement-II:
According to the Section 11 of the Act, the chief wildlife warden is empowered to trap, catch, and, if necessary, shoot wildlife.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 24th February 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 23rd February – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – c














