IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: Supreme Court closes curative petition against its 2013 judgement on section 377
Background:-
- A 5-judge bench of the Supreme Court on Thursday held that the curative petition filed against the 2013 judgment, which upheld Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code (which criminalised homosexuality), has become infructuous in the light of the 2018 judgment which decriminalised homosexuality.
About Curative Petition:-
- The Curative Petition is the last chance available in the court after the review petition is dismissed or has been exhausted.
- It is a concept evolved by the Supreme Court of India in the matter of Rupa Ashok Hurra vs. Ashok Hurra and Anr. in which the question was whether an aggrieved person is entitled to any relief against the final judgement or order of the Supreme Court after the dismissal of a review petition.
- It’s objectives are twofolds- avoid miscarriage of justice and to prevent abuse of process.
- The concept of the curative petition is supported by Article 137 of the Indian Constitution.
Conditions laid by SC for curative petition:
- The petitioner must establish that the principles of natural justice were violated, and he has been adversely affected by the judgment.
- The petition shall state specifically that the grounds mentioned had been taken in the review petition and that it was dismissed by circulation.
- A curative petition must be first circulated to a bench of the three senior-most judges of the Supreme Court and the judges who had passed the concerned judgment, if available.
- If the majority of the judges conclude that the matter needs hearing, then it is listed before the same Bench.
- The Bench at any stage of the curative petition can ask a senior counsel to assist it as amicus curiae (friend of the court).
- A curative petition is usually decided by judges in the chamber unless a specific request for an open-court hearing is allowed.
MUST READ: https://www.scobserver.in/journal/court-in-review-curative-petitions/
SOURCE: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims-Current event of national importance
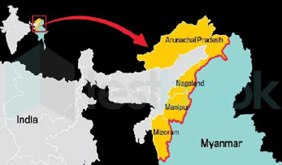
Context: Home Ministry recommends immediate suspension of free movement regime which allows people residing close to India and Myanmar border to venture 16 km into each other’s territory.
Background:
- The main reasons for this decision are to limit the spill-over effects of the conflict in Myanmar since the military coup in February 2021, and to reduce the risk of illegal migration, human and drug trafficking and ensure internal security.
About free movement regime:
- The Free Movement Regime (FMR) is a pact between India and Myanmar that allows tribes living along the border on either side to travel up to 16 km inside the other country without a visa.
- The FMR was implemented in 2018 as part of the government’s Act East policy at a time when diplomatic relations between India and Myanmar were on the upswing.
- However, the FMR has been suspended by India since September 2022 due to the conflict in Myanmar following the military coup in February 2021.
- The India-Myanmar border extends for approximately 1,643 kilometers (1,021 miles), running from the tripoint with China in the north to the tripoint with Bangladesh in the south.
- The India-Myanmar border passes through the States of Arunachal Pradesh (520 km), Nagaland (215 km), Manipur (398 km), and Mizoram (510 km).
Syllabus
- Prelim and Mains-Polity
Context: Recently the Uttarakhand Assembly passed the State’s Uniform Civil Code.
Background:
- With the passing of UCC bill Uttarakhand Assembly had become the first legislature in independent India to pass a Bill that imposes common rules for all communities — except Scheduled Tribes — on marriage, divorce, inheritances, and live-in relationships.
About UCC:
- Uniform Civil Code (UCC) is a proposal in India to formulate and implement personal laws of citizens which apply on all citizens equally regardless of their religion, gender and sexual orientation.
- They cover areas like- Marriage, divorce, maintenance, inheritance, adoption and succession of the property.
- In India, currently personal laws of various communities are governed by their religious scriptures.
- UCC is mentioned in Article 44 of the Indian Constitution, which is one of the Directive Principles of State Policy. It says, “The State shall endeavour to secure for the citizens a uniform civil code throughout the territory of India.
- Uttarakhand is the first state to implement a law on Uniform Civil Code (UCC) in India.
- The UCC Bill encompasses various facets of personal law, but it excludes Scheduled Tribes from its purview. This exemption recognizes the unique customary practices and traditions of tribal communities.
Goa Uniform Civil Code
- Goa Uniform Civil Code is the common name for the Goa Civil Code, which is a set of laws that govern personal matters such as marriage, divorce, succession, and property for all residents of Goa, irrespective of their religion.
- However, Goa UCC does not cover all aspects of personal law, such as adoption and succession, which are still governed by different laws for different communities.
- Goa UCC also has some special provisions for certain communities, such as allowing bigamy to Hindu men under certain conditions. Therefore, Goa UCC is not truly uniform, as it has some exceptions and variations based on religion and custom.
- Goa’s civil code was introduced during the Portuguese rule.
Syllabus
- Prelims-Economy
Context: The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on Thursday, February 8, 2024 after a detailed assessment decided to keep the policy repo rate under the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF) unchanged at 6.50 per cent.
Background:
- The repo rate increase cycle was paused in April last year after six consecutive rate hikes aggregating to 250 basis points since May 2022.
About MPC:
- Monetary policy is a set of tools used by a nation’s central bank to control the overall money supply and promote economic growth.
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is a committee constituted by the Central Government and led by the Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) was constituted under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, which was amended by the Finance Act, 2016. This amendment provided a statutory and institutionalized framework for the MPC.
- The MPC is required to meet at least four times a year and it publishes its decisions after each meeting.
- The factors constituting failure to meet inflation target under the MPC Framework have also been notified in the Gazette.
Purpose of MPC:
- The MPC was formed with the mission of fixing the benchmark policy interest rate (repo rate) to restrain inflation within a specific target level. Repo rate is the rate at which the central bank lends money to commercial banks.
- The current mandate of the committee is to maintain 4% annual inflation until 31 March 2026 with an upper tolerance of 6% and a lower tolerance of 2%.
Composition:
- The MPC comprises six members – three officials of the RBI and three external members nominated by the Government of India.
- The members appointed by the Central Government hold office for a period of four years.
- Decisions are taken by majority with the governor having the casting vote in case of a tie.
Previous Year Question
Q1.)Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)?
- It decides the RBI’s benchmark interest rates.
- It is a 12-member body including the Governor of RBI and is reconstituted every year.
- It functions under the chairmanship of the Union Finance Minister.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
Solution (a)
Syllabus
- Prelims-Current event of national and international importance
Context: Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project, one of India’s flagship connectivity projects has faced a setback after an important town in Myanmar was captured recently by a rebel group.
Background:
- The Kaladan project was aimed at addressing the geo-economic and geo-political challenges of northeast India. The $484 million project is being constructed by India, under the Grant in Aid Scheme.
About KMMTTP
- The Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project (KMTTP) is a significant initiative jointly identified by India and Myanmar.
- Its primary aim is to create a multi-modal mode of transport for the shipment of cargo from the eastern ports of India to Myanmar, as well as to the North-Eastern part of India through Myanmar.
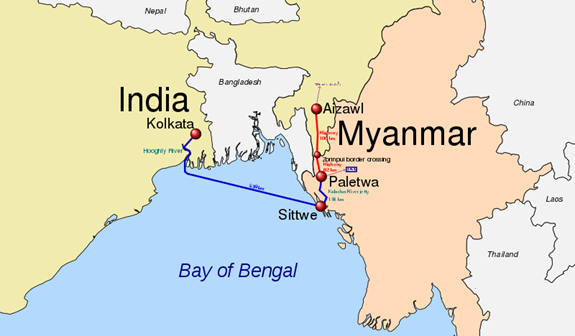
- The Kaladan Project aims to reduce the distance from Kolkata to Sittwe by approximately 1,328 kilometers (825 miles).
- It provides an alternative route that bypasses the narrow Siliguri corridor, also known as the “Chicken’s Neck.”
- It strengthens connectivity between India’s northeastern states and the mainland.
- Route and Components:
- The project connects the eastern Indian seaport of Kolkata with the Sittwe seaport in Rakhine State, Myanmar via sea.
- In Myanmar, it further links the Sittwe seaport to Paletwa in Chin State through the Kaladan river boat route.
- From Paletwa, the project extends by road to Mizoram state in Northeast India.
- All components of the project, including Sittwe port, power, river dredging, and Paletwa jetty, have been completed except for the under-construction Zorinpui-Paletwa road.
- The project has faced challenges due to conflicts in the region and the construction of hydro-electric projects on the tributaries of the Kaladan River.
Syllabus
- Mains– GS 3
Significance of India-Canada Relations:
- Bilateral trade in goods was approximately $ 9.9 billion and in services, it was 6.5 billion in 2022.
- Canada hosts one of the largest Indian Diasporas in the world, accounting for more than 3% of the total Canadian population.
- The science and technology collaboration mainly promotes industrial R&D with a focus on creating new IPs, processes, prototypes, and products. Since the 1990s, India and Canada have cooperated in space science. ANTRIX, the Commercial arm of ISRO, has launched several nanosatellites from Canada.
- The Civil Nuclear Agreement of 2010 facilitated Canada to provide uranium for Indian nuclear reactors as part of the agreement.
- Canada’s Indo-Pacific Policy acknowledges China as a “disruptive global power” and underscores India as a “critical partner” for collaboration in shared interests.
Issues/Challenges in India-Canada Relations:
- During the Cold War, Canada was a founding member of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), while India pursued a policy of non-alignment.
- Canada endorsed a plebiscite in Kashmir, which ran counter to India’s interests.
- After India’s nuclear tests in 1998, Canada temporarily halted potential nuclear cooperation with India.
- Canada’s immigration system enables individuals with a contentious past to acquire citizenship and utilize that position to engage in activities against other nations. This presents a substantial obstacle to upholding robust bilateral relations in today’s interconnected global landscape.
- The current coalition government in Canada is with the alliance of Pro-Khalistan parties enabling the particular stand.
- A Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) between these countries is pending since 2010. CEPA between them could boost bilateral trade by as much as $6.5 billion, yielding a GDP gain of $3.8 billion to $5.9 billion for Canada by 2035.
- Canada is meddling in India’s domestic affairs. For example, during the farmers’ protests in India, the Canadian PM expressed his support for the farmers, stating that the situation was a cause for concern.
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following statements about Curative petition:
- It is explicitly mentioned in the constitution of India.
- Supreme Court has to mandatorily accept curative petition as it is the right of aggrieved person.
- It cannot be filed in the case of a death sentence.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- None of the above
Q2) With reference to Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), which of the statements given below is correct?
- Monetary Policy Committee is a constitutional body.
- Union Finance Minister is the chairperson of the Monetary Policy Committee.
- The current mandate of the committee is to maintain 4% annual inflation until 31 March 2026.
- The MPC is required to meet at least two times a year and it publishes its decisions after each meeting.
Q3) With reference to Uniform Civil Code (UCC) in India, consider the following statements:
- Uttarakhand is the first state to implement a law on Uniform Civil Code in India.
- All the people in Uttarakhand comes under the scope of Uniform Civil Code.
- UCC is mentioned in Article 44 of the Indian Constitution.
How many statements given above is/are not correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 9th February 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 8th February – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – c











