IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current event
Context: Exercise Samudra Laksamana is underway from 28 Feb – 02 Mar 24 at/ off Visakhapatnam.
Background:-
- Exercise Samudra Laksamana holds strategic significance as it reinforces the enduring partnership between the Indian and Royal Malaysian Navies.
About EXERCISE SAMUDRA LAKSAMANA:-
- It is a joint naval exercise between the navies of India and Malaysia.
- This is the third edition of the exercise; first of which was conducted in 2019.
- Indian Naval Ship Kiltan and Royal Malaysian Ship KD Lekir are participating in the 3rd edition.
- It has both harbour phase and sea phase
- At harbour, crew of both ships will have various professional interactions, Subject Matter Expert Exchange on topics of mutual interest, sports fixtures, and other interactions. These interactions are aimed to enhance knowledge base, share best practices and further cooperation on maritime aspects.
- During sea phase, units would be jointly honing skills while conducting various operations at sea.
Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims and Mains – GS2
Context: On February 29, Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Prime Minister Pravind Jugnauth of Mauritius jointly inaugurated an airstrip and a jetty that India has built on Agaléga, a two-island Mauritian dependency 1,100 km to the north of Port Louis and 2,500 km southwest of Malé.
Background:
- As Indian Ocean outposts, Mauritius have great strategic significance for India. New Delhi’s maritime security and strategic imperatives in the Indian Ocean are linked to the presence and increased activities of China in the region.
About Mauritius
- Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about 2,000 kilometres (1,100 nautical miles) off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar.
- It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Agaléga, and St. Brandon .
- The main island of Mauritius, where the population is concentrated, hosts the capital and largest city, Port Louis.
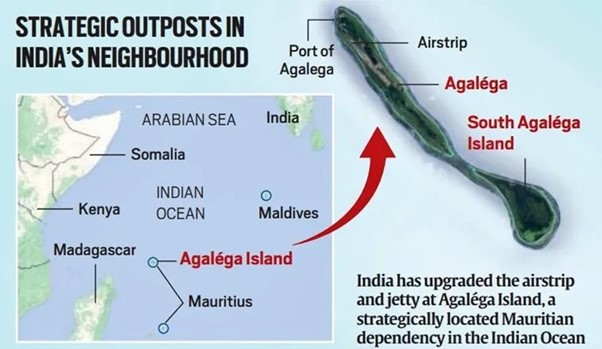
Significance and the china angle:
- The new facilities are intended to project India’s power in the southwestern Indian Ocean, in response to the increasing forays of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA) in the region.
- The inauguration of the airstrip and the jetty at Agaléga Island in Mauritius took place even as President Mohammed Muizzu’s government in the Maldives, another Indian Ocean nation, of late started steering his nation into China’s orbit of geopolitical influence, ignoring the security concerns of India.
- The presence of India would lead to more effective monitoring of Mauritius’ vast 2.3 million sq km Exclusive Economic Zone, and equip it to better counter-piracy, terrorism, narcotics and human trafficking, and illegal and unregulated fishing as per Mauritius PM.
- New Delhi started building the facility after signing a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Port Louis “for the Improvement in sea and air transportation facilities” in Agaléga Island in March 2015.
- India officially maintains that the facility is intended to help Mauritius enhance its maritime security capabilities. However, given the strategic location of Agaléga Island, speculation has been rife that India may consider deploying some of its Boeing Poseidon 8I maritime patrol and reconnaissance aircraft in the newly constructed facilities, ostensibly to keep watch on the movement of the Chinese PLA Navy’s vessels in the Indian Ocean region.
- The project triggered protests from a section of the local people with the opposition parties in Mauritius, accusing the successive governments of undermining the sovereignty of the nation.
- Indian believes the protest has been triggered by china.
Source: Deccan Herald
Syllabus
- Prelims- Current Event
Context: The 55th session of the United Nations Human Rights Council has commenced
Background:
- The attendees of the 55th session of the United Nations Human Rights Council includes representatives from various nations, each contributing their perspectives and expertise.
About UNITED NATIONS HUMAN RIGHTS COUNCIL (UNHRC)
- The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) is an intergovernmental body within the United Nations system.
- It is responsible for strengthening the promotion and protection of human rights around the globe.
- The UNHRC is composed of 47 Member States.
- India was re-elected to the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) for the 2022-2024 term with an overwhelming majority in the General Assembly. This re-election marks India’s record sixth term as a member of the UNHRC.
- The UNHRC has the ability to discuss all thematic human rights issues and situations that require its attention throughout the year.
- The UNHRC meets at the United Nations Office at Geneva.
- It was established in 2006 by the General Assembly.
- It responds to human rights emergencies and makes recommendations on how to better implement human rights on the ground.
- The UNHRC reviews the human rights records of all United Nations Member States via the Universal Periodic Review.
- It authorizes commissions of inquiry and fact-finding missions, which produce evidence on war crimes and crimes against humanity.
Source: UNHCR
Syllabus
- Prelims : Economy
Context:Reserve Bank of India revised the guidelines for the Regulatory Sandbox (RS) scheme.
Background:
- Updated framework requires sandbox entities to ensure compliance with provisions of the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
About Regulatory Sandbox (RS) scheme :
- The Regulatory Sandbox (RS) scheme is an initiative by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- It involves live testing of new financial products or services in a controlled regulatory environment with potential relaxations for testing purposes.
- It allows regulators, innovators, financial service providers, and customers to test new financial innovations, collecting evidence on benefits and risks.
- The objective of the Regulatory Sandbox (RS) is to foster responsible innovation in financial services, promote efficiency, and bring benefit to consumers.
- Fintech companies, startups, banks, financial institutions, and other entities partnering with or supporting financial services businesses are eligible to participate in the RS.
- The RBI has recently extended the RS timeline from seven months to nine months.
- RS scheme Participants must ensure compliance with provisions of the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
Source: Economic Times
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
Context: According to a recent report, India’s leopard population rose by 8% from 12,582 in 2018 to 13874 in 2022.
Background:
- Indian Leopard is listed in Schedule I of the Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 and included in Appendix I of CITES.It is listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List
Findings:
- India’s leopard population is estimated at 13,874 individuals (with a range of 12,616 to 15,132).
- This represents a stable population compared to the similar area sampled in 2018, which had 12,852 individuals.
- The estimate covers 70% of leopard habitat, excluding regions like the Himalayas and semi-arid parts that are not tiger habitat.
Regional Trends:
- Central India: Shows a stable or slightly growing leopard population (2018: 8,071, 2022: 8,820).
- Shivalik Hills and Gangetic Plains: Experienced a decline (2018: 1,253, 2022: 1,109).
- Overall Growth Rate: Across India, the sampled area showed a 1.08% per annum growth.
- Highest Growth Rate: Central India and Eastern Ghats exhibited the highest growth rate at 1.5%.
State-wise Distribution:
- Madhya Pradesh: Houses the largest leopard population in the country with 3,907 individuals (2018: 3,421).
- Maharashtra: Follows with 1,985 leopards (2018: 1,690).
- Karnataka: Stands third with 1,879 leopards (2018: 1,783).
- Tiger Reserves: Nagarajunasagar Srisailam (Andhra Pradesh), Panna (Madhya Pradesh), and Satpura (Madhya Pradesh) have the highest leopard populations.
State-wise Trends:
- Madhya Pradesh: Witnessed the most significant uptick, with an increase of 486 leopards.
- Arunachal Pradesh: Led in terms of percentages, with a whopping 282% increase.
- Goa, Bihar, Telangana, Kerala, Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, and Odisha reported declines.
- Odisha witnessed a staggering drop of 192 leopards or 25% between 2018 and 2022.
- Uttarakhand experienced a decline in leopard numbers but significant growth in tiger numbers.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 4
Context: The recent directive by the Patan District Collector, mandating the transfer of all ration cards from a Dalit-run Fair Price Shop (FPS) in Kanosan village to a neighboring village, raises important ethical and constitutional questions.
Background:
- Patan District Collector Arvind Vijayan, via an order dated September 12, has shifted the ration cards of all 436 households in Kanosan to the neighbouring Edla FPS following an alleged social boycott by the Thakor community.This directive was issued when the majority of the Kanosan village’s non-Dalit residents stopped buying their monthly ration from the FPS run by a Dalit FPS vendor
About Fair Price Shop (FPS)::
- It is a government-run or government-regulated retail outlet or store in India.
- The primary purpose of fair-price shops is to distribute essential commodities like food grains, edible oils, sugar, and other necessities to the public at subsidized or fair prices.
- These shops are typically part of government welfare programs aimed at ensuring food security and reducing the economic burden on low-income households.
Ethical aspects involved in the incident:
- The core ethical issue in this case isdiscrimination based on caste leading to the transfer of ration cards.
- The district collector’s directive to transfer ration cards can be seen as adereliction of duty. The ethical principle of integrity, where public officials are expected to act in the best interest of all citizens without favouritism should be practiced.
- The mental trauma experienced by, the victim of caste-based discrimination, leading to a suicide attempt and physical injury, is a significant ethical concern. Ethical principles ofcompassion, empathy, and the duty to protect individuals’ well-being become important.
- The convenors of theRight to Food Campaign call for the application of legal frameworks like the SC/ST Act and the National Food Security Act. The ethical principle of upholding the rule of law and respecting the constitution should be abided by.
- The violation of the mandated principles related to the empowerment ofmarginalized communities is a key ethical concern. Ethical principles of fairness, equity, non-discrimination, justice, and equality should be adhered to.
- Themoral responsibility of the district collector and the upper caste households in addressing the consequences of their actions is raised.
Actions that could be taken in similar situations:
- Model ofMid-Day Meals Scheme implementation can be adopted where high dignitaries eat the cooked food to bust the myths of caste stigma and discrimination.
- Further legal action must be taken to address thecaste-based discrimination and social boycott effectively. Linking such erroneous activities with Annual Confidential Reports of bureaucrats such that it acts as a deterrence in the future.
- The impendingrevocation of the Dalit FPS dealer’s license raises concerns about economic repercussions and livelihoods.
- The Right to Food Campaign urges theHigh Courts or Chief Minister’s Office of the government to take Suo Motu cognizance of the discriminatory ration card transfers. Such action is essential to uphold the rule of law and constitutional values.
- FPSs play a crucial role inensuring food security and access to essential commodities for marginalized communities. Democratic empowerment of FPSs is vital to promote inclusivity and economic well-being.
Source: Down To Earth
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Consider the following:
- Nagarajunasagar- Srisailam
- Panna
- Satpura
Leopards are found in how many of the above given Tiger Reserves?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2.) With reference to Regulatory Sandbox (RS) scheme, consider the following statements:
- The Regulatory Sandbox scheme is an initiative of NITI Ayog.
- The RS aims to foster responsible innovation in financial services.
- It involves live testing of new financial products or services in a controlled regulatory environment.
- RS scheme Participants must ensure compliance with provisions of the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q3.)Consider the following statements about United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC):
- UNHRC is an intergovernmental body within the United Nations system.
- The UNHRC reviews the human rights records of all United Nations Member States.
- India is not a member of UNHRC.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 2nd March 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 1st March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – a











