IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – Geography, Security challenges
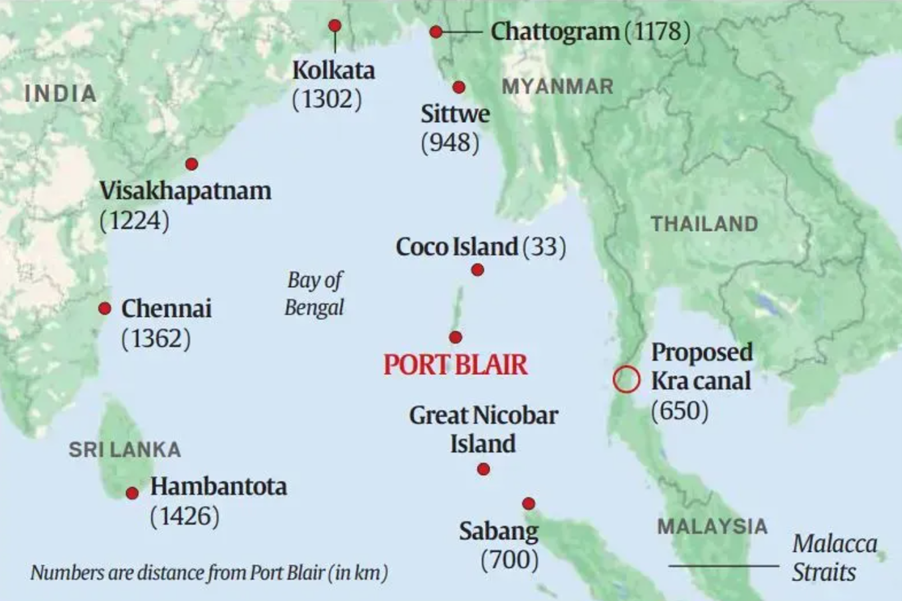
Context: Various geopolitical events leading to the realisation of the critical importance of ocean power, the rapid enhancement in the capabilities of the Chinese PLA Navy, and the transformation of India’s Look East policy into a robust Act East policy have brought new thrust to developing Indian island territories in general and the Andaman and Nicobar groups in particular.
Background:-
- The Andaman and Nicobar (A&N Islands) islands are located 700 nautical miles (1,300 km) southeast of the Indian mainland.
Key takeaways
- Andaman and Nicobar islands share four of India’s international maritime zone delimitations with Myanmar, Thailand, Indonesia, and Bangladesh.
- They also give India substantial ocean space under the United Nations Conference on the Laws of the Sea (UNCLOS) in terms of exclusive economic zone and continental shelf.
- The Malacca Strait, the main waterway that connects the Indian Ocean to the Pacific, is less than a day’s steaming from Port Blair.
- The severe disruption and re-routing of shipping, occasioned by the Houthi attacks in the Red Sea, have served as yet another harsh and expensive reminder that “maritime choke points” constitute critical vulnerabilities for world trade and commerce. In this context, the Malacca Strait — more than 90,000 merchant ships carrying about 30 per cent of the world’s traded goods pass through it every year — presents a challenge as well as a latent opportunity for India.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are of great strategic importance since they straddle one of the busiest sea lanes in the world and give India the reach to monitor the flow of traffic from the South China Sea (Pacific Ocean) to the Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) via the Strait of Malacca that’s key to trade and oil shipments in the Indo-Pacific.
- Of significance for Indian strategists is the location of the Great Nicobar Island, which sits astride the western entrance/exit of the Malacca Strait and can comprehensively dominate all shipping — merchant as well as naval — in transit.
- The A&N Islands should be the first line of offence against any attempt from the East to undermine India’s maritime security.
- While some effort was made to leverage this locational advantage with the Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) being constituted as a tri-services command in 2001, subsequent efforts have been grossly inadequate.
Reasons for the Slow Pace of Infrastructural Development in the A&N Islands:
- Distance from the mainland and difficulties in developing infrastructure.
- Complex procedures for obtaining environmental clearances.
- Significant coordination challenges among ministries, departments, and agencies.
Key areas to be focused on for the development of the A&N Islands:
- Development of separate airfields with long runways for monitoring and patrolling of sea areas by aircraft and surface platforms.
- Work on the Galathea Bay (Great Nicobar Island) transhipment port must be expedited.
- Maritime services such as repair and logistics must be developed for international and Indian shipping.
- Road networks, high-speed inter-island ferry services, and a seaplane terminal.
- Forest and environmental clearances must be accorded with minimum red tape.
- Planned habitation of uninhabited islands should be considered by providing incentives.
- Eco-friendly entrepreneurial efforts could be encouraged.
- Ports and fuel storages
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – Geography
Context: The effects of ocean warming are profound and well-documented. But sometimes changes in the patterns of winds and ocean currents cause seawater to suddenly cool, instead.
Background:
- When a “killer coldwave” manifested along South Africa’s southeast coast in March 2021, it killed hundreds of animals across at least 81 species. More worrying still was the fact these deaths included vulnerable manta rays and even specimens of notoriously robust migratory bull sharks.
About Cold waves
- Sometimes changes in the patterns of winds and ocean currents cause seawater to suddenly cool. Surface temperatures can plummet rapidly — by 10ºC or more over a day or two. When these conditions persist for several days or weeks, the area experiences a “coldwave”.
- Certain wind and current conditions can cause the sea surface to cool, rather than warm. This happens when winds and currents force coastal waters to move offshore, which are then replaced from below by cold water from the deep ocean. This process is known as
- In some places, such as California on the US west coast, upwelling happens regularly along hundreds of kilometres of coastline. But localised upwelling can occur seasonally on a smaller scale, too, often at the edges of bays on the east coasts of continents due to interactions of wind, current and coastline.
- Previous research had shown climate change induced changes in global wind and current patterns.
- Studies reveal an increasing trend in the number of annual upwelling events over the past 40 years. We also found an increase in the intensity of such upwelling events and the extent to which temperatures dropped on the first day of each event – in other words, how severe and sudden these cold snaps were.
- During the extreme upwelling event along the southeast coast of South Africa in March 2021, at least 260 animals from 81 species died. These included tropical fish, sharks and rays.
- Overall, our oceans are warming. The ranges of tropical and subtropical species are extending towards the poles. But along some major current systems, sudden short-term cooling can make life difficult for these climate migrants, or even kill them.
- This really shows the complexity of climate change, as tropical species would expand into higher-latitude areas as overall warming continues, which then places them at risk of exposure to sudden extreme cold events.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
Context: Ashwagandha is gaining global attention and popularity for its numerous health benefits.
Background:
- Scientific research highlights its potential in stress management, cognitive function, physical performance, and more.
About ASHWAGANDHA (WITHANIA SOMNIFERA)
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera), also known as Indian ginseng or winter cherry, is a prominent herb in Ayurveda, the traditional medicine system of India.
- It is renowned for its adaptogenic properties, which help the body manage stress.
Some of the Potential Benefits and Uses of Ashwagandha:
- Stress and Anxiety Reduction: Ashwagandha may lower cortisol levels and mitigate stress and anxiety symptoms.
- Athletic Performance: It could potentially enhance physical performance and strength.
- Cognitive Function: There’s evidence suggesting it may improve memory and brain function.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Withanolides in Ashwagandha have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Sleep Improvement: Some studies indicate it may help improve sleep quality.
Source: Hindu Businessline
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context:The Indian government has simplified the payment mechanism for traders importing pulses from Myanmar by implementing the Rupee/Kyat direct payment system through the Special Rupee Vostro Account (SRVA) via Punjab National Bank.
Background:
- This move aims to streamline trade transactions and enhance efficiency. India heavily relies on imports of pulses, including tur and urad dals, from Myanmar to meet domestic demand.
About SPECIAL RUPEE VOSTRO ACCOUNT (SRVA):
- Special Rupee Vostro Account (SRVA) is an account that domestic banks hold for foreign banks in the former’s domestic currency, which, in this case, is the Indian Rupee (INR).
- It allows domestic banks to provide international banking services to their clients who have global banking needs without physically being present abroad.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) introduced the SRVA mechanism to settle international transactions in rupees.
- The primary objectives were to promote the growth of global trade, emphasize Indian exports, and position the rupee as an international currency.
Why SRVA?
- The existing system primarily uses freely convertible currencies (like the US dollar or pound) for trade transactions.
- However, the SRVA serves as an additional arrangement to this system, specifically focusing on transactions denominated in INR.
- It aims to reduce costs associated with currency conversions and streamline trade processes.
Key Components of SRVA:
- Invoicing: All exports and imports must be denominated and invoiced in Indian National Rupee (INR).
- Exchange Rate: The exchange rate between the currencies of the trading partner countries is market-determined.
- Final Settlement: The ultimate settlement also takes place in INR.
Benefits and Significance:
- Promoting Trade: SRVA facilitates smoother trade between India and other nations, including those facing sanctions (e.g., Russia).
- Reducing Currency Risks: By using INR, both parties avoid currency fluctuations and associated risks.
- Cost-Efficiency: Eliminating the need for multiple currency conversions saves costs for businesses.
Source: Livemint
Previous Year Question
Q1. Convertibility of rupee implies
- being able to convert rupee notes into gold
- allowing the value of rupee to be fixed by market forces
- freely permitting the conversion of rupee to other currencies and vice versa
- developing an international market for currencies in India
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
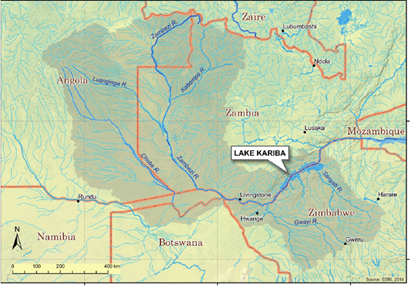
Context: Water levels at Lake Kariba in Zimbabwe have dropped dramatically because of the latest El Nino drought.
Background:
- El Niño leads to hotter temperatures and significantly reduced rainfall in southern Africa for extended periods.
About LAKE KARIBA :
- Lake Kariba is renowned as the world’s largest artificial lake and reservoir by volume.
- It situated along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe.
- It was created following the completion of the Kariba Dam at its northeastern end, which flooded the Kariba Gorge on the Zambezi River.
- The lake was filled between 1958 and 1963 and is a significant source of hydroelectric power for both countries.
- This drastic decline in the water level of the Lake Kariba has a severe consequence for local communities, affecting livelihoods, economic activities, and the environment.
- The Zimbabwean government has declared a national disaster in response to this unfolding crisis.
Source: Down To Earth
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1
Context: With the advent of the New Education Policy (NEP) and recent initiatives like the NIPUN Bharat Mission that stresses the importance of using the mother tongue in the teaching-learning process and creating educational materials, we have an opportunity to revolutionise education.
Background:
- In a diverse and culturally rich country like India, language is more than just a means of communication; it is the essence of our identity.
Multilingualism:
- It is the ability to speak, understand, read, and write more than one language.
- It can be individual or societal, depending on whether a person or a community uses multiple languages.
- It can also be classified into different types, such as additive or subtractive, balanced or dominant, sequential or simultaneous, depending on how languages are acquired, used, and valued.
- India is one of the most linguistically diverse countries in the world, with over 19,500 languages spoken throughout the nation.
- According to the 2011 Census of India, more than 25% of the population speaks two languages, while about 7% speak three languages.
Importance/Significance of Multilingualism in Education:
- Research shows that learning more than one language can boost brain functions, such as memory, attention, problem-solving, and creativity. It can also improve metalinguistic awareness, which is the ability to reflect on and manipulate language structures and rules.
- Learning multiple languages can expose students to different cultures, perspectives, and values. It can also help them develop intercultural competence, which is the ability to communicate effectively and appropriately with people from diverse backgrounds. With over 22 officially recognised languages and hundreds of dialects, each with its own unique cultural and historical significance, language is a crucial aspect of our identity.
- Studies have consistently shown that students who receive instruction in their mother tongue or home language perform better in school than those who are taught in a foreign or unfamiliar language. This is because they can access the curriculum content more easily and confidently, and transfer their skills and knowledge to other languages.
- Providing education in multiple languages can ensure that every child has equal access and opportunity to learn, regardless of their linguistic background. It can also foster a sense of belonging and identity among minority language speakers, and reduce discrimination and marginalization.
Ways to implement Multilingual Education:
- Multilingual education should be based on the linguistic realities and needs of the learners and the communities. It should also respect the constitutional provisions and the three-language formula of the National Education Policy (NEP 2020).
- Multilingual education should adopt a learner-centered and interactive pedagogy that fosters language awareness and proficiency. It should also promote cross-linguistic transfer and multiliteracy skills among the learners.
- Multilingual education should use fair and valid assessment tools and criteria that measure the learning outcomes and progress of learners in multiple languages. It should also provide constructive feedback and support to the learners to improve their language skills.
Benefits of Multilingual Education for India:
- Multilingual education can equip learners with the necessary language skills and competencies to participate in various domains of life, such as education, employment, research, innovation, etc. It can also increase their employability and mobility in the globalized world.
- Multilingual education can help preserve and revitalize the linguistic diversity and heritage of India. It can also promote the linguistic rights and dignity of the speakers of different languages, especially those who are endangered or marginalized.
- Multilingual education can foster mutual understanding and respect among speakers of different languages and cultures. It can also enhance social cohesion and harmony among the diverse groups of people in India.
- Starting education in one’s mother tongue provides a solid foundation for learning additional languages, including the national language and English, promoting multilingualism.
- When students can understand what they are being taught, they are more likely to stay in school and complete their education.
Issues/Challenges for Multilingualism in Education:
- Implementing multilingual education requires adequate resources, such as trained teachers, appropriate curricula, quality textbooks, assessment tools, and digital platforms. However, many schools lack these resources, especially in rural and remote areas.
- Although the NEP 2020 and the NIPUN Bharat Mission advocate for multilingual education, there is still a gap between policy and practice. There is also a need for more coordination and collaboration among different stakeholders, such as central and state governments, educational institutions, civil society organizations, and communities.
- Many parents, teachers, students, and policymakers are not aware of the benefits of multilingual education. They may have misconceptions or prejudices about certain languages or dialects.
- Balancing the use of mother tongues or regional languages with national or standardized curricula can be challenging. Ensuring that students have access to a well-rounded education while also valuing their linguistic backgrounds is crucial.
- Developing fair and standardized assessment methods across different languages can be difficult. Ensuring that students are evaluated fairly and consistently can be a challenge when using multiple languages.
- While multilingual education can be effective at the primary level, transitioning to higher education or the job market might require proficiency in a more widely spoken language, potentially disadvantageous to students who were educated in their mother tongue.
Source: Hindu Businessline
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Which among the following lake recently had a devastating impact due to the El Niño drought?
- Chilika
- Pangong Tso
- Caspian
- Kariba
Q2.) Withania somnifera, recently seen in news is
- a herb
- an invasive plant
- a vaccine
- a turtle
Q3.) With reference to the Special Rupee Vostro Account (SRVA), consider the following statements:
- SRVA is an account that domestic banks hold for foreign banks in the former’s domestic currency.
- SRVA facilitates smoother trade between India and other nations, including those facing sanctions.
- The exchange rate between the currencies of the trading partner countries is market-determined.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 17th April 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 16th April – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – c