IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: The unchecked population growth of spotted deer (Chital) is creating problems in Netaji Subhash Chandra Boss Island.
Background:-
- Introduced to the Andaman and Nicobar Islands for game hunting in the early 1900s by the British, the herbivore multiplied unchecked for years in the absence of large predators.It has become an “invasive” problem for the Union Territory’s authorities.
About Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Island
- Earlier Ross Island, now officially known as Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Island, is an island of the Andaman Islands.
- The Island is situated three kilometres East of Central Port Blair.
- It belongs to the South Andaman administrative district, Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are strategically located in the Indian Ocean between the Indian mainland, Myanmar, and Indonesia, and are close to important maritime routes.
- The islands were first controlled by the Dutch, then by the British, and were taken over by the advancing Japanese military during World War II.
- The Azad Hind government was able to obtain de jure control of the islands from the Japanese by the end of 1943, and Subhash Chandra Bose arrived in Port Blair on December 29.
- Keeping in mind the historical significance of the Andaman & Nicobar Islands and to honour the memory of Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose, Ross Islands was renamed as Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Dweep by Prime Minister during his visit to the Island in 2018. Neil Island and Havelock Island were also renamed Shaheed Dweep and Swaraj Dweep.
- All the three islands are major tourist spots.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – Environment
Context: The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has announced a Rs-496-crore (until 2025-26) scheme to support pilot projects that either test the viability of green hydrogen as a vehicle fuel or develop secure supporting infrastructure such as refuelling stations.
Background:
- Big Indian commercial vehicle manufacturers such as Tata Motors, Volvo Eicher, and Ashok Leyland are doubling down on efforts to develop hydrogen-powered trucks and buses by ramping up research and development, and building manufacturing capacities.
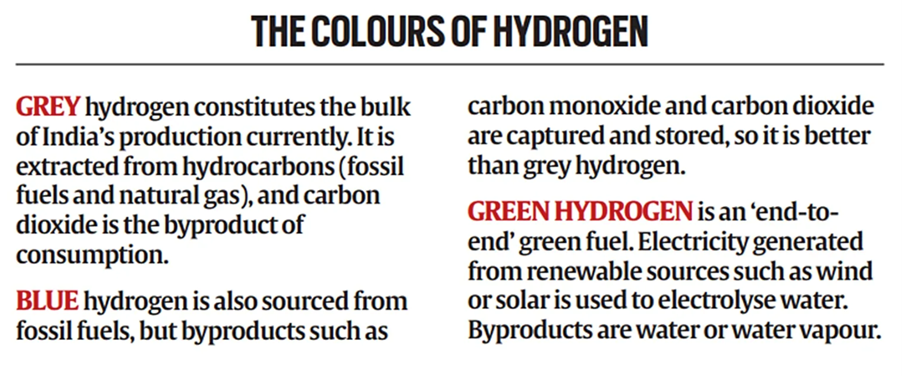
About Green Hydrogen :
- Hydrogen is colourless, and green hydrogen is ‘green’ only by virtue of the way it is produced, and the source of the energy used to manufacture it.
- Green hydrogen refers to hydrogen that is produced from the electrolysis of water — splitting it into hydrogen and oxygen — using an electrolyser powered by renewable energy.This is considered to be a virtually emission-free pathway for hydrogen production — it is ‘end-to-end’ green because it is powered by green energy, uses water as feedstock, and emits no carbon on consumption.
- Currently, most hydrogen produced for industrial consumption and applications is ‘grey’ hydrogen, which is produced from natural gas through energy-intensive processes, and has high carbon emissions.Except for a difference in the production pathway and emissions, green hydrogen is essentially the same as grey — or hydrogen categorised by any other colour.
Challenges to the large-scale use of green hydrogen in the transportation sector:
- The foremost among challenges is the prohibitive cost of production, followed by challenges of storage and transportation at scale.
- Green hydrogen-powered vehicles are not yet seen as a suitable alternative to four-wheel battery electric vehicles (BEVs) due to challenges arising from fuel costs and building supporting infrastructure.
- Hydrogen is extremely flammable, which means that special care would be needed in handling the fuel at retail stations compared to diesel, petrol, or even CNG. Robust and fool-proof handling and safety standards need to be developed before pushing large-scale adoption.
- Currently, most cylinders manufactured in India are designed to carry compressed natural gas (CNG). But hydrogen is stored at a much higher pressure, and CNG cylinders cannot carry hydrogen. For cylinders to carry a high mass of hydrogen, the carbon fibre needs to be stronger, which makes high-pressure hydrogen cylinders expensive. This is a key barrier to the adoption of hydrogen as a transport fuel. For the same reason, the existing natural gas pipeline infrastructure is also not seen as viable.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – History
Context: The NCERT recently introduced certain revisions to the history syllabus of Class 12 students, highlighting that Harappans were based out in Rakhigarhi.
Background:
- These revisions reflect a deeper understanding of the Harappan civilization and its historical context, shedding light on their origins and societal structures.
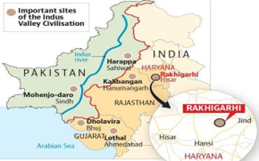
About RAKHIGARHI
- Rakhigarhi is an archaeological site located in Hisar, Haryana, and is recognized as one of the largest Harappan (Indus Valley Civilization) sites in the Indian subcontinent.
- Rakhigarhi is situated in the plains of the Saraswati River, about 27 km from the seasonal Ghaggar river.
- The site showcases continuity from the Harappan age to the present times.
- It is recognized for its extensive Harappan heritage, offering insights into ancient urban life and culture.
- Excavations were carried out at Rakhigarhi to study its evolution from 6000 BC (Pre-Harappan phase) to 2500 BC.
- In order to study the genetic history of the Harappans, DNA was extracted from the skeletal remains excavated at Rakhigarhi.
Previous Year Question
Q1. Which of the following characterizes/characterize the people of Indus Civilization?
- They possessed great palaces and temples.
- They worshipped both male and female deities.
- They employed horse-drawn chariots in warfare.
Select the correct statement/statements using the codes given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- None of the statements given above is correct
Source: Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: The World Bank warned that South Asian nations run the risk of “squandering its demographic dividend” because job creation is not keeping up with the growth in the working-age population.
Background:
- According to data in the report, between 2000 and 2023, When the working-age population grew by an average of 19 million per year, the region added 10 million employments annually on average.
About DEMOGRAPHIC DIVIDEND:
- The United Nations Population Fund defines demographic dividend as “the economic growth potential that can result from shifts in a population’s age structure, mainly when the share of the working-age population is larger than the non-working-age share of the population”.
- The demographic dividend in India presents various opportunities related to economic growth due to increased economic activities from a higher working-age population and lower dependent population.
Features of India’s Demographic Dividend:
- Large and Growing Working-Age Population: The working-age population (15-64 years old) in India has surpassed the dependent population since 2018.
- Uniqueness: The window of opportunity for India’s demographic dividend spans five decades from 2005-06 to 2055-56, which is longer than any other country in the world.
- Increasing Education Levels: Education levels in India are rising, providing a more skilled and productive workforce.
- Increasing Gender Equality: There has been significant progress in recent years toward gender equality, including increasing levels of education and workforce participation among women.
Source: Business Standard
Previous Year Question
India is regarded as a country of ‘Demographic Dividend’. This is due to:
- Its high population in the age group below 15 years
- Its high population in the age group of 15-64 years
- Its high population in the age group above 65 years
- Its high total population
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: The Indian Army has initiated the induction of control and reporting systems under ‘Project Akashteer’ to bolster its air defence capabilities.
Background:
- Akashteer revolutionizes air defence operations, empowering India’s armed forces with cutting-edge capabilities.
About PROJECT AKASHTEER:
- The ‘Project Akashteer’ is a significant initiative aimed at enhancing the air defence capabilities of the Indian Army.
- It is developed by Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) as part of the ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ initiative.
- This project is designed to automate air defence control and reporting processes by digitizing them.
- The system integrates radar and communication systems at all levels into a unified network, providing an unprecedented level of situational awareness and control.
- This enables swift engagement of hostile targets, significantly reduces the risk of fratricide, and ensures the safety of friendly aircraft in contested airspace.
- A noteworthy aspect of ‘Akashteer’ is its emphasis on mobility and resilience.
- The system’s control centers, designed to be vehicle-based and mobile, can maintain operational capabilities even in challenging communication environments.
- The project is expected to significantly enhance the operational efficiency and integration of the Army’s air defence mechanisms.
- The total cost of the project is nearly Rs 1,982 crore.
Source: Economic Times
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2
Context: The Union Cabinet had approved the Migration and Mobility Agreement between India and Italy last December.
Background:
- India and Italy are ancient civilisations with links going back 2,000 years. Italian port cities were important trading posts on the spice route. The Venetian merchant Marco Polo traveled to India in the 13th century and wrote about his experiences.After Independence, political relations between India and Italy were established in 1947. Since then, there has been a regular exchange of visits at political and official levels between both countries, including several visits by Heads of States.
India and Italy Relations:
- There has been a regular exchange of visits at political and official levels between both countries. For instance, the Indian PM paid his first official visit to Italy in October 2021 to attend the G20 Summit. In March 2023, the Italian PM paid her first-ever state visit to India as the guest of honour of Raisina Dialogue.
- Italy is India’s 4th largest trading partner in the EU. The bilateral trade between the two countries was valued at US$ 14.25 billion in 2022-23, with the balance of trade being in India’s favour.
- India – Italy Military Cooperation Group (MCG) is a forum established to boost defence cooperation. India and Italy signed a defence cooperation agreement (in 2023) to promote cooperation in varied defence domains such as security and defence policy, and defence industrial cooperation among others.
- The relationship between India and Italy was elevated to a Strategic Partnership in March 2023 during the visit of the Italian Prime Minister to India. A connection was identified between the Indo-Pacific, in which India plays a leading role, and the enlarged Mediterranean where Italy sits at the centre of the Mediterranean Sea and acts as a natural bridge towards the Indo-Pacific. Italy’s decision to withdraw from the Belt and Road Initiative aligns with common goals in global connectivity between Rome and New Delhi.
- Italy supported India’s entry into the Wassenaar Arrangement and Australia Group. The Blue-Raman project (with an Italian company at its core) will bring the Mediterranean and the Indian Ocean closer in exchange for digital data through a submarine cable system. Italy supported India’s major initiatives including the International Solar Alliance (ISA), the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC), and the Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA).
Concerns/Challenges/Issues in India-Italy Relations:
- India and Italy, despite having historical trade ties dating back to the Roman era have relatively low the current volume of trade and investment.
- Italian Mariners’ case sparked a conflict over legal jurisdiction and functional immunity, which ended only in 2020 with the verdict of the Permanent Court of Arbitration.
- In the Agusta Westland helicopter scandal, the defence firm owned by Italian company Leonardo was accused of bribery, resulting in India cancelling the procurement deal and banning Leonardo from the Indian defence market in 2015.
- In 2021, the India-Italy-Japan trilateral partnership was launched yet it has not been operationalised.
Way Forward:
- Strengthen trade ties to increase trade volume, explore new avenues for investment, and promote economic cooperation.
- If the India and EU sign a trade pact in the coming time, Italy and India can enjoy major two-way trade benefits. It would also add fodder to the reinvigorated EU-India partnership.
- Italy and India can converge on multilateral issues, sharing a common imperative to shape and endorse a new global agenda together.
- Celebrate and promote the culinary heritage of both countries through food festivals and gastronomic events, with Italian pasta and pizza finding a place on Indian tables, and Indian spices adding a punch to Italian dishes.
Source: MEA
Practice MCQs
Q1.) With reference to the ‘Project Akashteer’, consider the following statements:
- The ‘Project Akashteer’ is a significant initiative aimed at enhancing the air defence capabilities of the Indian Army.
- It is developed by Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) as part of the ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ initiative.
- This project is designed to automate air defence control and reporting processes by digitizing them.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2.) Consider the following:
- Growing working-age population
- Increasing education levels
- Increasing gender equality
How many of the above are the features of India’s demographic dividend?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q3.)With reference to Rakhigarhi, consider the following statements:
- Rakhigarhi is recognized as one of the largest Harappan sites in the Indian subcontinent.
- It is located in Rajasthan.
- The site showcases continuity from the Harappan age to the present times.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 8th April 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 6th April – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – b











