IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: On March 2, La Cumbre erupted for the first time since 2020, NASA’s Earth Observatory reported, when lava began slowly seeping out of a fissure near the summit of the volcano’s 4,850-foot-tall (1,480 meters) southeast flank and dribbling down the mountain’s tree-covered slopes. Since then, lava has continually poured out of the volcano, and in early April, the river of molten rock reached the island’s coastline around 6 miles (10 km) from La Cumbre
Background:-
- Fernandina, the youngest of the Galápagos islands, is also the most volcanically active. The island’s La Cumbre volcano lies directly atop the mantle plume, or hot spot, that produced all of the Galápagos islands.
About La Cumbre volcano
- La Cumbre is a shield volcano on Fernandina Island in the Galápagos Islands.
- Volcanic emissions from Galápagos volcanoes are typically rich in sulfur dioxide and have little ash.
- The La Cumbre volcano is located around 1,125 kilometres off mainland Ecuador.
- Since Fernandina – the most volcanically active island among the Galápagos Islands – is uninhabited, there is no risk to people or infrastructure, but the lava flow reportedly has proven to be a spectacle for people on passing ships.
- Most of Fernandina is rocky and inhospitable to vegetation due to recent lava flows, but a ring of vegetation grows on the volcano’s upper slopes. Vegetation covers more of the other Galápagos islands, where eruptions are less frequent.
- The island is also home to a large population of rare land iguanas which nest and lay eggs on the rim of the volcano’s large crater or caldera and deep within it.
About Galápagos Islands
- The Galápagos Islands are an archipelago of volcanic islands in the Eastern Pacific, located around the Equator 900 km (560 mi) west of South America. They form the Galápagos Province of the Republic of Ecuador.
- The Galápagos are famous for their large number of endemic species, which were studied by Charles Darwin in the 1830s and inspired his theory of evolution by means of natural selection.
- All of these islands are protected as part of Ecuador’s Galápagos National Park and Marine Reserve.
Source: Nasa
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: At least 42 people died when a dam burst its banks near a town in Kenya’s Rift Valley, as heavy rains and floods battered the country recently.
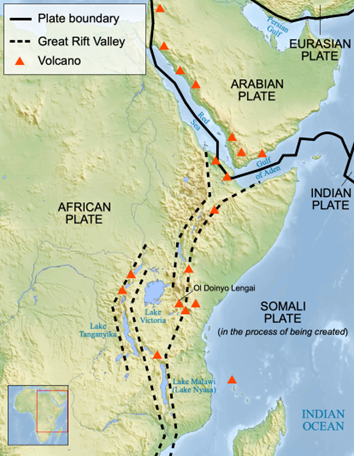
Background:
- A rift valleyis a lowland region that forms where Earth’s tectonic plates move apart, or Rift valleys are found on land and at the bottom of the ocean, where they are created by the process of seafloor spreading. Rift valleys differ from river valleys and glacial valleys in that they are created by tectonic activity and not the process of erosion.
About the Great Rift Valley
- The Great Rift Valley is a series of contiguous geographic trenches, approximately 7,000 kilometres (4,300 mi) in total length, that runs from Lebanon in Asia to Mozambique in Southeast Africa.
- While the name continues in some usages, it is rarely used in geology as it is considered an imprecise merging of separate though related rift and fault systems.
- The northern part of the system is the Jordan Rift Valley. The Jordan Rift Valley stretches from the Golan Heights, near Israel’s border with Syria and Lebanon, to the Dead Sea, to the Gulf of Aqaba—an inlet of the Red Sea that separates the Sinai Peninsula from the Arabian Peninsula.
- Associated with the Jordan Rift Valley to the south is the Red Sea Rift. Millions of years ago, the Arabian Peninsula was connected to Africa. Seafloor spreading caused the Arabian and African plates to rift apart. The Indian Ocean flooded the rift valley between the continents, creating the Red Sea.
- Today, Africa and Asia are connected by the triangle of the Sinai Peninsula. Eventually, the Red Sea Rift will separate Africa and Asia entirely and connect the Mediterranean and Red Seas.
- South of the Red Sea Rift lies the massive, complex East African Rift. Throughout the East African Rift, the continent of Africa is splitting in two. The African plate, sometimes called the Nubian plate, carries most of the continent, while the smaller Somali plate carries Horn of Africa.
- Several deep, elongated lakes, called ribbon lakes, exist on the floor of this rift valley: Lake Malawi and Lake Tanganyika are examples of such lakes. The region has a unique ecosystem and contains a number of Africa’s wildlife parks.
Source: National Geographic
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Recently, the Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency, a public sector undertaking company was granted ‘Navratna status’ from the department of public enterprises.
Background:
- IREDA provides funding and other services to projects focused on renewable energy and energy efficiency.
About NAVRATNA STATUS
- The Indian government classifies Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) into three categories: Maharatna, Navratna, and Miniratna.
- Navratna companies are a group of Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) in India that enjoy a certain degree of financial autonomy from the government.
- These companies have specific privileges and can invest up to Rs 1,000 crore without explicit government approval.
Eligibility Criteria for Navratna Status:
- A company must first be a Miniratna and have four independent directors on its board before it can be considered for Navratna status.
- The company must score at least 60 out of 100 based on specific parameters, including : PBDIT (Profit Before Depreciation, Interest, and Taxes), Total Manpower Cost, Cost of Services, Capital Employed, Net Worth, Net Profit.
- Additionally, the company must demonstrate significant global presence or international operations.
Benefits of Navratna Status:
- Navratna companies can invest up to Rs 1,000 crore or 15% of their net worth in a single project, whichever is lower.
- They can also invest up to 30% of their net worth over the entire year, again not exceeding Rs 1,000 crore.
- These companies have greater financial flexibility and can undertake strategic projects without seeking explicit government approval.
Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency (IREDA)
- Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency (IREDA) is a ‘Navratna’ Government of India Enterprise under the administrative control of the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE).
- Established in 1987, IREDA serves as a Non-Banking Financial Institution (NBFC) dedicated to promoting, developing, and extending financial assistance for projects related to renewable sources of energy and energy efficiency/conservation.
Source: Livemint
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: Recently, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has accused Apple of using conflict minerals.
Background:
- The DRC accuses Apple of purchasing minerals that have been smuggled out of the country into neighbouring Rwanda. These minerals are then integrated into Apple’s global technology supply chain, where their origin is allegedly obscured.
About CONFLICT MINERALS:
- Conflict minerals, also known as “blood minerals,” are extracted from regions affected by armed conflict or human rights abuses.
- These minerals play a significant role in funding violence and wars.
- These minerals play a crucial role in various industries, including electronics, automotive, and renewable energy.
- The DRC is rich in untapped reserves of precious metals and minerals.
- The primary conflict minerals include: Tin , Tantalum, Tungsten, Gold.
- These minerals are extracted from ores such as cassiterite (tin), columbite-tantalite (tantalum), and wolframite (tungsten).
Impact of Conflict Minerals: In politically unstable regions, the trade in these minerals can:
- Finance armed groups: The proceeds from mineral sales may directly fund armed conflict.
- Fuel forced labour: Miners, including children, may be subjected to exploitative working conditions.
- Support corruption and money laundering: Illicit trade can perpetuate corruption and criminal activities.
Source: Down To Earth
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: Ajrakh from Kutch gets GI tag
Background:
- Ajrakh’s GI tag was granted by the Geographical Indications Registry after a long process of documentation and verification of its origin and production techniques.

About AJRAKH :
- The Ajrakh fabric is a traditional hand-block printing technique that originated in Kutch, Gujarat.
- It uses natural dyes and intricate patterns to create beautiful textiles, which are then used to make sarees, dupattas, stoles, and other garments.
- The unique feature of Ajrakh is its use of geometric patterns and rich earthy colours like indigo, madder, and mustard.
- This fabric has been an integral part of the Kutchi culture for centuries and has now gained recognition on a global level with its GI tag.
What is a GI tag?
- A Geographical Indication (GI) tag is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin.
- It serves as an intellectual property right, attributing a product’s quality, reputation, or other characteristic to its geographical origin.
- In India, GI tags are issued by the Geographical Indication Registry under the Department of Industry Promotion and Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- The GI tag helps to ensure that only those registered as authorized users are allowed to use the popular product name.
- This system of tagging is beneficial as it prevents unauthorized use of a registered GI by others, promotes economic prosperity of producers of goods produced in a geographical territory, and helps consumers to get quality products of desired traits.
Some other Indian textiles that have received similar recognition.
- Banarasi Silk: It is a fine variant of silk originating from the city of Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh, India.
- Chanderi Fabric: Chanderi, a small town in Madhya Pradesh, is known for its delicate and lightweight fabric.
- Kanjeevaram Silk: The Kanjeevaram sarees from Tamil Nadu are famous for their vibrant colours, fine silk, and intricate zari work.
- Kota Doria: One of the many varieties of sari clothing produced in Muhammadabad Gohna, Mau in Uttar Pradesh and the surrounding area, as well as in Kota, Rajasthan, is kota doria.
- Odisha Ikat: One type of ikat, which is a resist dyeing method, comes from Odisha and is called Orissa Ikat.
Source: Times of India
Previous Year Question
- Q) Which of the following has/have been accorded ‘Geographical Indication’ status?
- Banaras Brocades and Sarees
- Rajasthani Daal-Bati-Churma
- Tirupathi Laddu
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3
Context: Scientists are testing a geoengineering technique called marine cloud brightening that involves using machines to inject tiny saltwater particles into marine stratocumulus clouds, aiming to increase their reflectivity and cool the Earth.
Background:
- The Brightening clouds is one of several ideas to push solar energy back into space — sometimes called solar radiation modification, solar geoengineering, or climate intervention.
Marine Cloud Brightening (MCB):
- It is a scientific initiative that explores how altering atmospheric particles (aerosols) can impact cloud reflectivity.
- By releasing tiny aerosol particles into the atmosphere, researchers aim to enhance cloud brightness, leading to increased sunlight reflection.
- Aerosols of the right size and concentration could significantly increase the reflectivity of specific types of clouds.
- This phenomenon is visible in satellite images of clouds brightened by ship emissions (known as “ship tracks”).
Goals of the Marine Cloud Brightening Program:
- It helps in better understanding of the present-day effects of pollution aerosols on clouds.
- Investigate whether aerosol particles made from sea salt could be used to intentionally reduce near-term climate warming while greenhouse gas concentrations are brought down to safer levels.
- It aims to understand the benefits, risks, and efficacy of the intentional use of aerosols to reduce warming through different implementations of marine cloud brightening.
Concerns/Challenges associated with Marine Cloud Brightening (MCB):
- MCB involves the large-scale spraying of seawater into the atmosphere at significant altitudes, which presents engineering complexities in terms of design, cost, maintenance, and operation of the spraying devices.
- Alterations in cloud patterns and precipitation due to MCB could affect regional climate and hydrological cycles, potentially causing unintended consequences like droughts or floods. Changes in clouds over broad regions affect the circulation of the atmosphere, weather, and precipitation. Both marine cloud brightening (MCB) and pollution aerosols can change clouds, which in turn affects regions both nearby and far from where the brightening occurs.
- MCB raises ethical dilemmas about human intervention in natural processes and the governance and decision-making processes surrounding its implementation.
- MCB might lead to complacency among policymakers and the public, diminishing their commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to climate change.
Source:NY Times
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Consider the following statements:
- Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency (IREDA) is a ‘Navratna’ Government of India Enterprise.
- Navratna companies have greater financial flexibility and can undertake strategic projects without seeking explicit government approval.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q2.) Consider the following pairs:
Fabrics with GI Tag State
- Chanderi Fabric – Madhya Pradesh
- Kanjeevaram Silk- Tamil Nadu
- Ajrakh fabric – Kerala
How many of the pairs given above are correctly matched:
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q3.) Consider the following pairs:
Minerals Ores
- Tin – Cassiterite
- Tantalum – Bauxite
- Tungsten – wolframite
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 3rd May 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 2nd May– Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – d













