IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – GEOGRAPHY
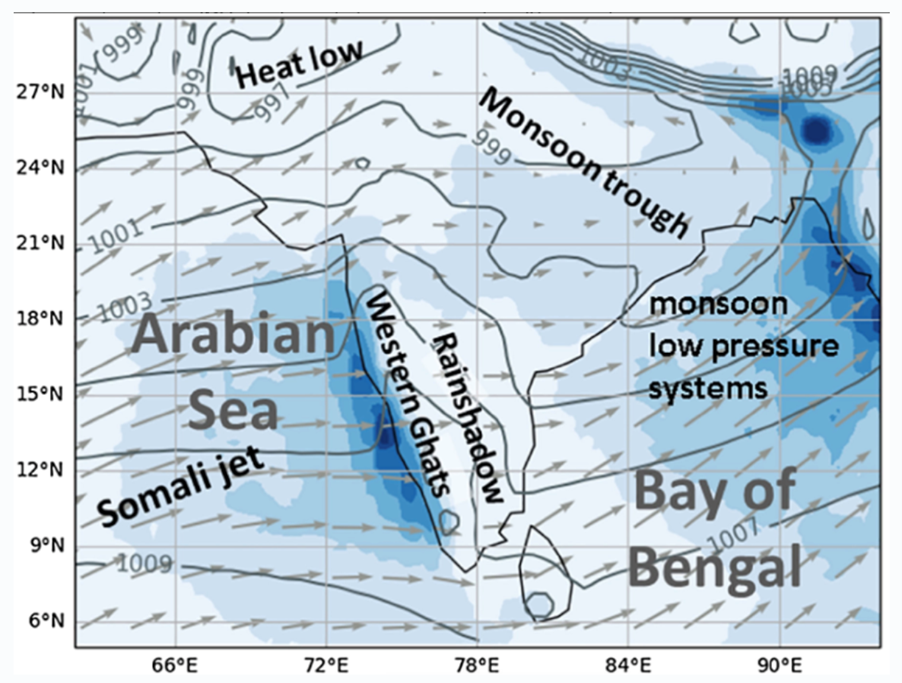
Context: Last week, widespread rainfall was reported in at least 80% of the country, with heavy to very heavy spells hitting Assam, West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Gujarat, coastal Maharashtra and Karnataka, Kerala, and Lakshadweep.
Background:-
- Since the start of this month, multiple favourable weather systems have kept the monsoon either active or vigorous (with respect to rainfall events) over southern peninsular, east, northeast, and central India regions.
What factors are causing widespread rains?
- There have been two main contributors to the enhanced rainfall:
- continuous incoming of moisture-laden strong westerly winds from the Arabian Sea.
- position of the monsoon trough (trough is a belt of low pressure extending to large area)
- Monsoon trough is a semi-permanent, low-pressure area extending between Pakistan and the Bay of Bengal during the monsoon season — which usually oscillates between north and south within the season.
- When monsoon trough moves towards the south, as it has done in the present case, more rainfall can take place in central, eastern and peninsular India.
- When the trough shifts towards the north, the Himalayan foothills are likely to receive more rainfall but the rest of India sees a drop in rainfall.
- Apart from these two factors, other weather systems have also contributed to the widespread rainfall over all regions, except the extreme north India. They are:
- The persistence of an off-shore trough (a shallow trough of low pressure, which develops along India’s coast during the monsoon) between south Gujarat and north Kerala.
- The intermittent development of a wind shear zone — where winds move with different velocities and directions — along latitudes 20 ° N between central and peninsular India.
- The development of a low pressure system over the west-central Bay of Bengal, off the Odisha coast. The system moved over Chhattisgarh and adjoining Vidarbha and over to southeast Madhya Pradesh.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: India successfully concluded its 4th periodic review by the Human Rights Committee under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR).
Background:
- The Human Rights Committee, comprising 18 independent experts serving in their individual capacity, monitors implementation of ICCPR and reviews reports of all States Parties (countries) by conducting periodic reviews, and then making observations and recommendations.
About International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR)
- The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) is a multilateral treaty that commits nations to respect the civil and political rights of individuals, including the right to life, freedom of religion, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, electoral rights and rights to due process and a fair trial.
- It was adopted by United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2200A (XXI) on 16 December 1966 and entered into force on 23 March 1976 after its thirty-fifth ratification or accession.
- As of June 2024, the Covenant has 174 parties and six more signatories without ratification, most notably the People’s Republic of China and Cuba;North Korea is the only state that has tried to withdraw.
- The ICCPR, together with the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the International Covenant on Economic Social and Cultural Rights, are considered the International Bill of Human Rights.
- The ICCPR obligates countries that have ratified the treaty to protect and preserve basic human rights, such as: the right to life and human dignity; equality before the law; freedom of speech, assembly, and association; religious freedom and privacy; freedom from torture, ill-treatment, and arbitrary detention; gender equality; the right to a fair trial; right to family life and minority rights.
- The Covenant compels governments to take administrative, judicial, and legislative measures in order to protect the rights enshrined in the treaty and to provide an effective remedy.
- Compliance with the ICCPR is monitored by the United Nations Human Rights Committee, which reviews regular reports of states parties on how the rights are being implemented.
- States must report one year after acceding to the Covenant and then whenever the Committee requests (usually every four years).
Source: Ministry of External Affairs
Syllabus
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
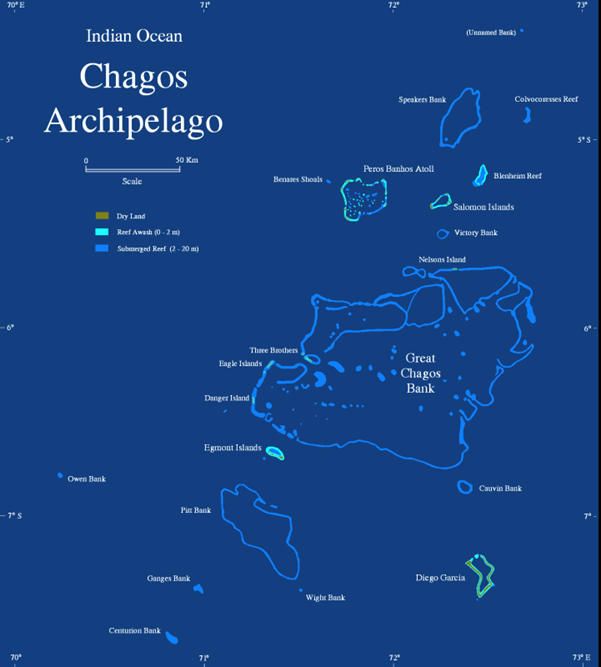
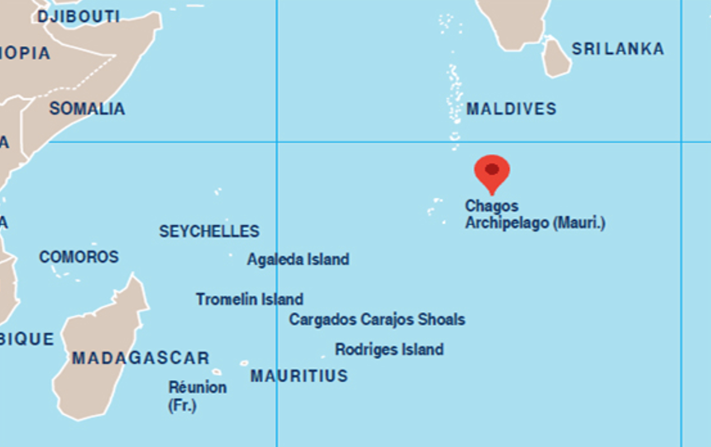
Context: India recently reaffirmed its support to Mauritius on the issue of the Chagos Archipelago.
Background:
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar, during his two-day visit to Mauritius, affirmed that India will maintain its steadfast support for Mauritius, aligning with its core principles on decolonization and the sovereignty and territorial integrity of nations.
About Chagos Archipelago
- The Chagos Archipelago or Chagos Islands is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres south of the Maldives archipelago.
- This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean.
- In its north are the Salomon Islands, Nelsons Island and Peros Banhos; towards its south-west are the Three Brothers, Eagle Islands, Egmont Islands and Danger Island; southeast of these is Diego Garcia, by far the largest island. All are low-lying atolls, save for a few extremely small instances, set around lagoons.
- When Mauritius was a French colony, the islands were a dependency of the French administration in Mauritius. By the Treaty of Paris of 1814, France ceded Mauritius and its dependencies to the United Kingdom.
- In 1965, while planning for Mauritian independence, the UK constituted the Chagos as the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT).
- Mauritius gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1968, and has since claimed the Chagos Archipelago as Mauritian territory.
- In 2019, the International Court of Justice (ICJ) issued a non-binding advisory opinion stating that the UK has an obligation to bring to an end its administration of the Chagos Archipelago as rapidly as possible, and that all Member States must co-operate with the United Nations to complete the decolonization of Mauritius.
- In 2021, the International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea confirmed for its jurisdiction that the UK has no sovereignty over the Chagos Islands and thus the islands should be handed back to Mauritius.
Source: The Wire
Syllabus
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: Davis Strait has long intrigued scientists due to its complex geological features. Recent research has uncovered a fascinating aspect of this region – a microcontinent that was formed through intricate plate tectonic processes.
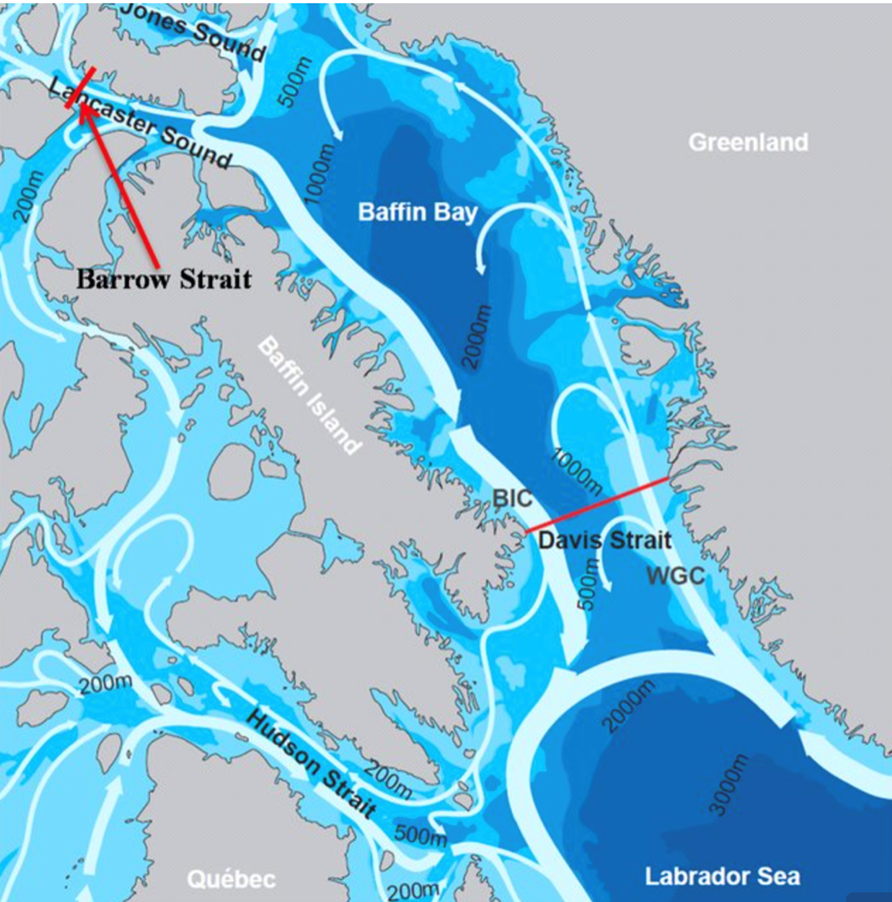
Background:
- A team of geologists identified an isolated block of thick continental crust in the Davis Strait. This formation, measuring 19-24 kilometres thick, was likely separated from Greenland due to east-west extension along its margin. It has been named the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent.
About Davis Strait :
- TheDavis Strait is a southern arm of the Arctic Ocean that lies north of the Labrador Sea.
- Davis Strait lies between thesoutheastern Baffin Island (Canada) and southwestern Greenland.
- The strait separates the depths of Baffin Bay (north) from those of the Labrador Sea (south) and forms part of the Northwest Passage, a route through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago linking the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
- It is approximately 400 miles (650 km) north to south and 200 to 400 miles wide.
Source: NDTV
Syllabus
- Prelims – SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Context: Fifteen children have died of a suspected viral infection, known as Chandipura virus, in Gujarat since July 10.
Background:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) had recognised the Chandipura virus as a potential priority disease in 2017.
About CHANDIPURA VIRUS INFECTION (CHPV) :
- The Chandipura virus (CHPV) belongs to the Rhabdoviridae family.
- It was first identified in 1965 in Chandipura, a village in Maharashtra.
Transmission:
- Sandflies, particularly species of the genus Phlebotomus, are the primary vectors for CHPV transmission.
- These tiny blood-sucking insects are prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions.
Symptoms:
- Initial symptoms include sudden onset of high fever, severe headache, and muscle pain.
- As the infection progresses, it can lead to altered consciousness, seizures, and, in severe cases, coma and death.
- Early detection and treatment are crucial for patient survival.
Treatment:
- As of now, there is no antiretroviral treatment or vaccine accessible for treatment.
Affected Regions:
- Most cases are reported from north Gujarat, where the dry temperature favours sandfly breeding.
- Children under 15 years are particularly vulnerable due to their lower immunity against viral infections.
Source: Business Standard
Syllabus
- Prelims – ECONOMY
Context: The government wants to increase the capital base of the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) to 1 trillion through support from banks.
Background:
- NaBFID plays a critical role in financing India’s infrastructure projects, and its capital expansion plans are aligned with the country’s development needs.
About National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) :
- National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) is a specialized Development Finance Institution (DFI) in India.
- It is a statutory body established by the Government of India.
- Its creation was formalized through the enactment of the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development Act, 2021.
- The primary objective of the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) is to address the long-term financing needs of critical infrastructure projects in India.
- It aims to strengthen the development of bonds and derivatives markets in India and sustainably boost the country’s economy.
- NaBFID is recognized by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) as an All-India Financial Institution (AIFI).
- As a Development Finance Institution (DFI) and All-India Financial Institution, NaBFID channels investments into critical infrastructure sectors such as energy, roads, railways, and urban infrastructure.
Source: Livemint
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Chagos Archipelago, recently seen in news is located in
- Indian Ocean
- Atlantic Ocean
- Pacific Ocean
- Arctic Ocean
Q2.)With reference to the Chandipura virus (CHPV) infection, consider the following statements:
- The Chandipura virus was first identified in Gujarat.
- The sandflies are the primary vectors for CHPV transmission.
- As of now, there is no antiretroviral treatment or vaccine accessible for treatment.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q3.)With reference to the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID), consider the following statements:
- National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development is a statutory body.
- NaBFID is recognized as an All-India Financial Institution by the Reserve Bank of India.
- NaBFID’s primary objective is to address the long-term financing needs of critical infrastructure projects in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 19th July 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 18th July – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – d











