IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – HISTORY
Context: November 28 marks the death anniversary of Jyotirao Phule.
Background: –
- He, along with Savitribai Phule, worked as a social reformer, fighting against social evils like untouchability and promoting women’s education.
Key takeaways
- Jyotirao Govindrao Phule, also known as Jyotiba Phule, was born on April 11, 1827, and belonged to the Mali caste of gardeners and vegetable farmers.
- Despite the societal norms of his time, Phule received an education at the Scottish Mission High School in Pune. He was a talented student and later became a teacher himself
- Phule along with his followers formed Satyashodhak Samaj which meant ‘Seekers of Truth’ in order to attain equal social and economic benefits for the lower castes in Maharashtra.
- He was married off when he was only 13, and was personally rebuked in 1848, while attending the wedding of a Brahmin friend. With time, he realised the state of women in society and challenged it by first educating his wife Savitribai, and then starting an indigenously-run school for girls in Pune.
- The couple went on to open a school for girls in Bhidewada, Pune, in 1848. This became the country’s first girls’ school. Many more such schools were opened for girls, Shudras and Ati-Shudras (the backward castes and Dalits, respectively) in Pune, leading to discontent among Indian nationalists like Bal Gangadhar Tilak.
- They opposed the setting up of schools for girls and non-Brahmins, citing a “loss of nationality”, and believing not following the caste rules would mean a loss of nationality itself.
- Authored several works highlighting social issues:
- Gulamgiri (1873): Critique of Brahmanical hegemony and social exploitation.
- Shetkarayacha Asud (The Cultivator’s Whipcord): Highlighted the exploitation of farmers by landlords and moneylenders.
- He was bestowed with the title of Mahatma in 1888 by a Maharashtrian social activist Vithalrao Krishnaji Vandekar.
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – ENVIRONMENT
Context: The centre has found out that eight carmakers including Hyundai, Kia, Mahindra, and Honda have higher than mandated fleet emission levels in financial year 2022-23, which could mean penalties of around Rs 7,300 crore.
Background: –
- For 2022-23, the Bureau of Energy Efficiency, under the Union Ministry of Power, required car companies of all units sold during the year to achieve India’s Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE) norms.
Key takeaways
- The CAFE norms were tightened in the beginning of financial year 2022-23.
- The quantum of penalties has become a point of contention between the Centre and the auto industry.
- In 2022-23, models and variants of 18 automobile manufacturers were tested at accredited laboratories by simulating actual driving conditions. When the results for a set of cars did not conform to specified CAFE standards, then penalties were calculated for the total number of cars sold in the full year.
- Those penalised include Hyundai (Rs 2,837.8 crore), Mahindra (Rs 1,788.4 crore), Kia (Rs 1,346.2 crore), Honda (Rs 457.7 crore), Renault (Rs 438.3 crore), Skoda (Rs 248.3 crore), Nissan (Rs 172.3 crore), and Force Motor (Rs 1.8 crore).
About Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE) norms
- Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFÉ) norms were first notified by the Government in 2017, under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001 to mitigate fuel consumption by lowering CO₂ emissions; aiming to reduce oil dependency and air pollution.
- Applicability: These norms apply to passenger vehicles with a gross vehicle weight (GVW) of less than 3,500 kg, including petrol, diesel, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), compressed natural gas (CNG), hybrid, and electric vehicles manufactured or imported for sale in the country.
- It may be noted that the standards apply to the Corporate Average Fuel Consumption i.e. the average of the standards fuel consumption of all vehicles sold by the manufacturers in the fiscal year, and not to the fuel consumption of an individual model.
- Phase I (2017-2022): The first phase of CAFE norms was implemented from April 1, 2017. The average fuel consumption target was set at less than 5.49 liters per 100 km, with an average kerb weight of 1,037 kg.
- Phase II (2022 onwards): The second phase came into effect from April 1, 2022, with stricter targets. The average fuel consumption target was reduced to less than 4.78 liters per 100 km, with an average kerb weight of 1,082 kg.
Calculation Method:
- Corporate Average Fuel Consumption (CAFC): The fuel consumption is measured in liters per 100 km and is calculated based on the corporate average curb weight of all vehicles sold by a manufacturer in a fiscal year.
- CO2 Emissions: The norms also set limits on CO2 emissions, with a target of less than 130 grams per km until 2022 and less than 113 grams per km from 2022 onwards.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: The Swedish prime minister, Ulf Kristersson, has said the Baltic sea is now a “high risk” zone as he met Nordic and Baltic leaders days after a suspected sabotage attack on undersea cables.
Background: –
- The Swedish PM declined to speculate on who may have been responsible for the severing of two fibre optic telecoms cables in the Baltic. A Chinese ship – the Yi Peng 3 – that sailed over the cables about the time they were severed has remained anchored in the Kattegat strait between Sweden and Denmark since 19 November.
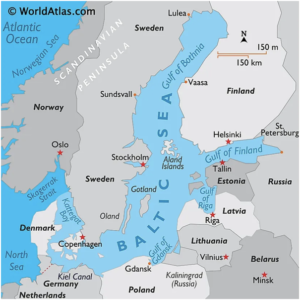
About Baltic Sea
- The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean, extending northward from southern Denmark almost to the Arctic Circle. It separates the Scandinavian Peninsula from the rest of continental Europe.
- Boundaries:
- West: Denmark and the Kattegat Strait connecting it to the North Sea via the Skagerrak.
- North: Sweden and the Gulf of Bothnia.
- East: Finland, Russia, and the Gulf of Finland.
- South: Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia.
- Countries Bordering the Baltic Sea: Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, and Sweden.
- Brackish water due to limited exchange with the North Sea and high inflow of freshwater from rivers.
- Coastline: Rugged with numerous islands, peninsulas, and gulfs such as the Gulf of Bothnia and Gulf of Finland.
- Major Rivers Flowing into the Baltic Sea: Vistula (Poland), Oder (Germany/Poland), Neva (Russia), and Daugava (Latvia).
- Shipping and Trade:
- Major shipping routes, linking Central and Eastern Europe to the global economy.
- Ports like Gdańsk (Poland), Tallinn (Estonia), and St. Petersburg (Russia) are crucial for trade.
- Coastal resorts and historical cities like Stockholm, Helsinki, and Riga attract millions of tourists.
Source: The Guardian
Syllabus:
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: After a steep rise in terror attacks in Jammu region, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has established a permanent hub for National Security Guard in the winter capital of J&K for quick response to any major attack. The NSG hub has been set up in Jammu city.
Background:
- In the recent past, Kathua, Doda, Kishtwar, Udhampur, Rajouri, Poonch and Reasi districts of Jammu have seen a spurt in terror attacks.
Key takeaways
- The National Security Guard (NSG), also known as the Black Cats, is Federal Contingency World Class Zero Error Force to deal with anti-terrorist activities in all its manifestation.
- The NSG is a Force specially equipped and trained to deal with specific situations and is therefore, to be used only in exceptional circumstances to thwart serious acts of terrorism.
- The organization was initially inspired by and modelled on the British Special Air Service as well as Germany’s GSG 9
- Formation: The NSG was established on October 16, 1984, following Operation Blue Star, to combat terrorist activities and protect states against internal disturbances.
- Legislation: The formation was formalized under the National Security Guard Act, 1986.
- Jurisdiction: The NSG operates under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- NSG personnel are recruited from both the Indian Army and Central Armed Police Forces.
- Motto: The NSG’s motto is “Sarvatra Sarvottam Suraksha”, which means “Best Security Everywhere”.
- Major Operations:
- 1988: Operation Black Thunder (Golden Temple) – Counter-terrorism operation.
- 1999: IC-814 Hijacking – NSG was on standby but could not intervene due to the aircraft being taken to Kandahar, Afghanistan.
- 2002: Akshardham Temple Attack – Neutralized terrorists in Gujarat.
- 2008: Mumbai Terror Attacks (26/11) – Played a key role in eliminating terrorists and securing locations like the Taj Hotel and Nariman House.
Source: New Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: In a historic move, the Jarawa tribe of the Andaman and Nicobar has been officially included in India’s democratic fold with their enrolment in the electoral roll.
Background: –
- A total of 19 Jarawa tribe members were enrolled. For the first time, members of the Jarawa community will participate in the electoral process.
Key takeaways
- The Jarawa tribe is an indigenous group residing in the Andaman Islands, specifically on the western coast of the South and Middle Andaman Islands.
- Current Population: The Jarawa population is estimated to be between 250 to 400 individuals.
- Historical Population: The population declined significantly during British colonial rule but has since stabilized.
- They are classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) due to their small population, primitive technology, and relative isolation.
- Jarawa Language: The Jarawa speak their own language, which is part of the Ongan language family. It is distinct from other languages spoken in the Andaman Islands.
- Lifestyle:
- Hunter-Gatherers: The Jarawa are traditionally hunter-gatherers. They hunt wild pigs and monitor lizards using bows and arrows, and fish in coastal waters.
- Diet: Their diet includes wild fruits, roots, honey, and fish. They are known for their excellent nutritional health and robust physique.
- Housing: They build temporary huts in their camps and use crude rafts to cross creeks and streams.
- Contact with Outsiders:
- Historical Isolation: The Jarawa have largely shunned interaction with outsiders until the 1990s.
- Recent Interactions: Since the 1990s, contact with settled populations has increased, with some Jarawa visiting nearby towns and settlements.
Source: Nicobar Times
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Which of the following statements about the Baltic Sea is/are correct?
- The Baltic Sea has brackish water due to limited exchange with the North Sea and high inflow of freshwater from rivers.
- It is bordered by only three Scandinavian countries: Sweden, Denmark, and Norway.
- Major rivers like the Neva, Vistula, and Oder flow into the Baltic Sea.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1 and 3 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Q2.) With reference to the National Security Guard (NSG), consider the following statements:
- The NSG operates under the Ministry of Defence.
- NSG personnel are drawn from both the Indian Army and Central Armed Police Forces.
- The NSG was modeled on Germany’s GSG 9 and Britain’s Special Air Service (SAS).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Q3.) Consider the following statements regarding the Jarawa tribe:
- The Jarawa tribe is classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG).
- They traditionally practice agriculture and animal husbandry for their subsistence.
- The Jarawa language belongs to the Ongan language family.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 1 and 3 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2, and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 28th November – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – b











