IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
- Mains – CURRENT EVENT
Context: A new government report has pegged the value of India’s bioeconomy in 2024 at more than $165 billion, accounting for over 4.2% of the country’s GDP.
Background: –
- The India BioEconomy Report, released by the Department of Biotechnology, says there is ample opportunity for this sector to grow to about $300 billion by 2030, and to $1 trillion by 2047.
Key takeaways
- Bioeconomy refers to the industrial use of biological resources (plants, animals, and microorganisms), and the replication of natural biological processes in the production of goods and services.
- Bioresources like plants or microorganisms are renewable, relatively cheap, and locally available, while natural processes are more sustainable and eco-friendly.
- An example is the use of ethanol, produced through fermentation of crops like sugarcane or corn by microorganisms, as an alternative to fossil fuels. Modern biology offers sustainable alternatives to clothes, plastics, construction materials, medicines, and a variety of chemicals.
- Even in traditional areas of healthcare and agriculture, there is a push for biotechnology. Development of biomedicines, which are derived from bioresources rather than chemicals, and synthetic biology involving the growth of specially-designed microorganisms with desired traits are areas in which biotechnology is playing an increasing role.
Growing footprint
- The report shows that the value of India’s bioeconomy nearly doubled in the last five years, from around $86 billion in 2020 to $165 billion in 2024.
- The number of companies operating in the bioeconomy has gone up by almost 90% in the last three years, from 5,365 in 2021 to 10,075 in 2024. This number is projected to double again by 2030, employing close to 35 million people, according to the report.
- Nearly half the value of the bioeconomy (roughly $78 billion) was generated in the industrial sector, for the development and use of biofuels and bioplastics, among other things. The pharma sector accounted for another 35% of the total value, with vaccines the major contributor.
- But the fastest growing segment in 2024 was research and IT, which includes biotech software development, clinical trials, and bioinformatics that helps in areas such as drug research.
- The report showed that only five states — Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana, Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh — accounted for more than two-thirds of the value generated in the bioeconomy. The entire eastern and northeastern region generated less than 6% of the total value.
- Maintaining the high growth rates of the past five years in the future will not be easy, the report said.
- While the 4.2% share in the overall GDP was comparable to figures in the United States and China, the bioeconomy of countries like Spain and Italy accounts for more than 20% of their GDP.
BioE3 Policy (2024) – The BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment) policy aims to:
- Establish India as a global bio-manufacturing hub with a focus on bio-based chemicals, enzymes, precision biotherapeutics, functional foods, and climate-resilient agriculture.
- Strengthen research and development through collaboration between universities, research institutions, start-ups, and industries.
- Promote sustainability by replacing hydrocarbon-based materials with bio-based alternatives.
- Encourage innovation and private sector participation in biotechnology advancements.
Way Forward
- Regulatory Reforms – Addressing concerns over GM crops and streamlining approval processes.
- Regional Development – Encouraging bioeconomy growth in underdeveloped regions.
- Public-Private Collaboration – Boosting investment in research, production, and commercialization of bio-based products.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Context: The Webb Space Telescope has captured a plume of gas and dust streaming from a star in the making.
Background: –
- The outflow is about 625 light-years from Earth in one of the closest star-forming regions of our Milky Way galaxy, according to NASA.
Formation of stars
- The process of star formation is an extraordinary sequence of events that occurs within massive clouds of gas and dust scattered throughout galaxies, often referred to as molecular clouds or stellar nurseries.
Formation of Molecular Clouds
- Initial Conditions: Star formation begins in regions of dense and cold interstellar gas and dust. These molecular clouds are primarily composed of hydrogen (H₂) with traces of helium and heavier elements.
- Triggering Mechanisms: External events like supernova explosions, galactic collisions, or shockwaves can compress the molecular cloud, initiating the process.
Gravitational Collapse
- Instability: Regions within the cloud become denser over time, leading to local instabilities.
- Formation of Dense Cores: As gravity overwhelms internal pressure, parts of the cloud collapse into compact, dense clumps known as protostellar cores.
Protostar Stage
- Heating and Rotation: During the collapse, gravitational potential energy converts into heat, increasing the core’s temperature. Conservation of angular momentum causes the core to rotate and form a rotationally flattened disk around it.
- Accretion Disk: Material from the surrounding envelope spirals inward onto the protostar through the accretion disk, fueling its growth.
Ignition of Nuclear Fusion
- Core Temperature and Pressure: When the protostar’s core temperature rises to approximately 10 million Kelvin, nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium begins. This marks the birth of a star.
- Radiative Pressure: The energy generated from fusion creates outward radiative pressure, balancing the inward pull of gravity and halting further collapse.
Main Sequence Stage
- Equilibrium: The star enters the main sequence phase, where it remains in hydrostatic equilibrium for millions to billions of years. During this time, it burns hydrogen in its core, producing energy.
Factors Influencing Star Formation
- Mass of the Star: The amount of material available determines whether the star becomes a low-mass star (like the Sun) or a high-mass star (more massive stars may end their lives as black holes or supernovae).
- Environmental Conditions: The metallicity (presence of elements heavier than helium) and external forces influence the efficiency of star formation.
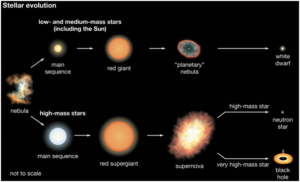
End States – the lifecycle of a star depends on its initial mass:
- Low-Mass Stars (e.g., red dwarfs): End as white dwarfs.
- Medium-Mass Stars (e.g., Sun-like stars): Become red giants before shedding their outer layers as planetary nebulae, leaving behind a white dwarf.
- High-Mass Stars: Explode as supernovae and may form neutron stars or black holes.
Source: AP News
Syllabus:
- Prelims – HISTORY
Context: Rajasthan Chief Minister Bhajanlal Sharma strongly criticised Samajwadi Party MP Ramji Lal Suman for calling Mewar ruler Rana Sanga a “traitor” and demanded that the Akhilesh Yadav-led party take action against him.
Background:
- Rana Sanga was the Rana of Mewar from 1508 to 1528 CE. He controlled parts of present-day Rajasthan, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh with his capital at Chittor.
Key takeaways
- Rana Sanga, also known as Maharana Sangram Singh, was a legendary Rajput ruler of Mewar from the Sisodia dynasty.
- Born in 1482 to Rana Raimal of Mewar.
- Ascended the throne of Mewar in 1508 after a succession struggle.
- Faced internal challenges but emerged as a strong and capable ruler.
Military Achievements and Battles
- Expansion of Mewar
- Consolidated Rajput power by forming alliances with Rajput clans.
- Defeated Malwa Sultan Mahmud Khalji II, expanding his territory.
- Fought against Gujarat Sultan Muzaffar Shah II and Lodhi rulers of Delhi.
- Battle of Khatoli (1518) – Defeated Ibrahim Lodi, capturing key territories in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh.
- Battle of Dholpur (1519) – Once again defeated Ibrahim Lodi, increasing his influence in North India.
- Battle of Khanwa (1527) –
- The most famous battle of his career, fought against Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire.
- Rana Sanga led a massive Rajput confederacy but was defeated due to Babur’s use of gunpowder, artillery, and superior tactics. The defeat marked the beginning of Mughal dominance in India.
- After the defeat at Khanwa, he attempted to regroup but was allegedly poisoned by his own nobles in 1528, who feared another battle with the Mughals.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: India is set to chair the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) starting November 2025.
Background: –
- As IORA chair for the next two years, India will have three priorities: creating funding opportunities to enlarge IORA’s budget; integrating technology for data management and policy analysis, and creating maritime-ready courses with academic and research institutions using collaborations.
Key takeaways
- The Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) is an intergovernmental organization established in 1997 to foster regional cooperation and sustainable development among countries bordering the Indian Ocean. It plays a pivotal role in addressing shared challenges and opportunities in the region.
Key Features
- Member States: IORA consists of 23 member countries, including India, Australia, South Africa, Indonesia, and the United Arab Emirates, among others. It also has 12 dialogue partners, such as the USA, China, and the European Union.
- Headquarters: The IORA Secretariat is located in Ebene, Mauritius.
- IORA’s apex body is the Council of Foreign Ministers (COM) which meets annually.
- Objectives:
- Promote sustainable growth and balanced development in the region.
- Enhance regional cooperation in areas like trade, investment, and social development.
- Address challenges such as maritime security, disaster risk management, and climate change.
- IORA focuses on six priority areas:
- Maritime Safety and Security: Ensuring safe and secure maritime trade routes.
- Trade and Investment Facilitation: Promoting economic integration and trade partnerships.
- Fisheries Management: Sustainable use of marine resources.
- Disaster Risk Management: Enhancing regional resilience to natural disasters.
- Academic and Science Cooperation: Encouraging research and innovation.
- Tourism and Cultural Exchanges: Promoting regional tourism and cultural understanding.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Prelims – ECONOMY
Context: Non-performing assets of banks at multi-year low, says Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman
Background: –
- FM reveals that the gross NPAs (Non-Performing Assets) of scheduled commercial banks have reached a multi-year low of 2.5% in September 2024. Public sector banks have also reported their highest-ever net profit of ₹1.41 lakh crores in the previous financial year, with expectations for even greater growth in the coming year.
Key takeaways
- Non-Performing Assets (NPA) refer to loans and advances that cease to generate income for banks because the borrower fails to repay principal or interest for a specified period.
- Definition of NPA (As per RBI) – A loan is classified as an NPA if interest or principal remains overdue for more than 90 days in the case of:
- Term loans – When interest or principal is unpaid for over 90 days.
- Overdraft & Cash Credit – If outstanding balance remains over the sanctioned limit for 90+ days.
- Agricultural loans – If the principal/interest remains unpaid for two crop seasons (short-term) or one season (long-term).
Categories of NPAs
- Substandard Assets – Loans that remain NPA for less than 12 months.
- Doubtful Assets – Loans that remain NPA for more than 12 months.
- Loss Assets – Loans that are unrecoverable, though officially not written off.
Causes of NPAs
- Internal Factors
- Poor credit appraisal by banks.
- Mismanagement of funds by borrowers.
- Wilful default by corporate borrowers.
- Lack of proper monitoring and follow-ups.
- External Factors
- Economic slowdown affecting businesses.
- Policy bottlenecks leading to delays in projects.
- Global financial crises reducing export earnings.
- Natural calamities impacting agricultural loans.
Impact of NPAs on Economy
- Reduces Bank Profitability – Banks earn lower interest income.
- Affects Credit Availability – Banks hesitate to lend, slowing economic growth.
- Erodes Investor Confidence – Weak balance sheets discourage investment.
- Burden on Taxpayers – Government may need to recapitalize public sector banks.
Measures to Tackle NPAs
- Legislative & Regulatory Measures
- SARFAESI Act (2002) – Allows banks to recover loans by auctioning assets.
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016 – Fast-tracks resolution of stressed assets.
- RBI’s Prompt Corrective Action (PCA) Framework – Imposes restrictions on weak banks.
- Institutional Mechanisms
- Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) – Buy NPAs from banks and manage recovery.
- Bad Bank (NARCL, 2021) – Aims to take over NPAs and resolve them efficiently.
- Bank-Level Reforms
- Strengthening credit appraisal & risk management.
- Encouraging loan restructuring and one-time settlement schemes.
Source: Business Today
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Which Sultan of Delhi did Rana Sanga defeat in the Battle of Khatoli (1518)?
a) Alauddin Khilji
b) Ibrahim Lodi
c) Balban
d) Sher Shah Suri
Q2.) Which of the following is NOT a member of IORA?
a) India
b) China
c) Australia
d) South Africa
Q3.) Which of the following is a key reason for rising NPAs in India?
a) Economic slowdown
b) Poor credit appraisal by banks
c) Wilful defaults by corporate borrowers
d) All of the above
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 26th March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – b











