IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
ART & CULTURE
Context: Prime Minister Modi who is on a state visit to Thailand was gifted the holy scripture of ‘World Tipitaka” by his Thailand counterpart Paetongtarn Shinawatra.
Decoding the context: The Tipitaka, also known as the Tripitaka in Sanskrit, is a revered compilation of Lord Buddha’s teachings and serves as the principal Buddhist scripture.
Learning Corner:
- The Tripitaka, also known as the Pali Canon, is the earliest and most authoritative collection of Buddhist scriptures.
- The term Tripitaka (Sanskrit: त्रिपिटक) or Tipitaka (Pali: तिपिटक) translates to “Three Baskets,” referring to the three main divisions of Buddhist scriptures:
- Vinaya Pitaka (Basket of Discipline)
- Deals with monastic rules and discipline for monks (bhikkhus) and nuns (bhikkhunis).
- Contains over 220 rules for monastics.
- Also includes stories and justifications for the rules (origin stories).
- Significance: Establishes the Sangha’s code of conduct, promoting harmony and discipline.
- Sutta Pitaka (Basket of Discourses)
- Contains the teachings and sermons of Gautama Buddha.
- Divided into 5 Nikayas (collections):
- Digha Nikaya – Long Discourses
- Majjhima Nikaya – Middle Length Discourses
- Samyutta Nikaya – Connected Discourses
- Anguttara Nikaya – Numerical Discourses
- Khuddaka Nikaya – Minor Collection (includes Dhammapada, Jataka tales, etc.)
- Significance: The main source of Buddhist philosophy and ethical teachings.
- Abhidhamma Pitaka (Basket of Higher Doctrine)
- Contains philosophical and psychological analysis of Buddhist doctrine.
- More abstract and systematic.
- Deals with classification of mind, matter, mental states, etc.
- Significance: Basis for later Buddhist metaphysics and psychology
- Vinaya Pitaka (Basket of Discipline)
- The Tripitaka was originally transmitted orally by Buddhist monks before being written down in various languages, including Pali, Sanskrit, Chinese, and Tibetan.
- The Theravāda school preserves the only complete Tripitaka in Pali, while other Buddhist traditions have their own versions, such as the Sarvāstivāda Tripitaka in Sanskrit.
- The texts were compiled and finalized during early Buddhist councils, particularly the First Buddhist Council, held shortly after the Buddha’s death.
Source : CNBC
Syllabus:
POLITY
Context: Lok Sabha on Thursday (April 3, 2025) made a record when the Zero Hour lasted for more than five hours and a whopping 202 MPs spoke.
Decoding the context: Fulfilling the promise made in the Business Advisory Committee (BAC) meeting, Speaker Om Birla ensured the extension of Zero Hour.
Learning Corner:
- Zero Hour is an important parliamentary device in India that allows Members of Parliament (MPs) to raise urgent matters without prior notice. It is an informal practice that takes place immediately after Question Hour, typically starting at 12 noon—hence the name “Zero Hour.”
Key Features of Zero Hour
- The concept of Zero Hour originated in India, not borrowed from any foreign parliamentary system.
- Not Mentioned in Rules of Procedure: Unlike Question Hour, Zero Hour is not formally listed in parliamentary rules but has evolved as a convention.
- Raising Urgent Issues: MPs can bring up matters of public importance that require immediate attention.
- Notice Requirement: MPs must submit their requests before 10 AM on the day of the session to the Speaker (Lok Sabha) or Chairman (Rajya Sabha). Note: Here, same day request is sufficient unlike other devices like question hour where prior notice is required.
- Discretion of Presiding Officers: The Speaker or Chairman decides whether to allow the issue to be raised.
Source : The Hindu
Syllabus:
ECONOMY
Context: India achieved a historic milestone by surpassing one billion tonnes (BT) of coal production on 20 March 2025, in FY 2024-25—11 days ahead of last year’s 997.83 million tonnes (MT).
Decoding the context: The coal sector’s success is attributed to the tireless efforts of Coal Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs), private players, and the dedicated workforce of around 5 lakh mine workers across more than 350 coal mines.
Learning Corner:
- India’s coal production has reached 1047.57 MT (Provisional) in FY 2024-25, compared to 997.83 MT in FY 2023-24, marking a 4.99% growth.
- Coal imports fell 8.4% to 183.42 MT in April-December 2024 from 200.19 MT in the same period of FY 2023-24, saving $5.43 billion (₹42,315.7 crore) in foreign exchange.
- Government initiatives like Commercial Coal Mining and Mission Coking Coal boosted domestic coal output by 6.11% during this period, reducing import dependence.
Economic significance of the coal sector:
- With the fifth-largest coal reserves and as the second-largest consumer, coal remains crucial, contributing 55% to the national energy mix and fuelling over 74% of total power generation.
- Despite renewable energy growth, coal-based thermal power will remain essential, with its share projected at 55% by 2030 and 27% by 2047.
- Railways & revenue: Coal stands as the single largest contributor to railway freight, with an average share of nearly 49% of total freight income amounting to Rs. 82,275 Crore in the fiscal year 2022-23 alone. This revenue contribution has surpassed 33% of total railway earnings.
- Government earnings: The coal sector contributes over Rs. 70,000 Crore annually to the central and state governments through royalties, GST, and other levies.
- Employment: The sector provides jobs to over 239,000 workers in Coal India Ltd and thousands more in contractual and transport roles.
- Economic growth: Substantial investments in capital expenditure, averaging Rs. 18,255 Crore annually over the past five years, have facilitated infrastructure development and resource optimization within coal sector PSUs.
Source : PIB
Syllabus:
NATIONAL
Context: A man was arrested in Andaman and Nicobar Islands for allegedly entering the prohibited tribal reserve area of the North Sentinel Island, home to the indigenous Sentinelese people, one of the last uncontacted tribes in the world.
Decoding the context: According to the police, Mykhailo Viktorovych Polyakov is a 24-year-old US national who arrived in Port Blair on March 26 and ventured to North Sentinel Island from the Khurmadera beach of the archipelago, police said.
Learning Corner:
- The Sentinelese are an indigenous people who inhabit North Sentinel Island, located in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India.
- Along with the Great Andamanese, the Jarawas, the Onge, the Shompen, and the Nicobarese, the Sentinelese are one of the six indigenous (and often reclusive) peoples of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- They are one of the most isolated tribes in the world and have consistently resisted contact with outsiders. Their language, known as Sentinelese, remains largely unclassified, and very little is known about its structure or relation to other Andamanese languages.
- They are believed to be the direct descendants of the first humans who migrated out of Africa, living in isolation for ~60,000 years.
- Population Estimate: Between 50 and 200 individuals, though exact numbers are unknown.
- Lifestyle: They are hunter-gatherers, relying on fishing, hunting, and foraging.
- Hostility to Outsiders: The Sentinelese have historically attacked anyone attempting to approach their island, including missionaries and fishermen.
- They are designated as particularly vulnerable tribal group (PVTG) and as a Scheduled Tribe.
- Legal Protection: Protected under the Andaman and Nicobar Protection of Aboriginal Tribes Regulation (ANPATR), 1956. The entire North Sentinel Island along with 5 km coastal sea from high water mark is notified as tribal reserve.
Source : Hindustan Times
Syllabus:
ENVIRONMENT
Context: The Supreme Court has directed the Central Empowered Committee (CEC) to conduct an extensive survey of the entire tropical forest ecosystems of the Agasthyamalai landscape in the southernmost Western Ghats to identify non-forestry activities and encroachments.
Decoding the context: SC termed the survey as an interim measure “to initiate the process of restoration of the pristine forest areas and to protect the tiger habitats, wildlife reserves and sanctuaries falling under the Agasthyamalai biosphere”.
Learning Corner:
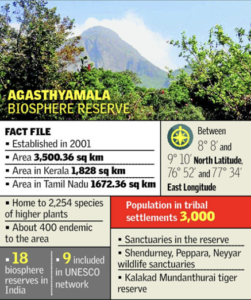
- Agasthyamala, also known as Agastya Mala, is a prominent peak in the Western Ghats, located at the border of Kerala and Tamil Nadu. It is part of the Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve, which is recognized for its rich biodiversity and ecological significance.
Key Features
- Includes the Agasthyarkoodam peak (approx. 1,868 m) – the second highest peak in Kerala.
- Geographical Location: Lies between Thiruvananthapuram district (Kerala) and Tirunelveli district (Tamil Nadu).
- Rivers Originating Here: The Thamirabarani River originates from the eastern side, while the Neyyar and Karamana Rivers flow westward.
Ecological and Cultural Importance
- Lies within the Western Ghats, a biodiversity hotspot.
- UNESCO Recognition: The Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve was included in the UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves in 2016.
- Spiritual Significance: Named after Sage Agastya, a revered figure in Hindu mythology, believed to have meditated in this region.
- The Biosphere Reserve is inhabited by the Kanikaran (also known as Kanis), who are classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG). Their traditional knowledge of medicinal plants is significant, and it notably led to the development of the herbal drug Jeevani, which is considered a major success story in bioprospecting and benefit-sharing in India.
Source : The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1. Consider the following statements about the Sentinelese Tribe:
- They practice subsistence agriculture and fishing.
- North Sentinel Island is a tribal reserve under Indian law.
- They are one of the most isolated tribes in the world and have consistently resisted contact with outsiders.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 2 and 3
Q2. Consider the following statements about the Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve:
- It is spread across Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka.
- It is part of the UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves.
- The reserve is inhabited by the tribal community known as the Kanis.
Which of the above statements are correct?
- A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Q3. Consider the following statements
- India’s coal imports increased despite a rise in domestic coal production.
- Coal-based thermal power generation still accounts for more than 70% of India’s electricity.
- Coal stands as the single largest contributor to railway freight, with a share of more than 40 % of total freight income.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 4th April – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – b











