IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Category: SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Context: The India Meteorological Department (IMD) on Monday adopted the Bharat Forecast System (BFS).
Decoding the context: The BFS, developed by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), has been tested since 2002 and has shown “notable improvements” in giving advance warning of heavy rainfall events.
Learning Corner:
Overview of BFS
- The Bharat Forecast System (BFS) is a new weather forecasting system adopted by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) for more accurate and localized rainfall predictions.
- Developed By: Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune.
- Purpose: To provide fine-tuned weather forecasts at the panchayat level, enhancing accuracy for short- and medium-term forecasts.
Key Features
- Forecast Resolution: For analysis, the current weather forecast models cut up the globe into gridded squares of 12-km sides; the newer BFS model breaks it down into 6-km sides.
- Grid Structure: Utilizes a a grid-structure called the triangular-cubic octahedral (TCO). This generates more grids, and therefore higher resolution, over the tropical regions than the poles. As weather over tropics is more volatile, this is important for India.
- Forecast Types: Improves short-term (3-day) and medium-term (7-day) forecasts but does not enhance long-range forecasts (e.g., monthly predictions).
- Computing Systems: Supported by high-performance computing systems ‘Arka’ and ‘Arunika’ located at IITM, Pune, and the National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting, Delhi.
Limitations
- Thunderstorm Forecasts: BFS does not significantly improve predictions for sudden thunderstorms, which rely on separate models and technologies like Doppler Weather Radars.
Significance
- Localized Forecasting: Enables weather forecasts at the panchayat level (covering a few villages), improving on previous block-level forecasts available five days in advance.
- Relevance for India: The higher resolution over tropical regions is critical due to the volatile weather patterns in India, aiding in better disaster preparedness and agricultural planning.
Source : The Hindu
Category: NATIONAL
Context: As many as 160 undocumented people from Bangladesh were flown on an Indian Air Force (IAF) plane from the NCR to Tripura on Sunday to be sent across to the neighbouring country.
Decoding the context: The transportation is in line with the government’s decision to send the undocumented immigrants to Bangladesh rather than wait for the deportation process which is “lengthy”.
Learning Corner:
- Length: 4,096.7 km, the fifth-longest land border in the world and India’s longest international border.
- Bordering Indian States (in order of length): West Bengal – ~2,217 km (longest stretch), Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram.
- Border Characteristics: Includes riverine areas (e.g., Muhuri River) and unfenced sections (864.482 km unfenced, including 174.514 km non-feasible gaps).
- Border Security Force (BSF) is the agency responsible for guarding the border.
Land Boundary Agreement (LBA), 2015:
- Implemented through the 100th Constitutional Amendment Act (2015).
- Key Outcomes:
- India transferred 111 enclaves (17,160 acres) to Bangladesh.
- Bangladesh transferred 51 enclaves (7,110 acres) to India.
- Affected ~50,000 people, most opted to remain in place.
- Ensured demarcation of nearly the entire land border.
Important Cross-Border Points & Initiatives:
- Integrated Check Posts (ICPs): Petrapole–Benapole, Agartala–Akhaura, Dawki–Tamabil.
- Feni River Water Agreement (2020): India allowed to withdraw 1.82 cusecs of water for Tripura.
- Moitree Setu over Feni River connects Sabroom (Tripura) and Ramgarh (Bangladesh) – enhances trade.
Source : The Hindu
Category: POLITY
Context: Biennial elections to eight Rajya Sabha seats — two from Assam and six from Tamil Nadu — will be held on June 19, the Election Commission announced.
Decoding the context: Currently, the NDA has 128 members in the Upper House while the Opposition has 89 MPs. Non-aligned parties like the YSRCP, BRS, BJD, BSP and MNF have 20 members while eight seats are currently vacant.
Learning Corner:
Overview of Rajya Sabha
- Rajya Sabha, or the Council of States, is the Upper House of the Indian Parliament, representing states and Union Territories.
- Article 80 of the Indian Constitution deals with the Council of States (Rajya Sabha). It outlines the maximum strength of the Rajya Sabha, which can be up to 250 members, including 12 nominated by the President and representatives of the states and union territories.
- Current strength: 245 members (233 elected from states/UTs + 12 nominated by the President).
- Term: Members serve a 6-year term, with one-third of seats retiring every 2 years, necessitating biennial elections.
- Permanent Body: Unlike the Lok Sabha, it is a continuing chamber and cannot be dissolved.
Election Process
- Election Body: Conducted by the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- Electorate: Members of State Legislative Assemblies (MLAs) vote for state representatives; for UTs, an electoral college is formed. UTs without legislature (e.g., Lakshadweep, Chandigarh) have no Rajya Sabha representation
- Voting System: Single Transferable Vote (STV) with proportional representation, allowing MLAs to rank candidates by preference.
- Quota for Election: Determined by the formula: Quota = [Total Valid Votes / (Number of Seats + 1)] + 1.
- Unlike the Lok Sabha and Assembly elections, where ballots are secret (no one can be shown whom the vote is cast for), the Rajya Sabha polls are “open”. This means that the votes that the MLAs of each state cast to choose the members of the Upper House are seen by their party representatives.
Key Features
- Eligibility: Candidates must be at least 30 years old, Indian citizens, and meet other criteria under the Representation of the People Act, 1951.
- The Fourth Schedule of the Indian Constitution specifies the allocation of seats in the Rajya Sabha (the Council of States) for each state and union territory. This allocation is based on the population of each state.
Source : The Hindu
Category: GEOGRAPHY
Context: Mumbai woke up to an unusual Monday in what has been an unusual May — monsoon arrived two weeks in advance, and in full force.
Decoding the context: Data show that this is the earliest that the monsoon has ever arrived in Mumbai (IMD has been keeping records since 1950), with the previous earliest onset date logged at May 29 in the years 1971, 1962 and 1956. For perspective, the normal date of monsoon onset in Mumbai is June 11.
Learning Corner:
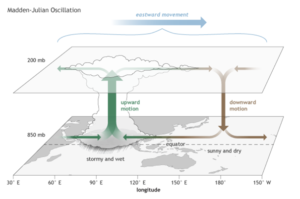
- Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) is an eastward-moving system of clouds, rainfall, winds, and pressure that circles the Earth along the equatorial region.
- Origin: Initiates in the Indian Ocean, playing a critical role in monsoon dynamics.
- Movement: Travels eastward at a speed of 4–8 meters per second, completing a global cycle in 30–60 days.
- MJO is divided into 8 Phases, each lasting a few days. Each phase represents MJO’s location and influence on rainfall in various regions. Phases 2 to 4 are usually favourable for enhancing Indian monsoon activity.
Role in Indian Monsoon
- Enhances convection (cloud formation) and rainfall over India during favourable phases.
- Boosts monsoon onset, progression, and intensity when present over Indian Ocean.
- In unfavourable phases, it may suppress rainfall and delay onset.
Source : Indian Express
Category: ART & CULTURE
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited the Karni Mata temple in Deshnok, a small town about 30 km from Bikaner, Rajasthan.
Decoding the context: Dubbed the “rat temple”, this historical place of worship is famous for
| Feature | MJO | ENSO |
| Nature | Intra-seasonal (30-60 days) | Inter-annual (2–7 years) |
| Movement | Eastward | Stationary pattern over Pacific |
| Impact Duration | Short-term | Long-term |
| Origin | Indian & Pacific Oceans | Equatorial Pacific Ocean |
being the home to tens of thousands of kabas (rats), which are considered sacred and protected.
Learning Corner:
- Karni Mata, also known as Ridhi Kanwar or Ridhu Bai, is believed to have been a 14th–15th sage, and an incarnation of Goddess Durga.
- Much of what is known about her comes from oral tradition and hagiographies, such as the Karni Mata Charitra, which portray her as a spiritual leader and supported rulers including Rao Jodha, the founder of Jodhpur, and Rao Bika ji, the founder of Bikaner.
- It is said that both Jodhpur and Bikaner were established in 1459 and 1488, respectively, with Karni Mata’s blessings.
Cultural and Religious Significance
- Kuldevi: Revered as the tutelary deity (kuldevi) by the Charan community.
- Karni Mata is also deeply venerated by Rathore Rajputs, the dominant warrior caste in the region. Her blessings to Rao Jodha and Rao Bika, led to many Rajput clans in Rajasthan considering her their royal protector and family deity.
- With Hinglaj Mata temple in Balochistan, one of the 51 Shakti Peeths, falling in Pakistan post Partition, the relevance of Karni Mata has only grown this side of the border, with pilgrimage to Hinglaj often affected by the relations between the two countries.
Relevance to Armed Forces
- Historical Association: Linked to pre-Independence Bikaner state forces, including Karni Battalion, Sadul Infantry, Dungar Lancers, Vijay Battery, and Ganga Risala.
- Sadul Infantry and Karni Battalion merged into 19 Rajput Battalion. Vijay Battery merged into 41 Field Regiment Artillery.
- Tradition: Commanding Officers of 19 Rajput Battalion visit the temple upon taking charge; during Navratra, two NCOs make offerings on behalf of the battalion.
- Symbolism: Karni Mata is invoked for courage, protection, and success, especially by Rajasthani soldiers before deployment.
Source : Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q1.With reference to the Karni Mata Temple in Rajasthan, consider the following statements:
- Karni Mata is believed to have been a 14th–15th sage.
- Karni Mata is believed to be an incarnation of Goddess Durga.
- The temple is renowned for housing thousands of sacred rats known as kabas.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Q2.The Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) is most appropriately described as:
A. A long-term oceanic temperature fluctuation in the Pacific Ocean.
B. A tropical intra-seasonal phenomenon that moves eastward and influences rainfall.
C. A stationary high-pressure system over the equator.
D. A permanent westerly wind belt around the globe.
Q3.Consider the following statements regarding Rajya Sabha elections:
- Members are elected by the public through direct elections.
- The voting system followed is the proportional representation by the single transferable vote.
- All members are elected for a term of 5 years.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 2 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 17th May – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – d











