IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – Science
Context: Recently, India loaded the core of its long-delayed prototype fast breeder reactor (PFBR) vessel.
Background:-
- Large-scale use of nuclear power is accompanied by a difficult problem: waste management.
About Nuclear Waste:-
- In a fission reactor, neutrons bombard the nuclei of atoms of certain elements. When one such nucleus absorbs a neutron, it destabilises and breaks up, yielding some energy and the nuclei of different elements.
- For example, when the uranium-235 (U-235) nucleus absorbs a neutron, it can fission to barium-144, krypton-89, and three neutrons. If the ‘debris’ (barium-144 and krypton-89) constitute elements that can’t undergo fission, they become nuclear waste.
- Fuel that is loaded into a nuclear reactor will become irradiated and will eventually have to be unloaded.At this stage it is called spent fuel.
- The spent fuel contains all the radioactive fission products that are produced when each nucleus breaks apart to produce energy, as well as those radioactive elements, produced when uranium is converted into heavier elements following the absorption of neutrons and subsequent radioactive decays.
- Handling the spent fuel is the main challenge: it is hot and radioactive, and needs to be kept underwater. Once it has cooled, it can be transferred to dry casks for longer-term storage.
- All countries with longstanding nuclear power programmes have accumulated a considerable inventory of spent fuel. For example, the U.S. had 69,682 tonnes (as of 2015), Canada 54,000 tonnes (2016), and Russia 21,362 tonnes (2014).
- Depending on radioactivity levels, the storage period can run up to a few millennia, meaning they have to be isolated from human contact for periods of time that are longer than anatomically modern Homo sapiens have been around on the planet.
How is nuclear waste dealt with?
- Once spent fuel has been cooled in the spent-fuel pool for at least a year, it can be moved to dry-cask storage, and is placed inside large steel cylinders and surrounded by an inert gas. The cylinders are sealed shut and placed inside larger steel or concrete chambers.
- Reprocessing — the name for technologies that separate fissile from non-fissile material in spent fuel — is another way to deal with the spent fuel. Here, the material is chemically treated to separate fissile material left behind from the non-fissile material. Because spent fuel is so hazardous, reprocessing facilities need specialised protections and personnel of their own. Such facilities present the advantage of higher fuel efficiency but are also expensive.
Source: Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: Assam Cabinet on March 10 decided to de-notify a prime one-horned rhino habitat – the Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary about 48km east of Guwahati.
Background:
- Environment activists says the decision, taken 26 years after the Assam Forest Department notified Pobitora as a wildlife sanctuary on March 17, 1998, is the first of its kind for any protected area in the country.
About Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary
- Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary is a wildlife sanctuary on the southern bank of the Brahmaputra in Morigaon district in Assam, India.
- The sanctuary has the highest concentration of the one-horned rhinos on earth.
- The Grasslands of Pobitora offer sightings of the Greater One Horned Rhinoceros, Wild Water Buffalo, Monitor Lizard, Wild Boar, etc.
- Pobitora also holds the distinction of being the source population of the Indian Rhinoceros Vision, 2020 (IRV), Eight Rhinos were translocated from Pobitora Wild life Sanctuary and introduced into Manas National Park
Source: Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: Recently, India successfully conducted the first flight test of indigenously developed Agni-5 missile with Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle (MIRV) technology from Dr A P J Abdul Kalam Island off the coast of Odisha.
Background:
- The flight test was conducted as part of India’s ‘Mission Divyastra’.
About Agni-V:
- The Agni-V is an advanced surface-to-surface ballistic missile developed under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP) in India.
- The Agni-V is an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of India.
- It’s a fire-and-forget missile, which means once fired, it doesn’t require further guidance and can’t be stopped without an interceptor missile.
- The missile has a range of over 5000 km, making it capable of hitting targets beyond this range.
- It can carry a warhead of about 1500 kg.
- The Agni series of missiles, which includes Agni-1 to Agni-5, forms the backbone of India’s nuclear launch capability.
- Agni-V has been successfully tested multiple times since 2012.
Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle (MIRV) Technology
- The latest variant of the Agni missile is equipped with MIRV (Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle) technology.
- MIRV technology allows a single missile to deploy multiple warheads at different locations or at the same location with a time gap.
- This technology significantly enhances the missile’s effectiveness by enabling it to hit multiple targets simultaneously.
- Agni-V’s MIRV capability is aimed primarily at countering challenges from China.
- These missiles can be launched from land or from sea from a submarine.
Global Context:
- Currently, only a handful of countries possess MIRV-equipped missiles.
- These countries include the United States, Russia, China, France, and the United Kingdom.
- While Pakistan is developing such a missile system, there are suspicions that Israel may also possess or be developing one.
Previous Year Question
Q1. With reference to Agni-IV Missile, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It is a surface-to-surface missile.
- It is fuelled by liquid propellant only.
- It can deliver one-tonne nuclear warheads about 7500 km away.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi virtually inaugurated the 3rd Land Port at Sabroom in South Tripura.
Background:
- In addition to the modern Land Port in Sabroom, the Prime Minister inaugurated 11 projects in Tripura.
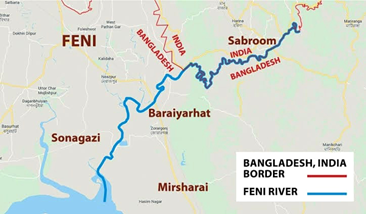
About SABROOM LAND PORT :
- The Sabroom Land Port is strategically located in the South Tripura district of the state of Tripura, India, along the international border with Bangladesh.
- It plays a vital role in linking India and Bangladesh, facilitating cross-border trade.
- Sabroom is directly connected to the Chittagong port of Bangladesh via the Maitree bridge over the River Feni, which is approximately 75 km from the proposed land port.
- The land port provides facilities such as a passenger terminal building, cargo administrative building, and warehouse.
- It aims to enhance connectivity and boost trade between India and Southeast Asia.
Source: Times of India
Syllabus
- Prelims -Current Event
Context: Recently, SIDBI has secured a substantial investment of $24.5 million from the Green Climate Fund (GCF) for its Avaana Sustainability Fund (ASF).
Background:
- The Green Climate Fund (GCF) is the world’s largest climate fund, established within the framework of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. Its mission is to assist developing countries in both adaptation and mitigation practices to counter the effects of climate change.
About AVAANA SUSTAINABILITY FUND (ASF):
- The Avaana Sustainability Fund (ASF) is a USD 120 million venture capital fund that aims to invest in early-stage climate technology companies in India.
- This fund is launched by the Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI).
- ASF focuses on supporting the transition to low-carbon and climate-resilient development pathways by investing in innovative technologies across key sectors such as sustainable resource management, mobility and supply chains, and sustainable agriculture and food systems.
- ASF’s strategies include investing in low-carbon and climate-resilient businesses, adding value for climate and sustainability leaders, establishing a virtuous cycle of sourcing and value addition for the larger ecosystem, and focusing on social, economic, and environmental impact with tailored investment strategies across various sectors.
- The ASF project has been approved by the Green Climate Fund (GCF) and aims to contribute to India’s efforts in addressing climate challenges and promoting sustainable solution.
Source: Economic Times
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2
Context: Parliament passed the Constitution (106th Amendment) Act, 2023, to provide for one-third reservation to women in the Lok Sabha, State Assemblies, and the Assembly of NCT of Delhi.
Background:
- The Constitution amendment Bill was passed by the Lok Sabha with near-unanimity, with only two members opposing it and was unanimously passed by the Rajya Sabha.
Key features of the Act:
- It provided for inserting Article 330A into the constitution, which borrows from the provisions of Article 330, which provides for the reservation of seats to SCs/STs in the Lok Sabha. It provided that reserved seats for women may be allotted by rotation to different constituencies in states or Union Territories.
- In the seats reserved for SCs/STs, it sought to provide one-third of the seats to be reserved for women on a rotational basis.
- It introduces Article 332A, which mandates the reservation of seats for women in every state legislative assembly. Additionally, one-third of the seats reserved for SCs and STs must be allocated for women, and one-third of the total seats filled through direct elections to the Legislative Assemblies shall also be reserved for women.
- It added a new clause in 239AA to the constitution that grants special status to the Union Territory of Delhi as the national capital concerning its administrative and legislative functioning. Article 239AA(2)(b) was amended to add that the laws framed by parliament shall apply to the National Capital Territory of Delhi.
- It added new Article 334A which states that the reservation will be effective after the census conducted after the commencement of this Act has been published. Based on the census, delimitation will be undertaken to reserve seats for women. The reservation will be provided for 15 years. However, it shall continue till such date as determined by a law made by Parliament.
- Seats reserved for women will be rotated after each delimitation, as determined by a law made by Parliament.
Issues/Concerns with the Act:
- The idea of reservation runs counter to the principle of equality enshrined in the Constitution, as women may not be competing on merit.
- Reservation of seats for women in legislature restricts voter’s choices and runs counter to the idea of self-determination.
- Women are not a homogeneous community, such as a caste group. Therefore, the arguments made for caste-based reservations cannot be made for women.
- There are larger issues of electoral reforms such as the criminalization of politics, internal democracy in political parties, etc., that might act as an impediment to the political empowerment of women.
- The act provides for the reservation of 1/3rd seats across all Lok Sabha seats as against the provision of reserving 1/3rd seats in each State/UT as mentioned in the 2008 bill.
- The act provides for the rotation of seats after every delimitation exercise as against after every general election to the Parliament/ State legislative assemblies.
- The Act does not contain any provision for reservation for women in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils of the States. Geeta Mukherjee Committee (1996) recommended providing reservations for women in Rajya Sabha and Legislative Councils as well.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q1.)With reference to the Avaana Sustainability Fund (ASF), consider the following statements:
- The Avaana Sustainability Fund (ASF) is a venture capital fund.
- It aims to invest in early-stage climate technology companies in India.
- It is launched by the Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI).
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2.) The Sabroom Land Port, recently seen in news is located in India, along the international border with
- Myanmar
- Bangladesh
- Nepal
- Bhutan
Q3.) With reference to the Agni-V Missile, consider the following statements:
- Agni-V is an advanced surface-to-surface ballistic missile.
- It is developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of India.
- Agni-V missile with MIRV technology can carry multiple warheads that can independently target different locations.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 13th March 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 12th March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – b











