IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – POLITY
Context: The Opposition has started efforts to move an impeachment motion against Allahabad High Court judge Shekhar Kumar Yadav for his controversial statements at a recent Vishwa Hindu Parishad event.
Background: –
- No High Court judge has been impeached in India so far.
Constitutional Provisions
- Article 217:
- Deals with the appointment and conditions of service of High Court judges.
- Specifies that judges hold office until the age of 62 unless they resign, are impeached, or are removed.
- Article 218:
- The process of impeachment of a judge of the Supreme Court is laid down in Article 124(4) of the Constitution of India. Article 218 says the same provisions shall apply in relation to a judge of the High Court as well.
- Grounds for Removal: Proved misbehavior or incapacity.
- The procedure to be followed for impeachment of a judge is laid down in the Judges Inquiry Act, 1968.
Procedure for Impeachment
- Initiation of Motion – A removal motion must be signed by:
- At least 100 members in the Lok Sabha, or
- At least 50 members in the Rajya Sabha.
- Upon admission of the motion, an inquiry committee is formed. A three-member committee is constituted, comprising:
- A Supreme Court judge.
- A Chief Justice of a High Court.
- An eminent jurist.
- The committee investigates the charges and submits its report.
- Parliamentary Approval:
- If the committee finds the judge guilty, both Houses of Parliament must pass the motion with a two-thirds majority of members present and voting, and the majority must be no less than 50% of the total membership of the House.
- President’s Order: Upon approval by both Houses, the President orders the removal of the judge.
Important Points
- High Threshold: The impeachment process is deliberately complex to ensure judicial independence.
- Significant Cases:
- Justice Soumitra Sen of the Calcutta High Court faced impeachment proceedings but resigned before the process was concluded.
- Justice V. Ramaswami of the Supreme Court faced impeachment, but the motion failed in the Lok Sabha.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Prelims – SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Context: According to the World Malaria Report 2024 by WHO, the South East Asia Region contributes about 1.5% of global malaria cases, with India accounting for nearly half of all estimated cases in the region in 2023.
Background: –
- New data from the WHO revealed that an estimated 2.2 billion cases of malaria and 12.7 million deaths have been averted since 2000, but the disease remains a serious global health threat, particularly in the WHO African Region.
About Malaria
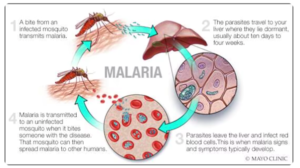
- Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by Plasmodium parasites, transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- Not all Anopheles mosquitoes have malaria, but if they bite a person with malaria, they can become infectious.
- People do not spread malaria to other people, like the common cold or the flu. Also, malaria is not sexually transmitted.
- Because the parasites that cause malaria affect red blood cells, people can acatch malaria from exposure to infected blood, including:
- From mother to unborn child
- Through blood transfusions
- By sharing needles used to inject drugs
Symptoms
- Fever, chills, headaches, muscle pain, vomiting.
- Severe cases: Organ failure, cerebral malaria, or death.
- Global Initiatives: WHO’s Global Technical Strategy for Malaria (2016-2030) aims to reduce global malaria cases by 90% by 2030.
India’s Measures:
- National Malaria Control Programme (NMCP): Aims to eliminate malaria by 2030.
- National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP): Comprehensive approach to combat mosquito-borne diseases.
- Use of insecticide-treated bed nets (ITNs), indoor residual spraying (IRS), and rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs).
Vaccination:
- RTS,S/AS01 (Mosquirix): First malaria vaccine approved by WHO in 2021 for pilot projects in high-burden regions.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Mains – ENVIRONMENT
Context: As the world becomes more reliant on space technology for vital functions like climate monitoring, the environmental consequences of space activities need more attention. The rapid growth of the number of satellites in orbit has led to concerns about interference with climate monitoring systems and the accumulation of orbital debris.
Background:
- Space activities currently fall outside international sustainability instruments like the Paris Agreement.
Key Concerns:
Climate Change:
- Rocket emissions (CO2, black carbon, water vapor) contribute to global warming.
- Chlorine-based propellants deplete the ozone layer.
- Satellite re-entry and burn up releases metallic ash, potentially altering the atmosphere.
- Energy-intensive satellite production and mining activities have significant carbon footprints.
Orbital Debris:
- Rapid growth of satellites and debris poses collision risks to functional satellites.
- Debris interferes with scientific observations and communication systems.
- Increases the cost and complexity of space missions.
- Poses a threat to human-crewed missions.
Challenges to Space Sustainability:
- Lack of International Regulation:
- No specific international regulations address space debris and environmental impact.
- Technological Limitations:
- Reusable rockets have limitations in terms of payload capacity and fuel efficiency.
- Cleaner fuels like hydrogen and biofuels face challenges in production and storage.
- Biodegradable satellite materials lack durability for space environments.
- Autonomous debris removal technologies are expensive and require legal clarity.
- International Cooperation:
- Data sharing and coordination among nations are hindered by security and commercial concerns.
Path Towards Space Sustainability:
- International Cooperation:
- International cooperation through bodies like the Committee on the Peaceful Use of Outer Space (COPUOS) is necessary to create enforceable standards.
- Standardize emission limits, debris mitigation, and data-sharing practices.
- Technological Innovation:
- Invest in research and development of cleaner fuels, biodegradable materials, and autonomous debris removal technologies.
- Policy and Incentives:
- Implement strict regulations and incentives for sustainable space practices.
- Encourage public-private partnerships to accelerate technological advancements.
- Establish a global space traffic management system to monitor and coordinate satellite activities.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Prelims – SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Context: Two years of data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has corroborated the observation by Hubble Telescope that the universe is expanding more rapidly than expected.
Background: –
- The observations by Webb, the most capable space telescope ever deployed, appear to rule out the notion that the data from its forerunner Hubble was somehow flawed due to instrument error
Key takeaways
- Data from James Webb Space Telescope have now validated the Hubble Space Telescope’s earlier finding that the rate of the universe’s expansion is faster — by about 8% — than would be expected based on what astrophysicists know of the initial conditions in the cosmos and its evolution over billions of years. The discrepancy is called the Hubble Tension.
- According to scientists, the current understanding of the universe contains a lot of ignorance about two elements — dark matter and dark energy — and these make up 96% of the universe.
- Dark matter, thought to comprise about 27% of the universe, is a hypothesised form of matter that is invisible but is inferred to exist based on its gravitational effects on ordinary matter – stars, planets, moons, all the stuff on Earth – which accounts for roughly 5% of the universe.
- Dark energy, believed to comprise approximately 69% of the universe, is a hypothesised form of energy permeating vast swathes of space that counteracts gravity and drives the universe’s accelerating expansion.
More about Hubble Tension
- Hubble Constant (H₀): Represents the rate of expansion of the universe, typically expressed in kilometers per second per megaparsec (km/s/Mpc)
- Hubble Tension: Discrepancy between values of H₀ measured using different methods, challenging our understanding of cosmology.
About James Webb Space Telescope (JWST)
- The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is the most powerful space telescope ever built, designed to explore the universe in unprecedented detail.
- Launch Date: JWST was launched on December 25, 2021.
- Location: It orbits the Sun at the second Lagrange point (L2), about 1.5 million kilometers (1 million miles) from Earth.
- Design and Features:
- Sunshield: It has a 5-layer sunshield the size of a tennis court, which protects its instruments from the Sun’s heat and light.
- Mirrors: JWST uses 18 hexagonal mirrors that unfold like a “Transformer” in space to form a single large mirror with a diameter of 6.5 meters (21 feet).
- Scientific Instruments:
- Instruments: JWST is equipped with four main instruments: Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec), Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), and Fine Guidance Sensor/Near InfraRed Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (FGS/NIRISS).
- Capabilities: These instruments allow JWST to observe the universe in infrared light, which can penetrate dust clouds and reveal objects that are too faint or distant for visible light telescopes.
- Scientific Goals:
- Early Universe: JWST aims to study the first galaxies formed after the Big Bang, providing insights into the early universe.
- Planetary Systems: It will observe the atmospheres of exoplanets to search for signs of habitability and possibly life.
- Star and Planet Formation: JWST will study the formation of stars and planets within dust clouds.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: Kazakhstan’s state-owned energy company said recently that it had decontaminated Soviet-era oil waste on the shores of the Caspian Sea.
Background: –
- In Central Asia, work to remove toxic waste dating back to Soviet times has gathered pace in recent years, particularly in Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan, where millions of cubic metres of radioactive waste are stored.
Key takeaways
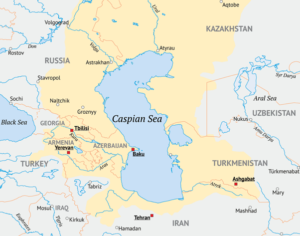
- Location: Lies between Europe and Asia, bordered by five countries: Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran, and Azerbaijan.
- Unique Feature: Largest enclosed inland water body, often called a sea due to its size and salinity.
Geographical Features
- Salinity: Lower than seawater but higher than freshwater.
- Important Rivers: Volga, Ural, and Kura rivers flow into the Caspian Sea.
Economic Importance
- Energy Resources: Rich in oil and natural gas reserves, contributing significantly to regional economies.
- Fishing Industry: Famous for sturgeon and caviar production.
- Trade and Transportation: Strategic hub for trade routes connecting Europe and Asia.
Environmental Significance
- Biodiversity: Home to unique species, including the endangered Caspian seal.
- Environmental Concerns: Pollution from oil exploration, industrial activities, and declining water levels due to climate change.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Consider the following statements regarding malaria:
- Malaria is caused by viruses transmitted through the bites of female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- People with malaria can spread the disease to others through casual contact, like shaking hands.
- Malaria parasites can be transmitted through blood transfusions or from mother to child.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 3
Q2.) Consider the following statements about the Caspian Sea:
- It is the largest enclosed inland water body in the world.
- The Caspian Sea has a higher salinity level than seawater.
- The Caspian Sea is a significant hub for global sturgeon production.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 3
Q3.) With reference to the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), consider the following statements:
- It operates in the visible light spectrum to study the early universe.
- JWST is stationed at the second Lagrange point (L2), which is approximately 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.
- It uses a 5-layer sunshield to protect its instruments from heat and light.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 11th December – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – a











