IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – CURRENT EVENT
Context: Greek Foreign Minister George Gerapetritis has affirmed Greece’s full support for the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC), describing it as a project for peace.
Background: –
- Minister acknowledged that the initiative, launched in September 2023, has faced delays due to conflicts in West Asia, particularly the Israel-Gaza war.
Key takeaways
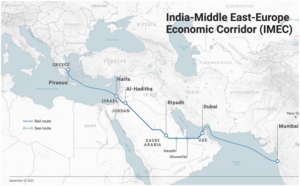
- The India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) aims at boosting economic development and enhancing inter-regional connectivity between Asia, the Persian Gulf, and Europe.
- Announced during the 2023 G20 New Delhi summit, the project seeks to create a modern trade route that reconnects historical pathways, linking India to Europe via key partners including the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Israel, and Greece.
Key Features and Objectives
- Bifurcated Route: IMEC is envisioned with two main legs: an eastern corridor that channels container traffic from India to the Gulf region and a northern corridor that connects the Gulf to Europe. This multimodal pathway will integrate high-speed rail, shipping lanes, digital connectivity (through undersea cables), and even renewable energy infrastructure like clean hydrogen pipelines
- Economic and Logistical Advantages: The corridor is expected to reduce transit times by up to 40 percent and lower logistics costs significantly. It is seen as a strategic tool to diversify trade routes away from traditional chokepoints like the Suez Canal
- Counterbalance to China’s Belt and Road Initiative: IMEC is interpreted as a counterweight to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Geopolitical Implications
- Enhanced Regional Integration: The corridor is designed to strengthen economic ties and promote regional stability.
- Strategic Diversification: In addition to facilitating faster and cheaper trade, IMEC is intended to reduce reliance on existing maritime routes, thereby mitigating vulnerabilities exposed by conflicts. This diversification is critical for future-proofing supply chains.
- Diplomatic and Economic Synergies: By linking diverse economies through coordinated infrastructure projects, the corridor can serve as a catalyst for deeper engagement among the participating countries.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus:
- Mains – GS 1 & GS 2
Context: Bhopal district collector issued orders prohibiting begging in the district, a month after the Indore collector passed similar orders, and introduced stringent measures including registration of FIRs for receiving and giving alms.
Background: –
- The criminalisation of begging has been a contentious issue in many parts of the country with some states having stringent laws, often criticised for being ‘anti-poor’ and mandated in the place of rehabilitation-centric interventions.
Key takeaways
- The orders are under section 163 of the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS), 2023. This law gives officials including the district magistrate, sub-divisional magistrate or any other executive magistrate, the power to issue an order in urgent cases of ‘nuisance or apprehended danger’.
- The order can direct any person from abstaining from a certain act. It may apply to persons residing in a particular place or area, or the public generally frequenting or visiting a particular place or area.
- The orders state that action will be taken under section 223 of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS). The section punishes those disobeying an order announced by a public servant, who is lawfully empowered to do so. If an order under the section is not obeyed, the person can be punished with imprisonment or fine or both.
- Section 163 BNSS, however, also says that an order under the section shall remain in force for not more than two months, provided the state government considers it necessary that the order remain in force for a period not exceeding six months.
Is begging termed illegal anywhere else?
- The first law against begging was the Bombay Prevention of Beggary Act, 1959. Its roots were colonial, when there were laws against ‘vagrants’, in various provinces, including the Bengal Vagrancy Act, 1943 and the Cochin Vagrancy Act, 1945.
- In 2018, the Delhi High Court struck down various sections of the Bombay Prevention of Begging Act, 1959, as extended to the NCT of Delhi, declaring them unconstitutional and effectively decriminalizing begging. However, the court did not invalidate provisions related to ancillary offences, such as Section 11, which penalizes those who employ or cause others to beg.
- Many states including Maharashtra continue to criminalise begging under the Act. There is no central Act on begging in the country but many states have enacted their own laws, most of them based on the 1959 Act.
- While some argue that Act is needed to address forced begging or ‘begging rackets’, activists say that it can be addressed in existing provisions, like laws against trafficking.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – CURRENT EVENT
Context: President Donald Trump signed an executive order withdrawing the US from the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC).
Background:
- Trump pulled the US out of UNHRC in 2018 during his first term in office. Former President Joe Biden reinstated the US’ membership of the organization in 2021.
Key takeaways
- The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) is an intergovernmental body within the United Nations system.
- It was established in 2006 to replace the former United Nations Commission on Human Rights. The UNHRC is responsible for strengthening the promotion and protection of human rights around the globe.
- Membership: The Council consists of 47 Member States elected directly and individually by a majority of the 193 UN General Assembly states. Members serve for three-year terms and can serve a maximum of two consecutive terms.
- Functions: The UNHRC addresses human rights violations and makes recommendations on them. It holds regular sessions three times a year and can also hold special sessions to respond to urgent human rights situations.
- Universal Periodic Review (UPR): The Council reviews the human rights records of all UN Member States through the UPR process.
- Special Procedures: The UNHRC appoints independent human rights experts, known as Special Rapporteurs, who monitor and report on human rights situations in specific countries or themes.
- Commissions of Inquiry: The Council can authorize commissions of inquiry and fact-finding missions to investigate human rights violations.
Source: DW
Syllabus:
- Prelims – SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Context: India’s commitment to cutting-edge biomedical research and innovation took a significant leap forward with the launch of the GARBH-INi-DRISHTI data repository.
Background: –
- It is part of the GARBH-INi program, which stands for Interdisciplinary Group for Advanced Research on Birth Outcomes – DBT India Initiative. This initiative is led by the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI) in collaboration with the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India.
Key takeaways
- Garbhini-Drishti is a comprehensive data dashboard that provides an extensive overview of one of South Asia’s largest pregnancy cohort datasets.
- Data Collection: The platform collects clinical, epidemiological, imaging, and biospecimen data from over 12,000 pregnant women, newborns, and postpartum mothers. This data is collected at multiple time points throughout pregnancy and the postpartum period.
- Research Focus: The primary aim is to improve maternal and neonatal health outcomes by enabling transformative research.
- Data Accessibility: Garbhini-Drishti provides clear guidance on accessing the dataset for approved research purposes, fostering collaboration and impactful discoveries.
- Comprehensive Assessments: Participants undergo detailed assessments during pregnancy, including clinical evaluations, ultrasound imaging, and collection of various biospecimens. Post-natal follow-ups continue to capture critical maternal and neonatal health outcomes.
- Quality Control: The platform ensures the accuracy, reliability, and consistency of data collection through regular training of the research team and concurrent monitoring for errors.
Source: PIB
Syllabus:
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: The 13th edition of joint military exercise ‘Ekuverin’ between the Indian Army and the Maldives National Defence Force has commenced in the archipelago nation.
Background: –
- The term “Ekuverin” means “Friends” in the Dhivehi language of the Maldives. This exercise aims to strengthen the bilateral military ties between the two countries and enhance their ability to work together in various operations.
Key takeaways
- Ekuverin is a joint military exercise conducted annually between the Indian Army and the Maldives National Defence Force (MNDF).
- Inception: The exercise was first held in 2009 and has been conducted alternately in India and the Maldives.
- Participants: A platoon-level contingent from both the Indian Army and the MNDF participates in the exercise.
- Focus Areas: The primary focus is on enhancing interoperability in counter-insurgency and counter-terrorism operations, as well as conducting joint humanitarian assistance and disaster relief operations.
- Recent Edition: The 13th edition of the exercise commenced on February 2, 2025, in Maafilaafushi, Lhaviyani Atoll, Maldives, and will run until February 16, 2025.
- Significance: The exercise reflects the strong political and defence relationship between India and the Maldives, promoting regional security and stability.
Source: News on AIR
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Consider the following statements regarding the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC):
- The UNHRC was established in 2006 to replace the United Nations Commission on Human Rights.
- The UNHRC consists of 47 member states elected by the United Nations Security Council.
- The Universal Periodic Review (UPR) process of the UNHRC reviews the human rights records of UN member states.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Q2.) With reference to the Garbhini-Drishti initiative, consider the following statements:
- It is a data repository launched as part of the GARBH-INi program under the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India.
- It focuses primarily on collecting data from newborn infants to improve post-natal healthcare.
- The data platform includes clinical, epidemiological, imaging, and biospecimen data from pregnant women and newborns.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Q3.) Consider the following statements regarding the Ekuverin military exercise:
- It is a joint military exercise conducted between India and Sri Lanka.
- The exercise was first held in 2009 and has been conducted alternately in India and the Maldives.
- The 13th edition of Ekuverin commenced in February 2025 in the Maldives.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 5th February – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – a











