Ethics Theory, TLP-UPSC Mains Answer Writing
Q. 5. The location of software industries in India follows a different pattern compared to traditional manufacturing sectors. Examine the factors influencing the growth of software hubs like Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Pune. (250 words, 15 marks)
Introduction
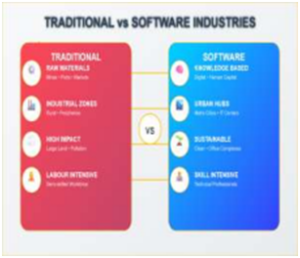
Unlike traditional industries that depend on raw materials and physical infrastructure, software industries in India are concentrated in urban, knowledge-driven hubs. This shift represents a new geography of development driven by human capital and digital connectivity.
Body
Contrast with Traditional Manufacturing Industries
- Raw Material Dependency vs Knowledge Dependency: Traditional sectors locate near mines, ports, or markets; software industries depend on skilled human capital and digital infrastructure.
- Rural/Industrial Belt vs Urban Centres: Manufacturing clusters are found in industrial zones or rural peripheries, whereas IT hubs are concentrated in metro cities.
- Pollution and Land Needs vs Sustainability: Manufacturing requires large land and causes pollution; software industries are cleaner and operate from office complexes.
- Labour-Intensive vs Skill-Intensive: Traditional industries use semi-skilled labour; software sectors rely on highly educated, technically skilled professionals.
Factors Influencing the Growth of Software Hubs in India
- Skilled Human Capital: Availability of engineering graduates from premier institutes like IITs, NITs, and state engineering colleges created a vast talent pool. Example: Bengaluru has over 120 engineering colleges within reach.
- Government Policy Support: Initiatives like Software Technology Parks of India (STPI), tax incentives, and SEZ policies encouraged IT investments. Example: Hyderabad’s HITEC City and Bengaluru’s Electronic City are products of such support.
- Urban Infrastructure and Connectivity: Better road, air connectivity, internet bandwidth, and availability of commercial space helped in urban IT clustering. Example: Pune’s Hinjewadi IT Park is well connected and well-planned.
- Presence of Anchor Firms: Early establishment of firms like Infosys, Wipro, TCS in Bengaluru, and later Google, Microsoft in Hyderabad created an ecosystem that attracted others. Example: Infosys was founded in Pune and moved to Bengaluru due to ecosystem advantage.
- Cosmopolitan Culture and Quality of Life: Modern amenities, open culture, and relative social stability attract talent from across the country. Example: Pune offers a balance of affordability and lifestyle.
- Role of Diaspora and Global Linkages: Indian tech diaspora returning from Silicon Valley contributed to the knowledge transfer and entrepreneurship ecosystem.
- Cluster Effect and Startup Culture: Agglomeration economies led to innovation and startup growth. Example: Bengaluru is now known as the “Silicon Valley of India” with over 10,000 startups.
Conclusion











