TLP-UPSC Mains Answer Writing
SYNOPSIS: IASbaba’s TLP – 2018: UPSC Mains General Studies Questions [1st February 2018]- Day 49
Q.1) what is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? What are its applications? Is it a potential threat to humanity? Examine.
Body:
Artificial Intelligence:
Artificial intelligence (AI) makes it possible for machines to learn from experience, adjust to new inputs and perform human-like tasks. Most AI examples that you hear about today – from chess-playing computers to self-driving cars – rely heavily on deep learning and natural language processing. Using these technologies, computers can be trained to accomplish specific tasks by processing large amounts of data and recognizing patterns in the data.
AI applications:
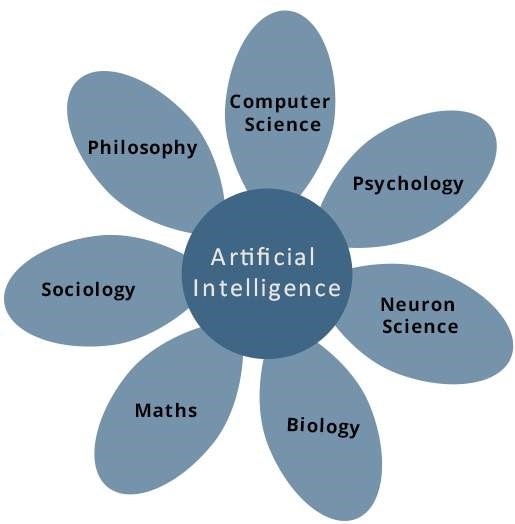
- AI automates repetitive learning and discovery through data. But AI is different from hardware-driven, robotic automation. Instead of automating manual tasks, AI performs frequent, high-volume, computerized tasks reliably and without fatigue.
- AI adds intelligence to existing products. In most cases, AI will not be sold as an individual application. Rather, products you already use will be improved with AI capabilities, much like Siri was added as a feature to a new generation of Apple products.
- AI adapts through progressive learning algorithms to let the data do the programming. AI finds structure and regularities in data so that the algorithm acquires a skill: The algorithm becomes a classifier or a predicator.
- AI achieves incredible accuracy though deep neural networks – which was previously impossible. For example, your interactions with Alexa, Google Search and Google Photos are all based on deep learning – and they keep getting more accurate the more we use them.
- AI gets the most out of data. When algorithms are self-learning, the data itself can become intellectual property. The answers are in the data; you just have to apply AI to get them out.
- Health Care: AI applications can provide personalized medicine and X-ray readings. Personal health care assistants can act as life coaches, reminding you to take your pills, exercise or eat healthier.
- Manufacturing: AI can analyze factory IoT data as it streams from connected equipment to forecast expected load and demand using recurrent networks, a specific type of deep learning network used with sequence data.
Its potential threat to humanity:
There is a lot of uncertainty about the kind of AI we may one day reach that would achieve human-level intelligence or possibly more.
- In the near term AI serves as a tool that can magnify the amount of power an individual has. For example, someone could buy thousands of cheap drones, attach a gun to each of them, and develop AI software to send them around shooting people. If the software was good enough this could result in far more destruction than a normal terrorist attack.
- In the short term, there is a threat being posed too many job markets in the form of automation, and for many automation problems.
- Gap between developed and developing countries to increase-due to skill difference.
Conclusion:
The power of artificial intelligence that unintentionally causes destruction and damage cannot be ignored. What will help us control it better is research and in-depth study of the importance of artificial intelligence. Research alone can control the potentially harmful consequences of AI and help us enjoy the fruit of this innovation.
Best Answer: Abhishek Naik
2. What is Big Data? Examine its role in facilitating governance.
Approach:
- Introduction- Definition
- Importance for government
- Challenges
- Way forward
- Conclusion
Introduction:
Big data is the term for a collection of data sets so large and complex that it becomes difficult to process using on-hand database management tools or traditional data processing applications. It exceeds the processing ability of conventional data systems and requires us to use an alternate way to process it so as to gain value from the data.
The data could be from social networks, web server logs, traffic flow sensors, satellite imagery, banking transactions, the content of web pages, scans of government documents, GPS trails, financial market data and so on.
Role in facilitating government:
Big Data and associated analytics are beneficial in various areas, such as
- The possible benefits of Big Data analytics in government could range from transforming government programmes and empowering citizens to improving transparency and enabling the participation of all stakeholders.
- Big Data can enhance the government’s ability to serve its citizens and address major national challenges.
- Benefits can range from- Solving traffic problems in cities, targeting healthcare delivery, efficient supply chain management, providing a personalized educational experience for students, enabling security to individuals and society at large.
- Helping predict natural phenomenon like monsoon, natural disasters etc.
- Strengthening economy by checking tax evasion, for businesses to produce customized products.
Overall it would help in informed policymaking and evidence-based decision making.
Challenges:
- Any breach of confidentiality regarding data that is collected and processed by the government could have serious ramifications.
- Sharing data between departments and across ministries is a challenge, given the jurisdictional boundaries that exist.
- Authenticity of data is another challenge.
Way forward:
- A change in mindset and effective training is required to make data-driven decisions.
- A comprehensive Big Data programme across Central and state government ministries/departments with help from industry, academic and research institutions should be formulated.
Best answer: Kanishka
3. What is Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT)? Discuss its technology and potential applications.
- Introduction: Define Somatic cell nuclear transfer.
- Body: In body, the answer should contain two parts, one about its technology and second part potential applications.
- Conclusion: 2-3 line conclusion.
Introduction
In genetics and developmental biology, somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is a laboratory technique for cloning for creating an ovum with a donor nucleus.
Body
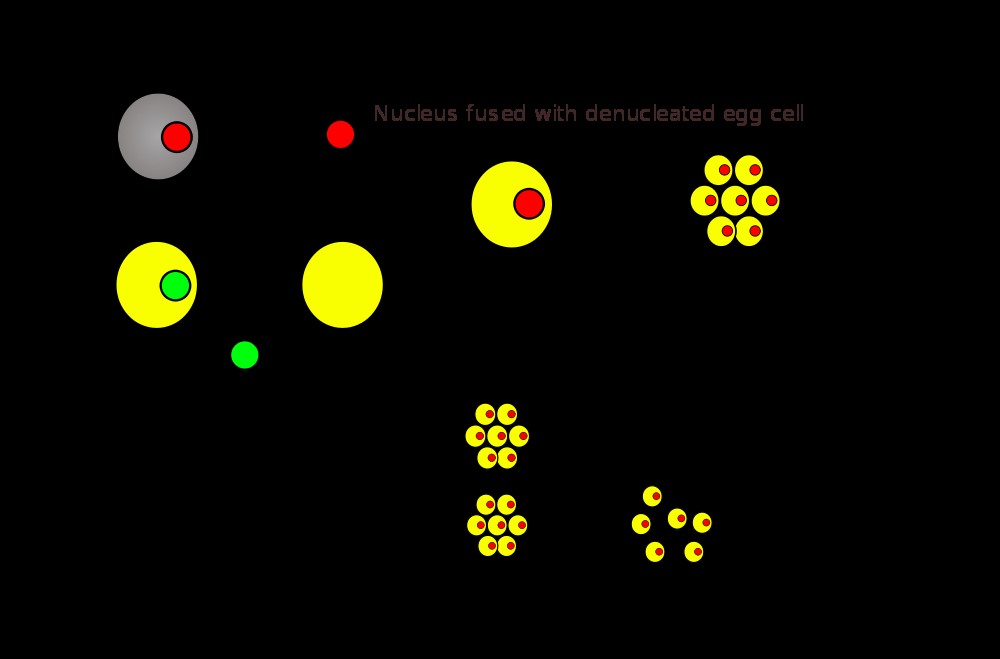
Technology:
- In SCNT the nucleus, which contains the organism’s DNA, of a somatic cell (a body cell other than a sperm or egg cell) is removed and the rest of the cell discarded.
- At the same time, the nucleus of an egg cell is removed.
- The nucleus of the somatic cell is then inserted into the enucleated egg cell.
- After being inserted into the egg, the somatic cell nucleus is reprogrammed by the host cell.
- The egg, now containing the nucleus of a somatic cell, is stimulated with a shock and will begin to divide.
- After many mitotic divisions in culture, this single cell forms a blastocyst (an early stage embryo with about 100 cells) with almost identical DNA to the original organism.
Potential Application:
- Studies, Research and Development.
- Embryonic stem cell research.
- Regenerative medicine also known as Therapeutic cloning
- Reproductive cloning.
- Preservation: Extent and endangered species.
Note: Explanation is needed for all points in 2nd part for a line or two.
Conclusion
It can be both boon and bane. It might help in many ways but it also has its share of effects which might include reduction of gene diversity, Nature’s rule like survival of fittest, ethical and moral issues. If got into wrong hands( Terrorists, crime syndicate) it might prove to be a disaster in waiting.
Connecting the dots:
- Ethical and Moral issues in cloning.
Best Answer: Jupiter.
4. What are gravitational waves? How do they get detected? What can the study of gravitational waves reveal? Discuss.
- Introduction: Define what Gravitational Waves are.
- Body: In body, the answer should contain two parts, one about how they are detected, explain the experiment conducted to identify them and second part what the study reveals.
- Conclusion: 2-3 line conclusion.
Introduction
Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of space time caused by some of the most violent and energetic process in the universe. Albert Einstein predicted the existence of such waves in 1916 in his general theory of relativity.
Body
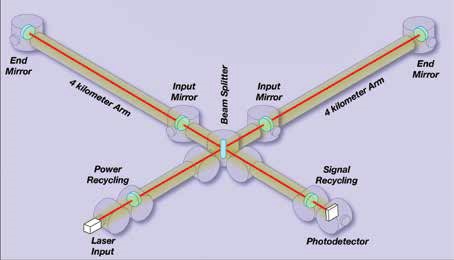
How do they are detected:
- It was first detected at an experiment facility at US by two precise detectors one in Livingston, Louisiana and other at Washington.
- Each detector looks like a giant “L” stamped on the landscape – two four-kilometer arms at right angles to one another.
- Inside each arm is a tunnel carrying a laser beam.
- The laser bounces up and down each arm of the detector before recombining at a detector.
- Any expansion of one of the arms relative to the other will shift a mirror slightly, changing the pattern revealed on the detector.
- But with such sensitive equipment, local effects – even traffic rumbling 10 kilometers away – can create vibrations that might be confused with gravitational waves.
- That’s why LIGO needs two detectors set up far apart from one another. Any local noise will only affect one of the detectors, while a real ripple in space time will show the same signal for both.
- Meanwhile, astrophysicists have used general relativity to work out what signals of extreme events would look like.

What studies can reveal:
- Origin of universe.
- Black hole.
- Our own earth origin.
- Understanding of effects of those waves on humans.
- Effects of waves on other stars and planets.
Note: Explanation is needed for all points in 2nd part for a line or two.
Conclusion
Hingoli District in Maharashtra has been selected for a project in India to study move about these waves. The study can not only help astrophysicists but also various other disciplines like biologists, doctors, neurologists etc. which can help them in creating different form of medicine for human welfare.
Connecting the dots:
- Voyager- The golden record
Best Answer: Krishna
Q5. Highlight the achievements of ISRO as a pioneer organisation in space technology.
Approach
- It’s a simple one part question
- Take a timeline approach and highlight its major achievement since ISRO’s inception to present date
Body
Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) was established in 1969. Since its beginning, ISRO has created a niche for itself in the space technology world through continuous low-cost innovations.
Major Achievements of ISRO:
- Aryabhata 1975 – within 6 years of its establishments, ISRO developed its first satellite which was launched by Soviet Union
- Rohini 1980 – first satellite to be place in orbit why an Indian made launch vehicle – the SLV-3
- INSAT 1983 – ushered a revolution in India’s radio and television broadcasting, communication and meteorological sector
- PSLV 1993 – the polar satellite launch vehicle will go onto become the most successful launch vehicle in the world with one of the lowest launch costs and unmatched success rate
- Chandrayan 2008 – was India’s first lunar probe. The mission was a major boost to India’s space program, as India researched and developed its own technology in order to explore the moon
- Mangalyaan 2014 – ISRO became the first organization to successfully send a probe to Mars in its first attempt. It did so at 1/10th of the cost by NASA.
- IRNSS – ISRO helped launch India’s own GPS system consisting of 7 satellites. It is capable of navigating the entire Indian subcontinent
- Reusable Launch Vehicle 2016 – demonstrated successfully. This would help reduce the cost of future launches to a fraction of present ones
- Launch of 100+ satellites in single launch in 2017 – the PSLV created a world record by simultaneously launching 104 satellites with 101 coming from foreign countries
- GSLV Mak III – developed by ISRO with its own cryogenic engine. The launch vehicle is capable of carrying 4 ton satellites into the geosynchronous transfer orbits.
The success of ISRO is testament to India’s capability in frugal engineering and finding solutions with severe resource constraints and international non-cooperation. With the successful completion of GSLV Mak III, ISRO is well on its way in achieving space self-sufficiency. Even more, ISRO has emerged as a pioneering player in the low-cost commercial satellite launch market.
Best Answer: Gaurav Sharma











