IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 25th February 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Rainfall to increase over next 100 years
Part of: GS Prelims –Geography and GS-I- Natural phenomena
In news:
IISC research tells:
- Indian monsoon rainfall increased from the last glacial maximum to the present
How?
- Increasing temperatures result in increase in water vapour in the atmosphere, which causes an increase in the quantum of rainfall.
- Concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere going up, resulting in more water vapour, rainfall is expected to increase in the next 100 years.
Karnataka and 9 other states accounts for 65% of TB cases
Part of: GS Prelims –Sci & Tech and GS-II- Health
In news:
- Assam, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal are States where TB cases are high.
- The Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare takes measures in these States to eliminate TB by 2025 ahead of the Sustainable Development Goals target year of 2030.
IASbaba’s Value addition:
Tuberculosis:
World Health Organization (WHO) has recently released 2019 Global Tuberculosis (TB) Report.
- TB remains the top infectious killer in the world claiming over 4,000 lives a day.
- Eight countries that accounted for two thirds of the global total include India (27%), China (9%) and Indonesia (8%).
- India (27%), China (9%) and Indonesia (8%) are in WHO’s list of 30 high TB burden countries that accounted for 87% of the world’s cases in 2018.
WHO End TB Strategy:
- Aims to end the global TB epidemic, with targets to reduce TB deaths by 95% cut new cases by 90% between 2015 and 2035, sets interim milestones for 2020, 2025, and 2030.
India:
- The Government has set a target of Zero-Tuberculosis deaths by the year 2025.
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has launched the National Strategic Plan for TB Elimination in 2017.
National Strategic Plan (NSP) for TB Elimination :
- VISION: TB-Free India with zero deaths, disease and poverty due to tuberculosis.
- GOAL: To achieve a rapid decline in the burden of TB, morbidity and mortality while working towards the elimination of TB in India by 2025.
- PILLARS : Detect – Treat – Prevent – Build [DTPB]
Tuberculosis:
- Tuberculosis is a contagious airborne disease, which can be acquired from close contact with an infected person.
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
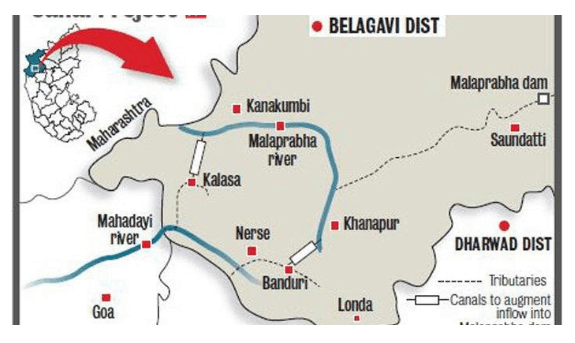
Mahadayi project cost skyrockets by 1,674% since inception
Part of: GS Prelims –Polity and GS-II- river dispute
In news:
- Kalasa-Banduri Nala project in the Mahadayi basin drags on over the inter-State river water dispute, the cost over the last 20 years has risen steeply from about ₹94 crore in 2000 to ₹1,677.30 crore now.
From Prelims Point Of View
Kalasa-Banduri Nala Project
- Undertaken by the Government of Karnataka to improve drinking water supply to the three districts of Belagavi, Dharwad, and Gadag.
- Involves building across Kalasa and Banduri, two tributaries of the Mahadayi river to divert water to the Malaprabha river.
- Malaprabha river supplies the drinking water to Dharwad, Belgaum, and Gadag districts.
- The Mahadayi Water Disputes Tribunal was set up in 2010. Goa, Karnataka and Maharashtra
Mahadayi :
- The west-flowing river
- originates in Bhimgad Wildlife Sanctuary (Western Ghats), Belagavi Karnataka.
- Called as Mandovi in Goa.
- Joined by a number of streams to form the Mandovi which is one of two major rivers (the other one is Zuari river) that flows through Goa.
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 25th February 2020
ASI planning barricade around famed stone chariot at Hampi
Part of: GS Prelims –Art & culture and GS-I- Heritage
In news:
- Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is contemplating installing a wooden barricade around the stone chariot inside Vittala Temple complex at the UNESCO World Heritage site of Hampi in a bid to protect it from vandalism.
From Prelims Point Of View
Hampi :
- UNESCO world heritage site.
- Part of the Mauryan Empire 3rd century BC.
- The capital city during the four different dynasties in the Vijayanagar city
- It is located near the Tungabhadra river.
- Hampi-Vijayanagara was the world’s second-largest medieval-era city after Beijing,
- Described by UNESCO as an “austere, grandiose site” of more than 1,600 surviving remains of the last great Hindu kingdom in South India.
Income scheme to cover fewer farmers
Part of: GS Prelims –Polity and GS-II- Policies
In news:
- One year after the launch of the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi, the Centre has revised the farmer income support scheme’s beneficiary target down to just under 12 crore from 14 crore
From Prelims Point Of View
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi
- Under this programme, vulnerable landholding farmer families, having cultivable land upto 2 hectares, will be provided direct income support at the rate of Rs. 6,000 per year.
- This income support will be transferred directly into the bank accounts of beneficiary farmers, in three equal installments of Rs. 2,000 each.
- Expenditure : Rs 75000 crore for the scheme will borne by the Union Government in 2019-20.
(MAINS FOCUS)
Environment
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
Human-wildlife conflict
Context
Death of four tigers in Mhadei, Goa, and the arrest of the locals who poisoned the animals after their complaints were not attended by forest authorities
As a result, CM of Goa stated to demarcate and fence the borders of the wildlife sanctuaries in order to end 80 per cent of the problem. Although the intentions are good, this isn’t a solution.
Some examples of human-wildlife conflict include:
- Predation on livestock or domestic animals by wild animals
- Damage to crops and fences
- Wildlife strewing about residential garbage
- Vehicle/wildlife collisions, aircraft/bird collisions
- Damage caused by squirrels or bats to fruit and fruit trees
- Bird nesting in undesirable residential locations
Reasons for man-animal conflict:
- Expansion of human settlements into forests – expansion of cities, industrial areas, railway/road infrastructure, tourism etc.
- Allowing livestock to graze in forest areas
- Land use transformations such as change from protected forest patches to agricultural and horticultural lands and monoculture plantations are further destroying the habitats of wildlife.
- Unscientific structures and practices of forest management in the country
- Infestation of wildlife habitat by invasive exotic weeds leads to decreased availability of edible grasses for wild herbivores
- Decreased prey base caused by poaching of herbivores has also resulted in carnivores moving out of forests in search of prey and to indulge in cattle lifting.
India’s Conservation culture
- Despite a billion people India still has most of our large wildlife species- India today has the largest population of the tiger, Asian elephant, leopard, sloth bear, gaur and many others
- Part of Culture: People have accepted coexistence of human & animals, and incorporated it in our culture. All our deities have animals associated with them; it shows the inclusion of these animals in our mind space.
- The Velip community in Goa worship the tigers and this practice is done even today.
- Animals are viewed also as renewable resource: Unlike activities such as mining, tigers are a renewable resource. They are always going to be there, and so will the rivers and the forests, giving the local people income and development — as long as there are tigers.
Fencing is not the solution but alternative measures like:
- Inclusion of local community in forest wildlife management
- To ensure that money which comes in through tourism (of Tiger reserves) should be used for the development of the local villages as has been done in Tadoba tiger reserve, Maharashtra
- Also, compensation procedures need to be improved- In Maharashtra, a decade ago, the compensation amount was poor, and the process was cumbersome as well as time consuming. Today, a helpline has been established, compensation rates have increased vastly, and the process is under the Right to Services Act
Conclusion
The solutions are simple: Inclusive development with a long-term vision that cares for the environment. We need to involve local communities who will be the custodians of the tigers and tigers who can, in turn, provide the communities much-needed development in such remote areas.
Did You know about these Innovative practices to minimise man-animal conflicts ?
- In the Western Ghats of India, a new conservation initiative has utilized texting as an early warning system to prevent human-elephant encounters. Elephant tracking collars embedded with SMS chips automatically text nearby residents, warning them of recent elephant movements.
- In Canada, authorities have constructed wildlife corridors, areas of preserved native habitat in human dominated regions, providing wildlife with a safe pathway as they travel between one to another.
- To keep elephants at a safe distance from their farms and homes, some African villagers have turned to two unlikely, all-natural solutions: bees and hot peppers. Elephants dislike the chemical capsaicin found in chili peppers, prompting farmers in Tanzania to smother their fences with a mixture of oil and chili peppers.
Governance
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Statutory, regulatory and various quasi-judicial bodies.
Personal Data Protection (PDP) Bill, 2019 – Part I
The bill was introduction of in Lok Sabha during the winter session of Parliament. The Bill was referred to a joint parliamentary committee, which is currently engaged in a process of public consultation.
The draft law is a comprehensive piece of legislation that seeks to give individuals greater control over how their personal data is collected, stored and used.
The Bill also establishes a Data Protection Authority for the same.
Some of the other features of the bill are:
Applicability: The Bill governs the processing of personal data by: (i) government, (ii) companies incorporated in India, and (iii) foreign companies dealing with personal data of individuals in India.
Obligations of data fiduciary:
- Personal data can be processed only for specific, clear and lawful purpose.
- All data fiduciaries must undertake transparency & accountability measures such as:
- Implementing security safeguards (such as data encryption and preventing misuse of data), and
- Instituting grievance redressal mechanisms to address complaints of individuals.
- Institute mechanisms for age verification and parental consent when processing sensitive personal data of children.
Rights of the individual: This includes Right to
- Obtain confirmation from the fiduciary on whether their personal data has been processed
- Seek correction of inaccurate, incomplete, or out-of-date personal data
- Restrict continuing disclosure of their personal data by a fiduciary
Grounds for processing personal data
- Data Processing only if consent is provided by the individual.
- However, in certain circumstances, personal data can be processed without consent. These include:
- If required by the State for providing benefits to the individual
- Legal proceedings
- To respond to a medical emergency.
Social media intermediaries:
- The Bill defines these to include intermediaries which enable online interaction between users and allow for sharing of information.
- All such intermediaries which have users above a notified threshold, and whose actions can impact electoral democracy or public order, have certain obligations, which include providing a voluntary user verification mechanism for users in India.
Transfer of data outside India:
- Sensitive personal data may be transferred outside India for processing if explicitly consented to by the individual, and subject to certain additional conditions.
- However, such sensitive personal data should continue to be stored in India.
- Certain personal data notified as critical personal data by the government can only be processed in India.
Sharing of non-personal data with government:
- The central government may direct data fiduciaries to provide it with any non-personal data and anonymised personal data (where it is not possible to identify data principal) for better targeting of services.
Exemptions: The central government can exempt any of its agencies from the provisions of the Act in interest of security of state, public order, sovereignty and integrity of India and friendly relations with foreign states,
Amendments to other laws: The Bill amends the Information Technology Act, 2000 to delete the provisions related to compensation payable by companies for failure to protect personal data.
Part –II – Will cover the criticism of the bill with focus on data localisation
Connecting the dots
- Justice B.N.Srikrishna Committee report
- EU data regulations
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q 1. For short-term climatic predictions, which one of the following events, detected in the last decade, is associated with occasional weak monsoon rains in the Indian sub-continent?
- La Nina
- Movement of Jet Stream
- El Nino and Southern Oscillations
- Greenhouse effect at global level
Q 2. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), the disease which causes the death of the largest number of people today is
- AIDS
- Tuberculosis
- Malaria
- Ebola
Q 3. Which one of the following antimicrobial drugs, is suitable for treatment of both tuberculosis and leprosy?
- Isoniazid
- P-aminosalicylic acid
- Streptomycin
- Rifampicin
Q 4. Where is the famous Vijaya Vittala temple having its carved pillars emitting musical notes and Virupaksha temple located?
- Belur
- Bhadrachalam
- Hampi
- Srirangam
Must Read
About Syria’s Civil War :
About Judiciary :
About Sri Lanka refugees:
About Trumps Visit and Indo-US relationship:














