IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis, IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Feb 2016, Science and Technology, UPSC
Archives
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs – 22th February, 2016
ECONOMICS
TOPIC: General studies 2:
- Separation of powers between various organs dispute redressal mechanisms and institutions
- Statutory, Regulatory and various quasi-judicial bodies
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
For a Robust Competition Law- Competition Commission of India (CCI)
Let us talk about insights on measures to make the competition law more effective—
- Upgrading of the institutional capacity-
- The foremost challenge for the fair-trade regulator is the upgradation of its institutional capacity, as it takes five to six years for the regulator to mature
- Since 2009, the commission has handled 688 anti-trust cases, and around 370 combination matters; while cracking down on cases of cartelisation (in the case of cement and airlines companies) as well as abuse of market power (those involving NSE, DLF, Coal India)—the commission has imposed fines worth around of Rs 14,000 crore over the past seven years, the actual recovery has barely been around one per cent
- Manpower Crunch:
- In 2014, according to the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, the nodal ministry for CCI, the regulator and Director General (DG)’s office had the strength of 84 and 19, as against the sanctioned posts of 156 and 41, respectively
- This shortage is more acutely felt at DG’s office – the investigating arm of the commission, with each officer handling 10-15 cases encompassing different sectors, all at once. As a result, there is a huge backlog of cases with it.
- Absence of institutional memory: Few permanent staff with most officers investigating a case being on deputation for three years
Need for the Ministry to comprehensively review the recruitment rules—
- Recruit or engage domain experts/professionals on a contractual basis with a view to professionalising the working of the commission and its offices
- Employ stricter screening process
2. Need for a strong, effective leniency programme
- Cartels are most damaging to consumers and poor evidence collected leads to poor enforcement of directives most of the time. Therefore, in order to ensure an effective anti-cartel regime, it is essential to have a strong and robust leniency programme.
- There is a case of not only unpredictability and non-incentivisation of the whistle-blowers but also the identity of the whistle-blower not being kept protected.
- EU- All cartel decisions have emanated from leniency applications; its advantage being provision of accurate evidence and ensuring a finding of breach. Therefore the CCI must revisit its leniency programme and follow international best practices.
- Huge number of cases has been set aside by the Competition Appellate Tribunal (COMPAT) for a failure by the CCI to adhere to basic natural justice norms and therefore, the CCI must not resort to short cuts disregarding the rights of the defence and should exercise their rights lawfully.
- Need to—
- The CCI must entertain only those cases where there is a clear competition law violation
- Introduction of additional exemption to help weed out harmless transactions
3. Strike a balance between regulator and judicial forum
- Set up in 2003, the commission could not commence enforcement till several years later due to a combination of—
- Constitutional challenges in the higher courts,
- Prolonged process of amendments to the Competition Act, and
- Delay in the notification of its powers by the government
- The commission too has to step back and review its journey— Some slippages:
- Not following the correct procedure for cross-examination,
- Not giving proper opportunity to a guilty party to defend and
- Lapses in the hearing of arguments
- A two-way path that needs to be addressed—
Commission- Introspect on remedial measures it needs in its procedures
Judiciary- Reflect on whether all the minute processes and rules of evidence that apply to courts must equally apply to the commission, which is a regulator, and not a judicial forum
A balance needs to be struck between the interests of the parties, and the broader interests of India’s markets and consumers
4. Eliminate ad hoc ways and consistently issue well-reasoned orders
- It is time for the CCI to focus more critically on its procedures and rights of the defence to lay the foundation of a strong and robust competition law regime; failure to do so will result in
- Significant decisions being reversed
- Hurting the international reputation of the CCI as a fair and just regulator
- Giving rise to a waste of valuable resources and time
- To achieve greater efficiency in the Director General’s (DG) Office, the CCI should adopt a two-fold approach –
- Enhance the capacities of the staff members by imparting adequate training, inter alia, relating to the rules of cross-examination
- Lay down well-defined rules and parameters for conducting ‘dawn raids’ (unannounced or surprise raids)
Plus—
- Improve their evaluation of circumstantial evidence
- Improve their assessment of the conduct of alleged violators
- Improvement in analysis of practices and framework under operation
- CCI must reject complaints that are in fact consumer matters and breach of contract issues, but are introduced to the CCI under the garb of competition infringement simply to get around the protracted nature of civil litigation (Real Estate Sector)
- Re-think the role of the competition laws in the overlap between IP laws and competition laws
Connecting the Dots:
- For achieving the desired objectives, it is necessary to ensure that the regulatory institutions remain independent and autonomous. Discuss in the light of experiences in recent past (specifically w.r.t. the CCI-India).
(Mains,2015)
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
TOPIC: General studies 3:
- Science and Technology – developments and their applications and effects in everyday life Achievements of Indians in science & technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
- Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nano-technology, bio-technology and issues relating to intellectual property rights.
Public Good named Life science
- Advances in scientific research, particularly in the fields of medicine and pharmaceuticals, have the power to transform our life into a ‘quality’ life and helps address some of the emerging health challenges in the changing global scenario.
- The present life sciences sector is working on building upon its understanding of the disease at the cellular and genetic level to usher in new and differentiated therapies into the market.
- Therefore, investing in science and innovation becomes directly proportional to a stronger and fairer economic future and hence, biomedical advances are likely to transform global health with early diagnosis and therapeutic intervention for chronic and killer diseases (autoimmune diseases and cancer)
Scientific developments to look out for—
Immuno-Oncology (I-O):
- “Immuno” refers to our immune system and (I-O) uses drugs known as immune-therapies that target your body’s immune system to help fight cancer. In simple terms, it uses the body’s immune system to help fight cancer
- While ‘chemotherapy’ and ‘Radiation therapy’ exits and is widely the most used method, it might as well harm some good tissues/cells in the process.
- With (I-O) the immune system is enriched in a way that it can itself weed out the malignant tissue—by identifying and selectively attacking the cancer cells and thus, providing a long lasting memory to the immune system
- PD-1 (programmed death-1) and PDL-1 (programmed death ligand-1) targeting antibodies and Chimeric antigen receptor T-cells (CART), have demonstrated how technology can be leveraged for developing path-breaking therapies in immuno-oncology
- Recently, the US Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) approved a drug that relies on a genetically-engineered version of the herpes virus to kill cancer cells and stimulate immune response against malignant tumours in skin cancer patients.
- Several other immune-stimulating viral therapies are also being evaluated
Eg: A genetically-modified polio virus to fight brain cancer and a re-engineered common cold virus for treating a form of bladder cancer
3D Bioprinting & Stem Cell Therapy:
- Additive manufacturing i.e., three-dimensional (3D) printing has been driving major innovations in and Stem cell therapy is providing new hope in not only curing a number of debilitating diseases but also building organs under laboratory conditions for patients.
- Thus, these therapies are redefining treatments (potential to save lives) by being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation
- According to a recent report, “Applications of 3D Printing 2014-2024: Forecasts, Markets, Players,” “The global 3D printing market will reach at least $7 billion by 2025, which includes a conservative estimate of $3 billion for bioprinting.”
- Some of its usages- generation and transplantation of several tissues, including multi-layered skin, bone, vascular grafts, tracheal splints, heart tissue and cartilaginous structures as well as in applications including the development of high-throughput 3D-bioprinted tissue models for research, drug discovery and toxicology
Progress:
- Therapeutic Goods Administration, Australia gave its first go-ahead to human studies for a revolutionary stem cell therapy aimed at halting/reversing the progression of Parkinson’s disease, which affects up to 10 million people worldwide.
- Scientists in Australia have also achieved a medical breakthrough of getting stem cells to form different cell types found in the kidney.
- In Bengaluru– a tissue engineering start-up has made India’s first artificial human liver tissue with the help of 3D printing technology, using 10 million liver cells.
Biomarkers & companion diagnostics:
- Biomarkers are useful in providing biological data which in turn helps predicting drug failures before expensive clinical trials.
- Also, allows scientists to identify patient pools that would respond favourably to a particular drug
- Led to the emergence of companion diagnostics, which screen patients for biomarkers that gauge the safety and efficacy of a particular treatment
- USFDA—Approved
- The first companion diagnostic to detect a protein associated with non-small cell lung cancer
- Merck’s Keytruda drug for the disease
Companion diagnostic:
- Enables doctors to determine whether patients have high enough levels of the PD-L1 biomarker for Keytruda to be effective
- Today- More sophisticated companion diagnostics are being developed to assess a patient for multiple biomarkers related to multiple drugs.
Genomic Sequencing:
Sequencing a person’s genome:
- Doctors need to collect less than a teaspoon of blood or saliva
- Chemicals are then used on this sample to break open the cell membranes and gather the DNA that had been housed inside them
- Enzymes strip away surrounding proteins to isolate a clump of tiny, whitish strands of DNA and that genetic material is placed in sophisticated machines that “read” each of the 3 billion base pairs that make up a person’s genetic code.
Initiatives-
- US-based medical geneticist Robert Green’s MedSeq project, are looking at ways in which the profusion of genomics data and other clinical information can be integrated with day-to-day medical practice in order to assist the medical fraternity in determining a specific line of treatment for their patients
- It is being combined with molecular diagnostics, imaging and data analytics to decipher the cellular structure of malignant tumours and tailoring treatment regimen
Biosimilars:
- Help in the provisioning of affordable access to complex biologics in the coming year—
Less costly imitations of drugs known as biologics, which are used to treat a range of diseases including cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, and anemia (not exact copies)
- 1st USFDA approval for a biosimilar- Granted to Filgrastim in 2015
- A highly regulated market exists for the entry of biosimilars and encouraging developments will allow speedier entry of biosimilars
- With $48 billion worth of patents, slated to expire soon, the global biosimilars market can very well be prepared for massive development
- India— Ready to play a significant role in the biosimilars area where companies like Biocon, Dr Reddy’s, Intas, ZydusCadila and others are engaged in developing high quality biosimilars to provide affordable access to these complex biologics
- Indian access to biosimilars- Insulins, Analogs, Filgrastim etc. since early 2000s and more recently complex antibodies like Trastuzumab, Rituximab, Adalimumab etc.
- Will help augment the capitalisation of Indian players on this unfolding global opportunity
IASbaba’s Views:
The extraordinary times require revolutionizing technology to pave way for better access to the progress made and made possible to/by life sciences. These innovative therapies that are acting like a boon to address the unmet patient needs to be worked upon more and research and development in this field be stepped up for the future of mankind.
MUST READ
To grow or not to grow
Gandhi and Ambedkar, a false debate
Unreasonable demands
Unemployment down in urban centres, but persists in rural areas, says survey
Give Soldiers Their Due- The armed forces should have a separate pay commission.
Apple-FBI stand-off: It’s privacy vs security
Ficci calls for reforms through executive action-The proposed reforms are spread across exports, taxation, and crucial sectors
Modi identifies 2nd village to develop; colleagues far behind-Under the Saansad Adarsh Gram Yojana, each MP has to develop one model village in their constituency by 2016 and two more by 2019
PM Modi launches Rurban Mission from Chhattisgarh- Expects to attract Rs 5,000-cr investment in next three years to give villages an urban look
India ranks 54th in internal policy support to global innovation-The report found a strong correlation between countries’ contributions to global innovation and their levels of domestic innovation success
MIND MAPS
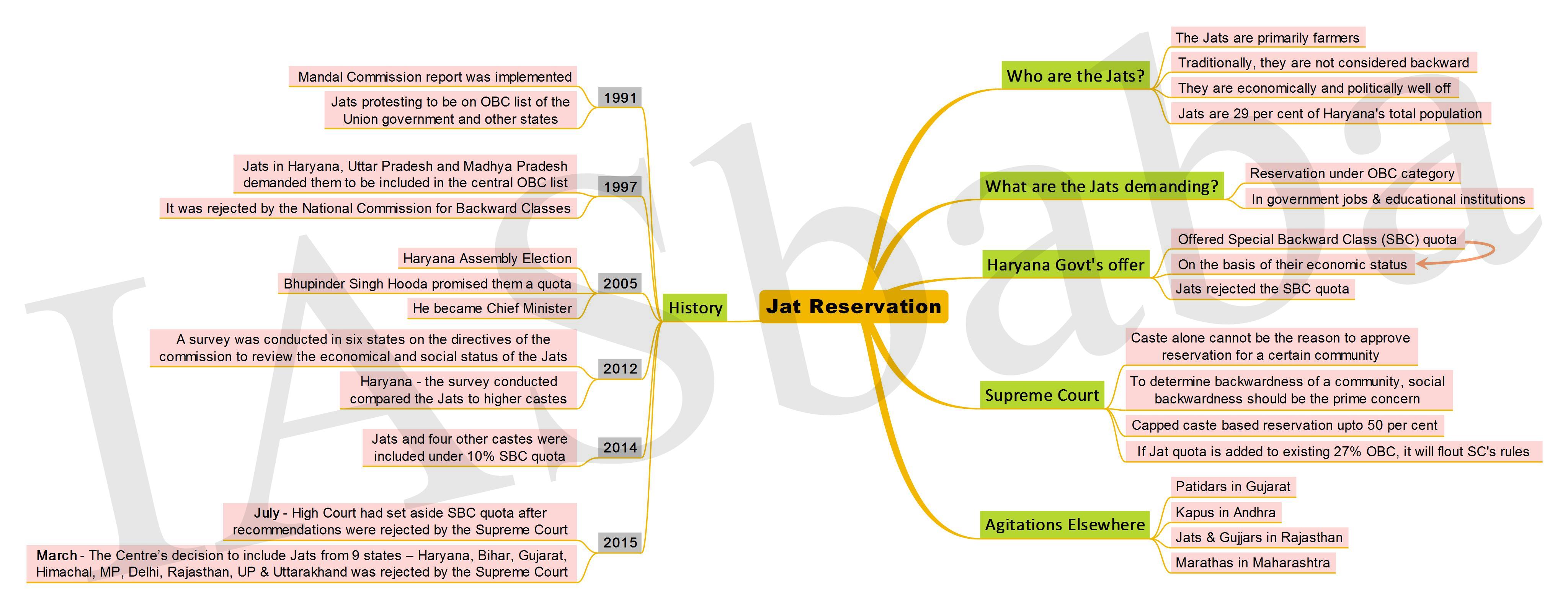
1. Jat Reservation