IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs (Prelims + Mains
Focus)- 30th July 2018
Archives
(PRELIMS+MAINS FOCUS)
‘ISRO-like’ ocean mission planned
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains III – Science and Technology; Geography
In news:
- Centre draws up a five-year, ₹8,000 crore plan to explore the deep recesses of the ocean.
- The Union Earth Sciences Ministry unveiled a blueprint of the ‘Deep Ocean Mission (DOM)’.
- The mission proposes to explore the deep ocean, similar to the space exploration started by ISRO about 35 years ago.
Proposed key deliverables to achieve these goals –
- Establish an offshore desalination plant that will work with tidal energy
- Developing a submersible vehicle that can go to a depth of at least 6,000 metres
- The focus will be on technologies for deep-sea mining, underwater vehicles, underwater robotics and ocean climate change advisory services, among other aspects.
Do you know?
- India has been allotted a site of 1,50,000 sq. km in the Central Indian Ocean Basin (CIOB) by the UN International Sea Bed Authority for exploitation of polymetallic nodules (PMN).
- These are rocks scattered on the seabed containing iron, manganese, nickel and cobalt.
- It is envisaged that 10% of recovery of that large reserve can meet the energy requirement of India for the next 100 years.
- It has been estimated that 380 million metric tonnes of polymetallic nodules are available at the bottom of the seas in the Central Indian Ocean
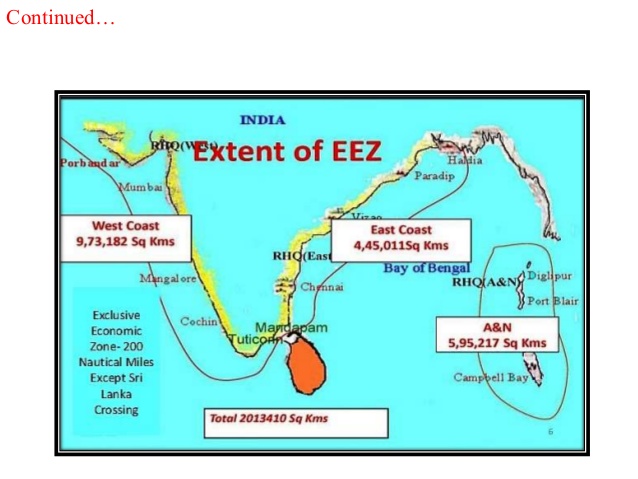
- India’s Exclusive Economic Zone spreads over 2.2 million sq. km and in the deep sea, lies “unexplored and unutilised.”
Important value addition:
- Article 297 – Things of value within territorial waters or continental shelf and resources of the exclusive economic zone to vest in the Union
- India was the first country in the world to have been given the Pioneer Area for exploration of deep-sea mineral viz. Polymetallic nodules in the Central Indian Ocean Basin in 1987.
India’s Exclusive Economic Zone
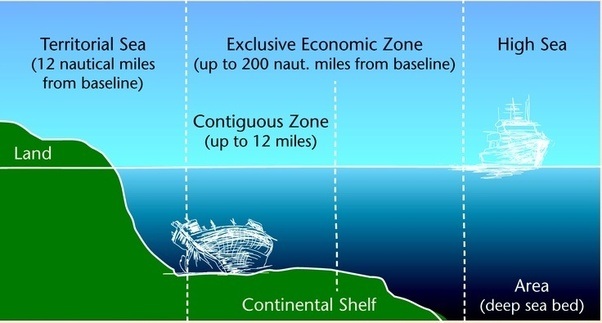
Pic: https://qph.fs.quoracdn.net/main-qimg-ff0cc396558c51551ba5f544383a2499-c
National Register of Citizens
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II and III – Welfare and Social issue; Internal Security
About NRC
- It is the register containing names of Indian Citizens. It was prepared first in 1951 after the conduct of the Census of 1951.
- It is used to identify who is a bona fide Indian citizen and those who fail to enlist in the register will be deemed illegal migrants.
Why is the National Register of Citizens (NRC) is being updated in Assam?
- The demands to update the NRC of 1951 were first raised by the All Assam Students’ Union (AASU) and Assam Gana Parishad more than three decades ago.
- Since 1950s, there is lot of controversy regarding migration and citizenship issues. Original inhabitants of Assam always fear that migrants from Bangladesh would compete them with jobs, land and eventually hamper their culture.
- Therefore, in 1970s, All Assam Students’ Union spearheaded a massive drive, popularly known as the Assam Agitation calling for the detection, deletion and deportation of illegal Bangladeshi migrants.
- However, for a very long time, the provisions in the Assam accord were not implemented.
- In 2013, the Supreme Court finally ordered to complete the exercise by December 31, 2017, leading to the present updation of NRC in Assam.
National Advanced Surface-to-Air Missile System (NASAMS)
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains III – Defence and Security
In news:
- India plans to procure missile shield from U.S.
- India is in talks with the U.S. to procure an advanced air defence system, called National Advanced Surface-to-Air Missile System-II (NASAMS-II)
- It will be used to defend the National Capital Region (NCR) from aerial attacks.
Fast recap:
- NASAMS system will complement other systems such as the medium and long-range surface-to-air missile (SAM) systems under procurement.
- India is also in an advanced stage of talks with Russia for the procurement of very long range S-400 air defence systems.
- Apart from these imports, India is also developing an indigenous Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) system.
(MAINS FOCUS)
NATIONAL
TOPIC: General studies 2 and 3
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Social issue
- Role of external state and non-state actors in creating challenges to internal security.
- Challenges to internal security through communication networks.
Death Penalty is no solution
Introduction:
Remember the Supreme Court’s recent order on mob lynching?
- On July 17, a Supreme Court bench termed incidents of mob-lynching in India as ‘horrendous acts of mobocracy’
- It directed the Parliament to draft a new legislation to effectively deal with incidents of mob lynching.
- The apex court also directed the police to register an FIR under Section 153A of the IPC and do everything in their power to ensure that social order was maintained.
The judgment endorses the belief that “it is the fear of law that prevents crimes”. However, effective policing of mob violence may not be the only cause for failure.
Is Death penalty a solution?
The political class has recently shown increasing liking or affinity for the death penalty.
- Earlier this month, Punjab Chief Minister suggested the death penalty for first-time drug offenders.
- In 2016, the Nitish Kumar government in Bihar introduced the death penalty for illicit liquor trade without any evidence to suggest its efficacy.
- This year, BJP MP Subramanian Swamy moved, and then withdrew, a private member’s Bill in the Rajya Sabha for death penalty for cow slaughter.
- More prominently, a Presidential ordinance was introduced by the Union government to impose the death penalty for the rape of girls under 12 years of age.
In doing so, our political class has opted too often in the recent past to declare certain categories of criminals worth eliminating.
Unfortunately, courts have often joined the chorus and actively sought and encouraged harsher punishments.
Death penalty is not the answer
- In January, the Uttarakhand High Court recommended that the State introduce the death penalty for cases of child rape.
- The courts have in the recent past showcased language with helpless frustration. ‘Monstrous,’ ‘beastly,’ ‘diabolical’ and ‘unfathomable’ have been used to refer to offenders.
Such language is then read and highlighted across media, feeding the public with an idea that – violence is the only means of justice.
Judicially expressed disgust does not aid in understanding crime, or preventing its recurrence.
Do you know?
- 2013 Justice Verma Committee restrained to recommend death penalty for rape.
- Law Commission recommended restricting the death penalty only to crimes against the state.
It should not be forgotten that the death penalty has never been a deterrent against any sort of crime.
There is little empirical evidence to show that those about to commit a capital offence would stop themselves merely out of the fear of being hanged. Further, there is a legitimate concern that the country’s judicial system has not been consistent in awarding the death penalty.
Lengthy prison sentences, constituting both well-deserved consequences for grave crimes and a life-long opportunity for penitence, will adequately meet the ends of justice.
The court must resist being the avenger for society in favour of nurturing a culture where justice and retribution are not the same.
The way ahead:
India’s growing violence culture can be best reversed by enhancing conviction rates through reforms in the police and judicial systems.
Need of the hour: greater allocation of state resources towards the setting up of fast-track courts; more one-stop crisis centres; proper witness protection; more expansive compensation for rape survivors, and an overhaul of existing child protection services.
There is no question that the country deserves much better legal protection, but the death penalty is not the answer.
Connecting the dots
- With more than 150 countries abolishing death penalty, is there a stressing demand in India to abolish death penalty. Critically analyse.
- Violence can breed justice as well as injustice. Elucidate.
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
TOPIC: General Studies 2
- India and its international relations
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Keeping friends close: India Iran Relations
In a recent interview, former Vice-President Hamid Ansari said –
- India’s relationship with Iran has been built carefully by all past governments as Iran for us is not just an energy supplier… For us, Iran is a land power on the other side of Pakistan that provides us with an alternative route to Afghanistan.
India-Iran relations:
For India, relations with Iran have a domestic political dimension. As the largest Shia country and home to some of the holiest shrines of the Shia community, Iran remains influential among India’s large Shia population.
India and Iran have always shared deep social, cultural, economic and political connections and relations that have enriched both civilizations. The use of the Persian language at the Mughal courts is just one example of Iranian cultural influence in north India. A growing number of Iranian students are enrolled at universities in India, most notably in Pune and Bengaluru.
It is noteworthy that Iran was one of the first countries with which India signed a Friendship Treaty in March 1950.
Significance of India-Iran relations
- Energy and to decrease the dependence on Saudi for oil
- Chabahar port
- Role in Afghanistan and Iran-Afghan railway link connectivity
- Geopolitical and strategic position etc
Recent developments:
The US has told India and other countries to cut oil imports from Iran to “zero” by November 4 or face sanctions.
U.S. Ambassador to the UN, Nikki Haley has threatened India to drastically reduce its energy imports from Iran by November 4 or else India would be subject to American sanctions.
US threat is in direct conflict with India’s strategic interests in the region and an insult to Indian sovereignty.
Recently, India-Iran relations have improved considerably because of growing energy and trade dependency and greater recognition on both sides of the conjunction of strategic interests. India should not allow relations with a potential regional ally to be disrupted by empty American threats.
Connecting the dots
- What should be India’s approach to Iran keeping in mind the recalibrated stance of the US in the region? Discuss.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1) Deep Ocean Mission to spur research activities in ocean science and develop technology to harness ocean resources was launched by –
- Ministry of Earth Sciences
- Ministry of Marine Affairs and Fisheries
- Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources
- Ministry of Ocean Development and Resources
Q.2) Consider the following statements with reference to International Seabed Authority (ISA)
- It has been established under the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- The authority is formed only for regulating all mineral-related activities in the international seabed.
- U.S.A. is the only major maritime power that is not its member.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding different maritime boundaries under United Nations Convention on the Law of the Seas (UNCLOS):
- The territorial boundary of a country exists up to 12 km from the edge of a continent.
- Up to 24 nautical mile from the coast the zone is called Contiguous Zone.
- From the edge of the coast to 200 nautical mile, the zone is called Special Economic Zone.
Which of the above statements are NOT correct?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Q.4) The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) is a nuclear agreement between
- India and USA
- China and Japan
- Iran and P5 +1
- India and Australia
Q.5) Caspian Sea is bordered by
- Iran
- Uzbekistan
- Armenia
- Georgia
Select the correct code:
- Only 1
- 1 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
- 2 and 4
MUST READ
Layers of protection: on changes in anti-corruption law
God cannot be privatised
The dwindling minority
Sins of commission
Borders For Doctors
Courts of injustice














