IASbaba Prelims 60 Days Plan
ARCHIVES
Hello Friends,
The most beloved 60 Days for UPSC IAS Prelims 2019 has finally begun 🙂
Once again the time has come for the battle (Prelims). And who else than your best companion in the last preparatory phase for UPSC IAS Prelims 2019 i.e 60 days plan.
It does not matter how slowly you go as long as you do not stop.
Hope the message given above makes sense to you all.
The productive utilization of this programme demands consistency, honesty, faith and strong determination to be in the process of learning and unlearning. You might not be fully prepared to solve all the questions but the learning and unlearning through these questions will prepare you for the real battle on 2nd June 2019.
You have to unlearn your repetitive mistakes, gut feeling on which you mark doubtful questions. You have to learn new things and also those concepts that you were very sure of but somehow because of traps in the option, got it wrong. You have to learn ‘how to convert knowledge into marks’ (Because most of the times, after ending the exam, you regret making mistakes in known concepts).
Secondly, keep a long distance from following too many things at this point. It will always backfire. Once you are here, put complete faith and follow this initiative along with whatever you were doing. It is very important to consolidate your preparation with many revisions. Simply following many things will leave you in despair. You can cross check this with veterans.
Everything that seems attractive is not productive. You should always go for productivity. Be wise!
Let us pledge to make it a big game changer (better than last year) in the next 60 days of this plan!
Importance of Self – Tracking: Learning from Last Year
Last year, aspirants used to type/post their answers in the comment box on a daily basis. There were huge participation and discussion below the test post. Putting answers in the comment box has been very effective to self-track yourself after updating the score. In the end, you can cross check your performance through Disqus profile.
It was highly effective in the last edition of 60 Days that propelled aspirants to monitor their performance and learn through discussion. Let you solve these questions with full honesty and write your result in the comment box. Interact with peers to know your mistakes.
The importance of this initiative stands time-bound and aggressive reverse engineering to learn the concepts. Many of you must be busy with your own strategy but let us tell you honestly that in the last few months, it is very important to revise and consolidate your learning. Just reading won’t suffice.
So, take out a few hours from your schedule and make it a revision exercise.
How can you make the best use of it?
Be honest to your effort and do not start competing with XYZ aspirants just for the sake of marks. It is more important for you to introspect and check your learning than focusing on others. Try to answer the questions in 25 minutes only.
Do not get into negative feeling that I don’t have enough knowledge to answer these questions. Feel like you are taking the real exam. What would be your response then?
The same will be replicated in the UPSC exam. Here, you get marks only and nothing else matters. So, make effort to know the answers to all questions. Do not cheat 😛
DETAILED MICRO ANALYSIS MATRIX SAMPLE– is given here. You can download this and do an assessment for yourself (the excel sheet must be modified as per this years planning. The provided excel sheet is only for reference). DOWNLOAD
- You can copy paste the same format/modify as per your need in Google Spreadsheet and update it on daily basis.
- Feedback talks about daily test results.
- Follow-up talks about daily target achieved from sources and the number of revisions to do/done and dates. Sources column is to ensure that aspirants do not run behind various sources and follow the same throughout.
Would like to end on this quote:
Either you run the day or the day runs you.
Are you ready? Let’s start!
Important Note
- Don’t forget to post your marks in the comment section. Also, let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- You can post your comments in the given format
- (1) Your Score
- (2) Matrix Meter
- (3) New Learning from the Test
Test-summary
0 of 30 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
Information
The following Test is based on the syllabus of 60 Days Plan-2019 for UPSC IAS Prelims 2019.
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 30 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 30
1. Question
In the context of the Indian history, ‘cartaz’ system refers to?
Correct
- Portuguese Cartaz system referred to a naval trade license or pass issued by the Portuguese in Indian Ocean during the sixteenth century.
- A similar system used by British was navicert system in 20th century.
Incorrect
- Portuguese Cartaz system referred to a naval trade license or pass issued by the Portuguese in Indian Ocean during the sixteenth century.
- A similar system used by British was navicert system in 20th century.
-
Question 2 of 30
2. Question
Consider the following statements
- Serampore Mission was founded by William Carey, and it is the India’s first Christian missionary organization.
- Serampore Trio worked many years for the upliftment of Bengal society in educational, social and religious movement.
- The first Catholic Church was built in serampore 1800.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Correct
- William Carey the founder of Serampore Mission has been called the patriarch, apostle, prophet, and pioneer of modern missionary movement.
- Serampore Mission (1800-1845) India’s First Christianity Missionary Organization. William carey and his associates established two the mission on 10 January 1800
- First Catholic church Bandel(West Bengal) 1599
- First protestant Church Serampore ( West Bengal) 1800
- William Carey started his ministry in Bengal with Joshua Marshman and William ward which is called as the Serampore Trio and they worked many years upliftment of Bengal society in educational, social and religious movement
Incorrect
- William Carey the founder of Serampore Mission has been called the patriarch, apostle, prophet, and pioneer of modern missionary movement.
- Serampore Mission (1800-1845) India’s First Christianity Missionary Organization. William carey and his associates established two the mission on 10 January 1800
- First Catholic church Bandel(West Bengal) 1599
- First protestant Church Serampore ( West Bengal) 1800
- William Carey started his ministry in Bengal with Joshua Marshman and William ward which is called as the Serampore Trio and they worked many years upliftment of Bengal society in educational, social and religious movement
-
Question 3 of 30
3. Question
Consider the Following statement about the Mahalwari System?
- It was introduced in Central provinces, NWFP, Agra, and Punjab
- It was introduced by William Bentick.
- It declares 10/11 for the British and 1/11 as the revenue for farmers
- It made village committee as the responsible for collection of taxes
Which of the above statements are correct?
Correct
- Mahalwari system was introduced in 1833 during the period of William Bentick.
- It was introduced in Central Province, North-West Frontier, Agra, Punjab, Gangetic Valley, etc of British India.
- The Mahalwari system had many provisions of both the Zamindari System and Ryotwari System.
- In this system, the land was divided into Mahals. Each Mahal comprises one or more villages.
- Ownership rights were vested with the peasants.
- The villages committee was held responsible for collection of the taxes.
Incorrect
- Mahalwari system was introduced in 1833 during the period of William Bentick.
- It was introduced in Central Province, North-West Frontier, Agra, Punjab, Gangetic Valley, etc of British India.
- The Mahalwari system had many provisions of both the Zamindari System and Ryotwari System.
- In this system, the land was divided into Mahals. Each Mahal comprises one or more villages.
- Ownership rights were vested with the peasants.
- The villages committee was held responsible for collection of the taxes.
-
Question 4 of 30
4. Question
Which of the following were the causes of ‘The Battle of Buxar’?
- Abolition of all duties on internal trade of British
- Bringing the people of India together to fight against the supremacy of the British
- Dastak misused by the British which challenged the Nawab authority.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
Correct
- Misuse of Farman and Dastak by British which challenged the Mir Qasim’s authority and sovereignty.
- Abolition of all duties on internal trade of British.
- Misbehavior of the Company’s servant- They compelled the Indian artisans, peasants and merchant to sell their goods at cheap price , and also started the tradition of bribes and gifts.
- Plundering attitude of British which not only abuses the trade ethics but also challenges the Nawab authority
Incorrect
- Misuse of Farman and Dastak by British which challenged the Mir Qasim’s authority and sovereignty.
- Abolition of all duties on internal trade of British.
- Misbehavior of the Company’s servant- They compelled the Indian artisans, peasants and merchant to sell their goods at cheap price , and also started the tradition of bribes and gifts.
- Plundering attitude of British which not only abuses the trade ethics but also challenges the Nawab authority
-
Question 5 of 30
5. Question
Consider the Following statements regarding ‘Doctrine of Lapse ‘?
- It is a policy to expand British territory in India on the basis of pre- imperialistic approach.
- According to this policy state must be hand over to British, if they have no heir or ruler.
- Adoptions of child were not accepted for heir.
- Continuation of the titles and pension for the kings.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Correct
- Doctrine of lapse was the pro-imperialist approach to expand the realm of British Kingdom in India.
- It was introduced by Dalhousie who was the Governor-General; it was used by him to annex the independent Indian States.
- It was basically, an idea to annex those states which have no heir means state have no heir they get lapsed the right of ruling and it will not reverted by adoption.
- Policy to expand British territory in India on basis of pro-imperialistic approach.
State must be handed over to British, if they have no heir or ruler - Adoptions of child were not accepted for heir
- Policy was not in support to give title and pension to adopted child of rulers.
- Adopted heir would inherit only the personal property of the ruler
- Ended the title and pension.
Incorrect
- Doctrine of lapse was the pro-imperialist approach to expand the realm of British Kingdom in India.
- It was introduced by Dalhousie who was the Governor-General; it was used by him to annex the independent Indian States.
- It was basically, an idea to annex those states which have no heir means state have no heir they get lapsed the right of ruling and it will not reverted by adoption.
- Policy to expand British territory in India on basis of pro-imperialistic approach.
State must be handed over to British, if they have no heir or ruler - Adoptions of child were not accepted for heir
- Policy was not in support to give title and pension to adopted child of rulers.
- Adopted heir would inherit only the personal property of the ruler
- Ended the title and pension.
-
Question 6 of 30
6. Question
Which among the following changes were brought in the army after the revolt of 1857?
- The proportion of Europeans to Indians in the army was decreased.
- Communal, tribal and regional loyalties were encouraged amongst the soldiers.
- Indians were excluded from the officer corps.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Correct
The Indian army was carefully reorganized after 1858. Some changes were made necessary by the transfer of power to the Crown. Firstly, the domination of the army by its European branch was carefully guaranteed.
- The proportion of Europeans to Indians in the army was raised. Moreover, the European troops were kept in key geographical and military positions..
- The organization of the Indian section of the army was based on the policy of divide and rule so as to prevent its chance of uniting again in an anti-British uprising. Communal, caste, tribal and regional loyalties were encouraged amongst the soldiers so that the sentiment of nationalism would not grow among them. For example caste and communal companies were introduced in most of the regiments.
- The older policy of excluding Indians from the officer corps was strictly maintained. Till 1914, no Indian could rise higher than the rank of a subedar.
Incorrect
The Indian army was carefully reorganized after 1858. Some changes were made necessary by the transfer of power to the Crown. Firstly, the domination of the army by its European branch was carefully guaranteed.
- The proportion of Europeans to Indians in the army was raised. Moreover, the European troops were kept in key geographical and military positions..
- The organization of the Indian section of the army was based on the policy of divide and rule so as to prevent its chance of uniting again in an anti-British uprising. Communal, caste, tribal and regional loyalties were encouraged amongst the soldiers so that the sentiment of nationalism would not grow among them. For example caste and communal companies were introduced in most of the regiments.
- The older policy of excluding Indians from the officer corps was strictly maintained. Till 1914, no Indian could rise higher than the rank of a subedar.
-
Question 7 of 30
7. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the Charter Act of 1833
- It made the Governor-General of Bengal as the Governor-General of India.
- It provided the legislative powers to the Bombay and Madras presidencies.
- It Introduced an Open Competition system of selection and recruitment of civil servants.
Which of the statement given above is/are correct?
Correct
- It made the Governor-General of Bengal as the Governor-General of India and vested in him all civil and military powers. Thus, the act created, for the first time, a Government of India having authority over the entire territorial area possessed by the British in India. Lord William Bentick was the first governor-general of India.
- It deprived the governor of Bombay and Madras of their legislative powers. The Governor-General of India was given exclusive legislative powers for the entire British India. The laws made under the previous acts were called as Regulations while laws made under this act were called as Acts.
- It ended the activities of the East India Company as a commercial body, which became a purely administrative body. It provided that the company’s territories in India were held by it ‘in trust for His Majesty, His heirs and successors’.
- This Act attempted to introduce a system of open competition for selection of civil servants, and stated that the Indians should not be debarred from holding any place, office and employment under the Company. However, this provision was negated after opposition from the Court of Directors.
- This act allowed wider space to the British in the India’s administration. It ended the British India Company’s commercial activities and transformed into the British Crown’s trustee in administering India.
- Open Competition system of selection and recruitment of civil servants.(Charter act of 1853).
Incorrect
- It made the Governor-General of Bengal as the Governor-General of India and vested in him all civil and military powers. Thus, the act created, for the first time, a Government of India having authority over the entire territorial area possessed by the British in India. Lord William Bentick was the first governor-general of India.
- It deprived the governor of Bombay and Madras of their legislative powers. The Governor-General of India was given exclusive legislative powers for the entire British India. The laws made under the previous acts were called as Regulations while laws made under this act were called as Acts.
- It ended the activities of the East India Company as a commercial body, which became a purely administrative body. It provided that the company’s territories in India were held by it ‘in trust for His Majesty, His heirs and successors’.
- This Act attempted to introduce a system of open competition for selection of civil servants, and stated that the Indians should not be debarred from holding any place, office and employment under the Company. However, this provision was negated after opposition from the Court of Directors.
- This act allowed wider space to the British in the India’s administration. It ended the British India Company’s commercial activities and transformed into the British Crown’s trustee in administering India.
- Open Competition system of selection and recruitment of civil servants.(Charter act of 1853).
-
Question 8 of 30
8. Question
The Carnatic wars (1740-1763) were fought between which of the following European powers?
Correct
- Anglo-French rivalry in India coincided with the wars between the English and French in Europe or primarily two reasons :
- For protection of commercial interests.
- Political developments in the south India and Europe provided pretexts to contest their claims which culminated in the three Carnatic wars.
- First Carnatic War (1740-48) – It was an extension of the Anglo-French rivalry in Europe and ended in 1748 with the treaty of Aix-La-Chapelle.
- Second Carnatic War (1749-54) – Although inconclusive, it undermined the French power in the south India vis-a-vis the English.
- Third Carnatic War (1758-63) – A decisive war, known for the Battle of Wandiwash.
- By the Treaty of Paris (1763), the French were allowed to use Indian settlements for commercial purposes only and fortification of settlements was banned.
Incorrect
- Anglo-French rivalry in India coincided with the wars between the English and French in Europe or primarily two reasons :
- For protection of commercial interests.
- Political developments in the south India and Europe provided pretexts to contest their claims which culminated in the three Carnatic wars.
- First Carnatic War (1740-48) – It was an extension of the Anglo-French rivalry in Europe and ended in 1748 with the treaty of Aix-La-Chapelle.
- Second Carnatic War (1749-54) – Although inconclusive, it undermined the French power in the south India vis-a-vis the English.
- Third Carnatic War (1758-63) – A decisive war, known for the Battle of Wandiwash.
- By the Treaty of Paris (1763), the French were allowed to use Indian settlements for commercial purposes only and fortification of settlements was banned.
-
Question 9 of 30
9. Question
With reference to Indian press, consider the following statements:
- Charles Metcalfe was the first governor general to place restrictions on the press in India.
- Vernacular Press Act in 1878 put restrictions on the freedom on both English and Indian language newspapers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
- The Indian press was freed of restrictions by Charles Metcalfe in 1835. He is called ‘Liberator of India Press’. This step had been welcomed enthusiastically by the educated Indians. It was one of the reasons why they had for some time supported British rule in India.
- But the nationalists gradually began to use the press to arouse national consciousness among the people and to sharply criticize the reactionary policies of the Government. This turned the officials against the Indian press and they decided to curb its freedom.
- This was attempted by passing the Vernacular Press Act in 1878. This Act put serious restrictions on the freedom of the Indian language newspapers only.
Incorrect
- The Indian press was freed of restrictions by Charles Metcalfe in 1835. He is called ‘Liberator of India Press’. This step had been welcomed enthusiastically by the educated Indians. It was one of the reasons why they had for some time supported British rule in India.
- But the nationalists gradually began to use the press to arouse national consciousness among the people and to sharply criticize the reactionary policies of the Government. This turned the officials against the Indian press and they decided to curb its freedom.
- This was attempted by passing the Vernacular Press Act in 1878. This Act put serious restrictions on the freedom of the Indian language newspapers only.
-
Question 10 of 30
10. Question
Consider the following statements regarding the Indian Council Act of 1909:
- Another name of the Indian Council Act of 1909 is Minto-Morley reforms.
- It introduces the parliamentary form of government in India.
- It enlarged the deliberative functions for the association of Indian Councils; members were not allowed to ask supplementary questions.
Which of the statement given above is/are correct?
Correct
- A Morley-Minto Reform was another name of Indian Council Act of 1909, AD which was named after the secretary of state and the Viceroy. It was instituted to placate the moderates.
- It may also be remembered that the elected members were not elected by the people but by landlords, organizations or traders and industrialists, universities and local bodies. The British also introduced communal electorates as a part of these reforms.
- This was meant to create disunity between Hindus and Muslims. Some seats in the councils were reserved for Muslims to be elected by Muslim voters.
- It considerably increased the size of the legislative councils, both Central and provincial. The number of members in the Central Legislative Council was raised from 16 to 60. The number of members in the provincial legislative councils was not uniform.
- It retained official majority in the Central Legislative Council but allowed the provincial legislative councils to have non-official majority.
- It enlarged the deliberative functions of the legislative councils at both the levels. For example, members were allowed to ask supplementary questions, move resolutions on the budget, and so on.
- It provided (for the first time) for the association of Indians with the executive Councils of the Viceroy and Governors. Satyendra Prasad Sinha became the first Indian to join the Viceroy’s Executive Council. He was appointed as the law member.
- It introduced a system of communal representation for Muslims by accepting the concept of ‘separate electorate’. Under this, the Muslim members were to be elected only by Muslim voters. Thus, the Act ‘legalized communalism’ and Lord Minto came to be known as the Father of Communal Electorate.
- It also provided for the separate representation of presidency corporations, chambers of commerce, universities and zamindars.
- Indian Council Act of 1909, AD was instituted to placate the moderates and appeasement to the disseminate Muslims from National Movement by granting them separate electorate.
Incorrect
- A Morley-Minto Reform was another name of Indian Council Act of 1909, AD which was named after the secretary of state and the Viceroy. It was instituted to placate the moderates.
- It may also be remembered that the elected members were not elected by the people but by landlords, organizations or traders and industrialists, universities and local bodies. The British also introduced communal electorates as a part of these reforms.
- This was meant to create disunity between Hindus and Muslims. Some seats in the councils were reserved for Muslims to be elected by Muslim voters.
- It considerably increased the size of the legislative councils, both Central and provincial. The number of members in the Central Legislative Council was raised from 16 to 60. The number of members in the provincial legislative councils was not uniform.
- It retained official majority in the Central Legislative Council but allowed the provincial legislative councils to have non-official majority.
- It enlarged the deliberative functions of the legislative councils at both the levels. For example, members were allowed to ask supplementary questions, move resolutions on the budget, and so on.
- It provided (for the first time) for the association of Indians with the executive Councils of the Viceroy and Governors. Satyendra Prasad Sinha became the first Indian to join the Viceroy’s Executive Council. He was appointed as the law member.
- It introduced a system of communal representation for Muslims by accepting the concept of ‘separate electorate’. Under this, the Muslim members were to be elected only by Muslim voters. Thus, the Act ‘legalized communalism’ and Lord Minto came to be known as the Father of Communal Electorate.
- It also provided for the separate representation of presidency corporations, chambers of commerce, universities and zamindars.
- Indian Council Act of 1909, AD was instituted to placate the moderates and appeasement to the disseminate Muslims from National Movement by granting them separate electorate.
-
Question 11 of 30
11. Question
Which of the following was/were reasons for the failure of the Revolt of 1857?
- Limited territorial base
- Lack of resources
- Lack of a central and coordinated leadership
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Correct
Explanation:
- Following were the failure reasons for 1857 revolt-
- Limited territorial spread was one factor; there was no all-India veneer about the revolt. The eastern, southern and western parts of India remained more or less unaffected.
- The Indian soldiers were poorly equipped materially, fighting generally with swords and spears and very few guns and muskets. On the other hand, the European soldiers were equipped with the latest weapons of war like the Enfield rifle. The electric telegraph kept the commander-in-chief informed about the movements and strategy of the rebels.
- The revolt was poorly organized with no coordination or central leadership. The principal rebel leaders- Nana Saheb,Tantia Tope, Kunwar Singh,Laxmibai – were no match to their British opponents in generalship. On the other hand, the East India Company was fortunate in having the services of men of exceptional abilities in the Lawrence brothers, John Nicholson, James Outram, Henry Havelock, Edward, etc.
Incorrect
Explanation:
- Following were the failure reasons for 1857 revolt-
- Limited territorial spread was one factor; there was no all-India veneer about the revolt. The eastern, southern and western parts of India remained more or less unaffected.
- The Indian soldiers were poorly equipped materially, fighting generally with swords and spears and very few guns and muskets. On the other hand, the European soldiers were equipped with the latest weapons of war like the Enfield rifle. The electric telegraph kept the commander-in-chief informed about the movements and strategy of the rebels.
- The revolt was poorly organized with no coordination or central leadership. The principal rebel leaders- Nana Saheb,Tantia Tope, Kunwar Singh,Laxmibai – were no match to their British opponents in generalship. On the other hand, the East India Company was fortunate in having the services of men of exceptional abilities in the Lawrence brothers, John Nicholson, James Outram, Henry Havelock, Edward, etc.
-
Question 12 of 30
12. Question
In the context of Lord Macaulay’s Education Policy, 1835, which of the below statement is/are not correct?
Correct
Explanation:
- was an attempt to create that system of education which educates only upper strata of society through English.
- English become court language and Persian was abolished as court language.
- Printings of English books were made free and available at very low price.
- English education gets more fund as compare to oriental learning.
- In 1849, JED Bethune founded Bethune School.
- Agriculture Institute was established at Pusa (Bihar)
- Engineering Institute was established at Roorkee.
Incorrect
Explanation:
- was an attempt to create that system of education which educates only upper strata of society through English.
- English become court language and Persian was abolished as court language.
- Printings of English books were made free and available at very low price.
- English education gets more fund as compare to oriental learning.
- In 1849, JED Bethune founded Bethune School.
- Agriculture Institute was established at Pusa (Bihar)
- Engineering Institute was established at Roorkee.
-
Question 13 of 30
13. Question
Which among the following were the economic impacts of British rule in India?
- Deindustrialization
- Deterioration of agriculture
- Rise of bourgeoisie class in India
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Correct
- Following were the economic impact of the British rule in India:
- Deindustrialization– India was a major player in the world export market for textiles in the early 18th century, but by the middle of the 19th century it had lost all of its export market and much of its domestic market. Other local industries also suffered some decline, and India underwent de-industrialization as a consequence. While India produced about 25 percent of world industrial output in 1750, this figure fell to only 2 percent by 1900.
- Ruralisation– Loss of peasantry during early years of British rule, along with the loss of handicrafts Industry in India led to formation of new urban centres and ruralisation of many ancient and medieval towns in India.
- Deterioration of Agriculture– Faulty Land revenue collection practices, plantation Crops cultivation with little or no revenue for the farmers, transferability of land, little spending by Government on improvement of land productivity made farmer miserable. The peasant turned out to be the ultimate sufferer under the triple burden of the Government, zamindar and moneylender. His hardship increased at the time of famine and scarcity.
- Rise of bourgeoisie class in India – There emerged the new class of Indian traders, moneylenders and bankers. But, the colonial situation retarded the development of a healthy and independent industrial bourgeoisie, and its development was different from other independent countries like Germany and Japan.
- Famine and Poverty – Regular recurrence of famines became a common feature of daily existence in India. These famines were not just foodgrain scarcity-based phenomena, but were a direct result of poverty unleashed by colonial forces in India.
Incorrect
- Following were the economic impact of the British rule in India:
- Deindustrialization– India was a major player in the world export market for textiles in the early 18th century, but by the middle of the 19th century it had lost all of its export market and much of its domestic market. Other local industries also suffered some decline, and India underwent de-industrialization as a consequence. While India produced about 25 percent of world industrial output in 1750, this figure fell to only 2 percent by 1900.
- Ruralisation– Loss of peasantry during early years of British rule, along with the loss of handicrafts Industry in India led to formation of new urban centres and ruralisation of many ancient and medieval towns in India.
- Deterioration of Agriculture– Faulty Land revenue collection practices, plantation Crops cultivation with little or no revenue for the farmers, transferability of land, little spending by Government on improvement of land productivity made farmer miserable. The peasant turned out to be the ultimate sufferer under the triple burden of the Government, zamindar and moneylender. His hardship increased at the time of famine and scarcity.
- Rise of bourgeoisie class in India – There emerged the new class of Indian traders, moneylenders and bankers. But, the colonial situation retarded the development of a healthy and independent industrial bourgeoisie, and its development was different from other independent countries like Germany and Japan.
- Famine and Poverty – Regular recurrence of famines became a common feature of daily existence in India. These famines were not just foodgrain scarcity-based phenomena, but were a direct result of poverty unleashed by colonial forces in India.
-
Question 14 of 30
14. Question
Which of the following was / were recommendations of the Saddler Commission?
- Creation of Boards of Secondary Education in the Provinces
- Making Education a Provincial subject
- Seperation of secondary education from University education
- Establishment of university Grants Commission
Select the correct statements from the codes given below:
Correct
The successors of Lord Curzon did not take any active interest in the improvement of the education system. The education system was ‘overloaded’ and the universities worked merely as examining bodies. A fresh commission under Dr. M E Saddler of Leeds University was set up to study and report the problems of university education. This was called Saddler Commission or Calcutta University Commission.
- The major objective of this commission was to free the universities from the burden of the secondary education, so that the wholly focus on the Higher education. This resulted in the creation of Board of secondary education in the Provinces; United Provinces was the first to have such board.
- The secondary education was separated from the University education and admission to the university was upgraded from metric level to intermediate level.
- The Saddler Commission also recommended the use of mother tongue as a medium of instruction in the intermediate colleges. The Education was made a ” provincial subject”.
- Creation of Inter University Board for coordination among the universities.
- As far as Calcutta University is concerned, this commission gave the following recommendations:
- More powers should be given to the university.
- A full time paid Vice Chancellor should be appointed in the University.
- Provisions should be made to differentiate the Pass Course from the Honors course.
- A residential university should be established at Dhaka.
- A special board of women education should be set up in Calcutta University.
The above recommendations were accepted and implemented in due course of time. After independence UGC was established in 1953 with the recommendation of a similar Radha Krishna Commission.
Incorrect
The successors of Lord Curzon did not take any active interest in the improvement of the education system. The education system was ‘overloaded’ and the universities worked merely as examining bodies. A fresh commission under Dr. M E Saddler of Leeds University was set up to study and report the problems of university education. This was called Saddler Commission or Calcutta University Commission.
- The major objective of this commission was to free the universities from the burden of the secondary education, so that the wholly focus on the Higher education. This resulted in the creation of Board of secondary education in the Provinces; United Provinces was the first to have such board.
- The secondary education was separated from the University education and admission to the university was upgraded from metric level to intermediate level.
- The Saddler Commission also recommended the use of mother tongue as a medium of instruction in the intermediate colleges. The Education was made a ” provincial subject”.
- Creation of Inter University Board for coordination among the universities.
- As far as Calcutta University is concerned, this commission gave the following recommendations:
- More powers should be given to the university.
- A full time paid Vice Chancellor should be appointed in the University.
- Provisions should be made to differentiate the Pass Course from the Honors course.
- A residential university should be established at Dhaka.
- A special board of women education should be set up in Calcutta University.
The above recommendations were accepted and implemented in due course of time. After independence UGC was established in 1953 with the recommendation of a similar Radha Krishna Commission.
-
Question 15 of 30
15. Question
Consider the following pairs:
Europeans Centre of Influence
- French Chandernagore
- Portuguese Goa
- Dutch Pulicat
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
Correct
- The Portuguese hold over the coastal areas and superiority in naval power helped them significantly. By the end of the 16th century, the Portuguese captured not only Goa, Daman, Diu, and Salsette but also a vast stretches along the Indian coast.
- The French establishments included Pondicherry, Karikal and Yanam on the Coromandel Coast, Mahe on the Malabar Coast and Chandernagor in Bengal.
- The Dutch, during their stay in India, tried their hands on the minting of coinages. As their trade flourished they established mints at Cochin, Masulipattam, Nagapatam Pondicherry and Pulicat. Even more, Gold pagoda with an image of Lord Venkateswara, (God Vishnu) was issued at Pulicat mint. The coins issued by the Dutch were all modelled on the local coinages.
Incorrect
- The Portuguese hold over the coastal areas and superiority in naval power helped them significantly. By the end of the 16th century, the Portuguese captured not only Goa, Daman, Diu, and Salsette but also a vast stretches along the Indian coast.
- The French establishments included Pondicherry, Karikal and Yanam on the Coromandel Coast, Mahe on the Malabar Coast and Chandernagor in Bengal.
- The Dutch, during their stay in India, tried their hands on the minting of coinages. As their trade flourished they established mints at Cochin, Masulipattam, Nagapatam Pondicherry and Pulicat. Even more, Gold pagoda with an image of Lord Venkateswara, (God Vishnu) was issued at Pulicat mint. The coins issued by the Dutch were all modelled on the local coinages.
-
Question 16 of 30
16. Question
With reference to Permanent Settlement System, consider the following statements:
- It recognized zamindars as the owner of the land.
- The revenue settled was revised every 20-30 years.
- It was introduced in Orissa, Bengal and Bihar.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Correct
Permanent Settlement System: The Permanent Settlement of Bengal was brought into effect by the East India Company headed by the Governor-General Lord Cornwallis in 1793. This system was also called the Zamindari System. This was basically an agreement between the company and the Zamindars to fix the land revenue.
First enacted in Bengal, Bihar and Odisha, this was later followed in northern Madras Presidency and the district of Varanasi.
Features of the system were as follows:
- Landlords or Zamindars were recognized as the owners of the land. They were given hereditary rights of succession of the lands under them. The Zamindars could sell or transfer the land as they wished.
- The Zamindars‘proprietorship would stay as long as he paid the fixed revenue at the said date to the government. If they failed to pay, their rights would cease to exist and the land would be auctioned off. The amount to be paid by the landlords was fixed. It was agreed that this would not increase in future (permanent). The fixed amount was 10/11th portion of the revenue for the government and 1/10th was for the Zamindar. (The revenue settled under the Ryotwari settlement was periodically revised after 20-30 years when the revenue demand was usually raised.) Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- The Zamindar also had to give the tenant a patta which described the area of the land given to him and the rent he had to pay the landlord.
Incorrect
Permanent Settlement System: The Permanent Settlement of Bengal was brought into effect by the East India Company headed by the Governor-General Lord Cornwallis in 1793. This system was also called the Zamindari System. This was basically an agreement between the company and the Zamindars to fix the land revenue.
First enacted in Bengal, Bihar and Odisha, this was later followed in northern Madras Presidency and the district of Varanasi.
Features of the system were as follows:
- Landlords or Zamindars were recognized as the owners of the land. They were given hereditary rights of succession of the lands under them. The Zamindars could sell or transfer the land as they wished.
- The Zamindars‘proprietorship would stay as long as he paid the fixed revenue at the said date to the government. If they failed to pay, their rights would cease to exist and the land would be auctioned off. The amount to be paid by the landlords was fixed. It was agreed that this would not increase in future (permanent). The fixed amount was 10/11th portion of the revenue for the government and 1/10th was for the Zamindar. (The revenue settled under the Ryotwari settlement was periodically revised after 20-30 years when the revenue demand was usually raised.) Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- The Zamindar also had to give the tenant a patta which described the area of the land given to him and the rent he had to pay the landlord.
-
Question 17 of 30
17. Question
Which of the following act of British also known as Anarchical and Revolutionary Crimes Act of 1919?
Correct
The Anarchical and Revolutionary Crime Act, 1919
Governor General Chelmsford had appointed a committee under the chairmanship of Justice Sydney Rowlatt in 1917 for retrospections of the nature of revolution and for suggestion which was popularly known as ‘Rowlatt Committee’. In 1918, committee submitted its report with recommendation for punitive as well as preventive measures. This act empowered the government to arrest any person without warrant and can detent for two years without trial.
Provisions of Act
- The Governor-General had power to implement the Act to any area.
- The Act envages for the speedy trial of offences.
- In the interest of public safety, suspected persons could be arrested and confined.
- It provided that persons interned under the Defence of India Act may not be released,
- In the trials of such cases the juris were to be dispensed with.
Incorrect
The Anarchical and Revolutionary Crime Act, 1919
Governor General Chelmsford had appointed a committee under the chairmanship of Justice Sydney Rowlatt in 1917 for retrospections of the nature of revolution and for suggestion which was popularly known as ‘Rowlatt Committee’. In 1918, committee submitted its report with recommendation for punitive as well as preventive measures. This act empowered the government to arrest any person without warrant and can detent for two years without trial.
Provisions of Act
- The Governor-General had power to implement the Act to any area.
- The Act envages for the speedy trial of offences.
- In the interest of public safety, suspected persons could be arrested and confined.
- It provided that persons interned under the Defence of India Act may not be released,
- In the trials of such cases the juris were to be dispensed with.
-
Question 18 of 30
18. Question
Assertion (A): Pitt’s India Act of 1784 distinguished between the commercial and political functions of the British East India Company.
Reason (R): Pitt’s India Act of 1784 allowed the Court of Directors to manage the commercial affairs but created a new body called Board of Control to manage the political affairs. Thus, it established a system of double government.
Select the code from following:
Correct
- In a bid to rectify the defects of the Regulating Act of 1773, the British Parliament passed the Amending Act of 1781, also known as the Act of Settlement.
- The next important act was the Pitt’s India Act of 1784. Thus, the act was significant for two reasons:
- First, the Company’s territories in India were for the first time called the ‘British possessions in India’; and
- Second, the British Government was given the supreme control over Company’s affairs and its administration in India.
- Hence, A is the correct option because both A and R is true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Incorrect
- In a bid to rectify the defects of the Regulating Act of 1773, the British Parliament passed the Amending Act of 1781, also known as the Act of Settlement.
- The next important act was the Pitt’s India Act of 1784. Thus, the act was significant for two reasons:
- First, the Company’s territories in India were for the first time called the ‘British possessions in India’; and
- Second, the British Government was given the supreme control over Company’s affairs and its administration in India.
- Hence, A is the correct option because both A and R is true and R is the correct explanation of A.
-
Question 19 of 30
19. Question
Under which reform/act, non-official majority was introduced in the provincial legislative councils?
Correct
Under Morley-Minto reforms, number of elected members in the Imperial Legislative Council and Provincial legislative Council was increased. In the Provincial Councils, non-official majority was introduced but since some of these non-official were nominated and not selected, the overall non-elected majority remained.
Incorrect
Under Morley-Minto reforms, number of elected members in the Imperial Legislative Council and Provincial legislative Council was increased. In the Provincial Councils, non-official majority was introduced but since some of these non-official were nominated and not selected, the overall non-elected majority remained.
-
Question 20 of 30
20. Question
which of the following initiatives taken by British contributed to the spread of communalism in India?
- Partition of Bengal, 1905
- McDonald Award, 1932
- Indian Councils Act, 1909
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Correct
- The decision to effect the Partition of Bengal was announced in July 1905 by the Viceroy of India, Lord Curzon. The partition took place on 16 October 1905 and separated the largely Muslim eastern areas from the largely Hindu western areas.
- The Communal Award was made by the British Prime Minister Ramsay MacDonald on 16 August 1932 granting separate electorates in India for the Forward Caste, Lower Caste, Muslims, Buddhists, Sikhs, Indian Christians, Anglo-Indians, Europeans and Untouchables (now known as the Dalits) etc.
- Indian Councils Act, 1909: The Indian Councils Act 1909 or Morley-Minto Reforms was passed by British Parliament in 1909. For the first time, the Indian Councils act gave recognition to elective principle for the appointment of nonofficial members to the councils. However, it introduced separate electorates.The electorate was decided on the basis of class & community. For the provincial councils a provision of three categories was made viz. general, special and chambers of commerce. However, for the central council, a fourth category Muslims was added.
Incorrect
- The decision to effect the Partition of Bengal was announced in July 1905 by the Viceroy of India, Lord Curzon. The partition took place on 16 October 1905 and separated the largely Muslim eastern areas from the largely Hindu western areas.
- The Communal Award was made by the British Prime Minister Ramsay MacDonald on 16 August 1932 granting separate electorates in India for the Forward Caste, Lower Caste, Muslims, Buddhists, Sikhs, Indian Christians, Anglo-Indians, Europeans and Untouchables (now known as the Dalits) etc.
- Indian Councils Act, 1909: The Indian Councils Act 1909 or Morley-Minto Reforms was passed by British Parliament in 1909. For the first time, the Indian Councils act gave recognition to elective principle for the appointment of nonofficial members to the councils. However, it introduced separate electorates.The electorate was decided on the basis of class & community. For the provincial councils a provision of three categories was made viz. general, special and chambers of commerce. However, for the central council, a fourth category Muslims was added.
-
Question 21 of 30
21. Question
Which one of the following best describes the term “Static Interchange Fee” sometimes seen in news?
Correct
It is the amount paid by one bank to the other when its customer uses the other bank’s ATM network.
Source: https://www.telegraphindia.com/business/atm-firms-for-rule-tweaks/cid/1309946
Incorrect
It is the amount paid by one bank to the other when its customer uses the other bank’s ATM network.
Source: https://www.telegraphindia.com/business/atm-firms-for-rule-tweaks/cid/1309946
-
Question 22 of 30
22. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to ‘White Label ATM (WLAs)’
- WLAs are those ATMs where hardware and the lease of the ATM machine is owned by a service provider but cash management and connectivity to banking networks is provided by a sponsor bank
- They can source cash only from Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
Select the correct statements
Correct
Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) set up, owned and operated by non-bank entities are called “White Label ATMs” (WLAs). They provide the banking services to the customers of banks in India, based on the cards (debit/credit/prepaid) issued by banks.
Non-bank entities that set up, own and operate ATMs are called “White Label ATM Operators” (WLAO). The WLAO’s role is confined to acquisition of transactions of all banks’ customers by establishing technical connectivity with the existing authorized, shared ATM Network Operators / Card Payment Network Operators.
In a step to boost activities of white label automated (WLA) teller machine operators, the RBI has allowed such entities to buy wholesale cash, above a threshold of 1 lakh pieces of any denomination, directly from the RBI and currency chests against full payment.
WLAs are also allowed to source cash from scheduled banks, including cooperative banks and regional rural banks.
Incorrect
Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) set up, owned and operated by non-bank entities are called “White Label ATMs” (WLAs). They provide the banking services to the customers of banks in India, based on the cards (debit/credit/prepaid) issued by banks.
Non-bank entities that set up, own and operate ATMs are called “White Label ATM Operators” (WLAO). The WLAO’s role is confined to acquisition of transactions of all banks’ customers by establishing technical connectivity with the existing authorized, shared ATM Network Operators / Card Payment Network Operators.
In a step to boost activities of white label automated (WLA) teller machine operators, the RBI has allowed such entities to buy wholesale cash, above a threshold of 1 lakh pieces of any denomination, directly from the RBI and currency chests against full payment.
WLAs are also allowed to source cash from scheduled banks, including cooperative banks and regional rural banks.
-
Question 23 of 30
23. Question
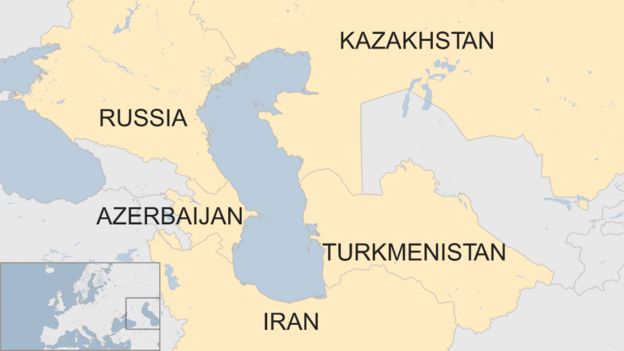
‘Caspian Sea’ is bordered by
- Azerbaijan
- Iran
- Kazakhstan
- Russia
- Turkmenistan
Select the correct code:
Correct
It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the west, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast.
 Incorrect
Incorrect
It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the west, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast.

-
Question 24 of 30
24. Question
Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched?
Tribes/Communities in news – States
- Yerukala – Kerala
- Savara – Andhra Pradesh
- Yakthung – Sikkim
Select the correct code:
Correct
Yerukala – Telangana/Andhra Pradesh (https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/telangana/its-dark-nights-for-bats-in-telanganas-nalgonda/article24604246.ece)
Savara – Andhra Pradesh (https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/andhra-pradesh/savara-tribal-art-gasps-for-survival/article24637087.ece)
Yakthung – Sikkim (https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/other-states/more-assembly-seats-for-sikkim/article24667220.ece)
Note – Go through Wikipedia pages of the mentioned tribes/communities.
Incorrect
Yerukala – Telangana/Andhra Pradesh (https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/telangana/its-dark-nights-for-bats-in-telanganas-nalgonda/article24604246.ece)
Savara – Andhra Pradesh (https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/andhra-pradesh/savara-tribal-art-gasps-for-survival/article24637087.ece)
Yakthung – Sikkim (https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/other-states/more-assembly-seats-for-sikkim/article24667220.ece)
Note – Go through Wikipedia pages of the mentioned tribes/communities.
-
Question 25 of 30
25. Question
Consider the following statements with respect to ‘TReDS Platform’
- It is a digital platform where small businesses (MSMEs) can get access to capital by auctioning their trade receivables
- It is governed by the Payment and Settlement Systems Act
Select the correct statements
Correct
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has given license to three entities to launch Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS) — a digital platform where small businesses (MSMEs) can get access to capital by auctioning their trade receivables and they are governed by the Payment And Settlement Systems Act.
The TReDS will facilitate the discounting of both invoices as well as bills of exchange.
Read More – https://rbi.org.in/scripts/bs_viewcontent.aspx?id=2904
Incorrect
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has given license to three entities to launch Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS) — a digital platform where small businesses (MSMEs) can get access to capital by auctioning their trade receivables and they are governed by the Payment And Settlement Systems Act.
The TReDS will facilitate the discounting of both invoices as well as bills of exchange.
Read More – https://rbi.org.in/scripts/bs_viewcontent.aspx?id=2904
-
Question 26 of 30
26. Question
‘Bhoomi Rashi Portal ‘recently in news is aimed at and developed by:
Correct
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, Govt. of India has designed Bhoomi Rashi as a single point platform for online processing of land acquisition notifications to accelerate highway infrastructure development projects in India.
Bhoomi Rashi will fast track the process of land acquisition and result in greater benefits for all stakeholders.
Farmers, landowners, contractors and investors will benefit from the transparency introduced by the portal in the land acquisition process.
The Bhoomi Rashi portal will be a new milestone in the nation’s journey towards DIGITISATION and TRANSPARENCY.
Bhoomi Rashi portal is developed by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways and National Informatics Centre.
Source: http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=181568
Incorrect
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, Govt. of India has designed Bhoomi Rashi as a single point platform for online processing of land acquisition notifications to accelerate highway infrastructure development projects in India.
Bhoomi Rashi will fast track the process of land acquisition and result in greater benefits for all stakeholders.
Farmers, landowners, contractors and investors will benefit from the transparency introduced by the portal in the land acquisition process.
The Bhoomi Rashi portal will be a new milestone in the nation’s journey towards DIGITISATION and TRANSPARENCY.
Bhoomi Rashi portal is developed by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways and National Informatics Centre.
Source: http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=181568
-
Question 27 of 30
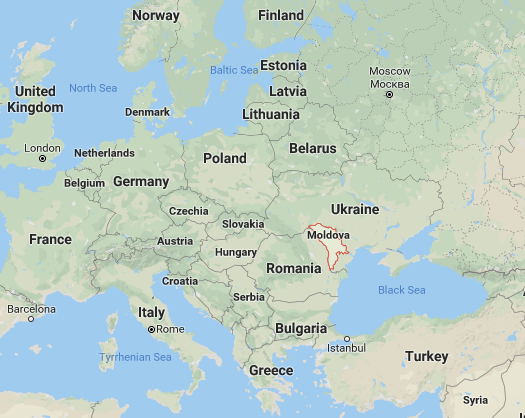
27. Question
Minister for Foreign Affairs and European Integration of the Republic of Moldova gave a historic visit (as it is the first time that a Foreign Minister of Moldova has visited India) to India. Which of the following countries borders Moldova?
-
Question 28 of 30
28. Question
To tackle the garbage crisis in Ladakh, Bengaluru-based Tesla has come up with a machine that works without fuel or electricity, and converts all waste, except glass, into ash. What is the name of that machine?
-
Question 29 of 30
29. Question
Recently Google has launched ‘Project Navlekha’. What is the aim of this project?
Correct
Google has launched Project Navlekha to expand the reach of Indian content. The project would allow Indian vernacular news publishers to get their content online
Source: https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/info-tech/googles-project-navlekha-to-help-regional-publications-go-online/article24799483.ece
Incorrect
Google has launched Project Navlekha to expand the reach of Indian content. The project would allow Indian vernacular news publishers to get their content online
Source: https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/info-tech/googles-project-navlekha-to-help-regional-publications-go-online/article24799483.ece
-
Question 30 of 30
30. Question
E-Government Survey 2018: Gearing E-Government to Support Transformation towards sustainable and resilient societies was launched recently. It is published by:
Correct
The UN E-Government Survey 2018 has ranked India at 96 positions for its performance in development and execution of information technologies, up from 107 in 2016 and 118 in 2014, a massive leap over the years.
The survey, published every two years, ranks 193 UN member states on basis of their performance on mainly three dimensions or e-governance development index (EGDI): online service index (OSI), telecommunication infrastructure index (TII), and human capital index (HCI).
UN carried out this year’s survey with the theme “gearing e-government to support transformation towards sustainable and resilient societies”.The survey is aimed at serving as a development tool for countries to identify areas of strength and challenges in e-government and shape their policies and strategies
Source: https://publicadministration.un.org/egovkb/en-us/Reports/UN-E-Government-Survey-2018
Incorrect
The UN E-Government Survey 2018 has ranked India at 96 positions for its performance in development and execution of information technologies, up from 107 in 2016 and 118 in 2014, a massive leap over the years.
The survey, published every two years, ranks 193 UN member states on basis of their performance on mainly three dimensions or e-governance development index (EGDI): online service index (OSI), telecommunication infrastructure index (TII), and human capital index (HCI).
UN carried out this year’s survey with the theme “gearing e-government to support transformation towards sustainable and resilient societies”.The survey is aimed at serving as a development tool for countries to identify areas of strength and challenges in e-government and shape their policies and strategies
Source: https://publicadministration.un.org/egovkb/en-us/Reports/UN-E-Government-Survey-2018