IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 12th March 2019
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
10% economic reservation law
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Social/Welfare issue; Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population
In news:
- Supreme Court decided to consider the question of whether the challenge to the 10% economic reservation law should be heard by a Constitution Bench.
- The court refused to pass any interim order to stay or hamper the implementation of the Constitution (103rd Amendment) Act that provides for 10% reservation in government jobs and educational institutions to the economically backward in the unreserved category.
The 10% economic reservation law was considered (by the petitioners) to be violating the basic features of the Constitution. 50% quota limit was part of the Basic Structure of the Constitution and the new amendment tinkered with it.

https://d39gegkjaqduz9.cloudfront.net/TH/2019/03/12/DEL/Delhi/TH/5_01/50ea3011_2793288_101_mr.jpg
Animal in news: Wood snake
Part of: Prelims and Mains III – Environment and Biodiversity; Animal conservation
In news:
- A species of wood snake that wasn’t seen for 140 years has resurfaced in a survey conducted by scientists in the Meghamalai Wildlife Sanctuary.
- The species is endemic to the Meghamalai forests and the Periyar Tiger Reserve landscape. (Tamil Nadu)
Do you know?
- The local population of wood snakes was last spotted and recorded by British military officer and naturalist Colonel Richard Henry Beddome in 1878, who went on to describe it as a new species, Xylophis indicus.
- The rediscovery of the snake indicated that the quality of the habitat was good.
- The documentation of the existence of this species will aid in both the management and conservation of biodiversity in this region.
‘Sirsi Supari’ gets GI tag
Part of: GS Prelims – Indian Economy and development
In news:
- For the first time in the arecanut sector, ‘Sirsi Supari’ grown in Uttara Kannada has received the GI tag.
- It is cultivated in Yellapura, Siddapura and Sirsi taluks of Karnataka.
- Its GI number is 464.
- The arecanut grown in these taluks have unique features like a round and flattened coin shape, particular texture, size, cross-sectional views, taste, etc.
- These features are not seen in arecanut grown in any other regions.
Important value additions:
Geographical Indication
- According to the World Intellectual Property Rights, “Geographical Indication is the sign used on the products that have specific geographical origin and posses’ reputation and some qualities that are due to the origin.”
- In India Geographical Indication tag is governed by the Geographical Indication of Goods (Registry and Protection) Act of 1999.
About GI Act, 1999:
- GIs indicate goods as originating in a specific geographical region, the characteristics, qualities or reputation thereof essentially attributable to such region.
- Complying with the World Trade Organisation-Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (WTO-TRIPS) obligations, India enacted the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration & Protection) Act, 1999 (GI Act) and has set up a registry in Chennai to register such names.
- Covering agricultural goods, manufactured and natural goods, textiles, handicrafts and foodstuffs, the GI Registry’s website lists popular GIs like Basmati rice, Darjeeling tea and Pashmina shawls etc.
Do you know?
- Darjeeling tea became the first product to get this tag in 2005.
- The Pashmina from Kashmir, Nagpur mangoes, Madhubani paintings of Bihar, are some of the examples.
Early Harappan ritual site: Khatiya village of Kutch
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains I – Indian Heritage and Culture, History
In news:
- Archaeologists unearthed several skeletal remains from a cemetery-like burial site at Khatiya village of Kutch.
- The rectangular graves, each of varying dimensions and assembled using stones, contained skeletons that were placed in a specific manner.
- They were oriented east-west with the heads positioned on the eastern side. Next to the legs on the western side, the archaeologists found earthen pots and pottery shards and other artefacts, including conch-shell bangles, beads made of stones and terracotta, numerous lithic tools and grinding stones.
- The discovery shed light on the custom and burial rituals that were prevalent during the early Harappan phase.
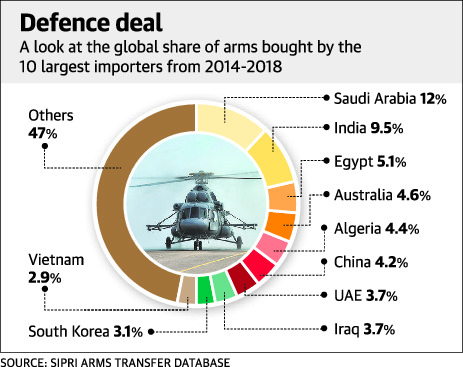
India is world’s 2nd largest arms importer
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains III – Defence and Security issues
In news:
According to the latest report published by the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) –
- India was the world’s second largest arms importer from 2014-18.
- India was accounted for 9.5% of the global total.
- Russia accounted for 58% of Indian arms imports in 2014–18, compared with 76% in 2009-13.
- Israel, the U.S. and France all increased their arms exports to India in 2014-18.
However, the Russian share in Indian imports is likely to sharply go up for the next five-year period as India signed several big-ticket deals recently, and more are in the pipeline.
India-Russia defence ties –
- S-400 air defence systems
- Four stealth frigates
- AK-203 assault rifles
- a second nuclear attack submarine on lease (Akula class)
- Kamov-226T utility helicopters
- Mi-17 helicopters
- Short-range air defence systems etc.
Do you know?
- Despite the long-standing conflict between India and Pakistan, arms imports decreased for both countries in 2014-18 compared with 2009-13.
- Pakistan stood at the 11th position accounting for 2.7% of all global imports. (Its biggest source was China, from which 70% of arms were sourced, followed by the U.S. at 8.9% and Russia at 6%.)
- The five largest exporters in 2014-18 were the United States, Russia, France, Germany and China together accounting for 75% of the total volume of arms exports in 2014-18.
https://d39gegkjaqduz9.cloudfront.net/TH/2019/03/12/CNI/Chennai/TH/5_10/62aab5fa_2791973_101_mr.jpg
India discusses terror with 4 countries
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – India and the World; International Relations; Security related issues
In news:
- India held crucial discussions with Saudi Arabia, United States, Turkey and the UAE on countering Pakistan-based terror groups.
- India reiterated its position that terrorism “remains one of the gravest threats to global peace and security”.
- India asked for a united front against terrorism (during its appearance as a “Guest of Honour” at the recent ministerial of the OIC)
Meanwhile, China is still reluctant on listing Azhar. Beijing has thrice blocked efforts to label him a ‘terrorist’.
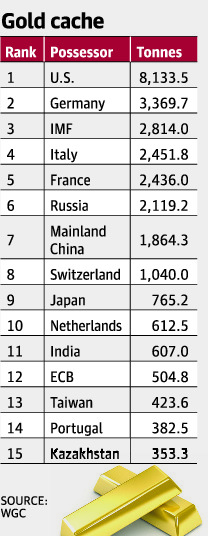
India ranks 11th in gold holding
In news:
- India, which is the world’s largest consumer of gold, has the 11th largest gold reserve, with the current holding pegged at 607 tonnes, as per the latest report by the World Gold Council (WGC).
Do you know?
- India’s overall position in terms of total gold holding would have been tenth had the list included only countries.
- Since IMF is included in the list, India stands at 11th (IMF stands 3rd with total gold reserves of 2,814 tonnes)
- US ranks 1st (8,133.5 tonnes) followed by Germany with 3,369.7 tonnes.
- Meanwhile, among Asian countries, China and Japan have more reserves of the precious metal when compared to India.
https://d39gegkjaqduz9.cloudfront.net/TH/2019/03/12/CNI/Chennai/TH/5_14/8de11abe_2791914_101_mr.jpg
WHO strategy to fight flu pandemics
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Health issues; Role of International Organizations – WHO
In news:
- The World Health Organization launched a strategy to protect people worldwide over the next decade against the threat of influenza, warning that new pandemics are “inevitable”.
- Influenza epidemics, largely seasonal, affect around one billion people and kill hundreds of thousands annually, according to WHO, which describes it as one of the world’s greatest public health challenges.
WHO’s strategy
- WHO’s new strategy, for 2019 through 2030, aims to prevent seasonal influenza, control the virus’s spread from animals to humans and prepare for the next pandemic.
- The new strategy called for every country to strengthen routine health programmes and to develop tailor-made influenza programmes that strengthen disease surveillance, response, prevention, control, and preparedness.
- WHO recommends annual flu vaccines as the most effective way to prevent the spread of the disease, especially for healthcare workers and people at higher risk of influenza complications.
- It also called for the development of more effective and more accessible vaccines and antiviral treatments.
- Due to its mutating strains, vaccine formulas must be regularly updated and only offer limited protection currently.
Indians face age-related issues earlier than Swiss
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Health issues
In news:
- People living in India experience the health problems associated with ageing at an early stage than those living in Japan or Switzerland, according to a first-of-its-kind study published in The Lancet Public Health.
- People living in India experience age-related health problems sooner than other countries.
- Age-related health problems can lead to early retirement, a smaller workforce, and higher health spending.
- Government leaders and other stakeholders influencing health systems need to consider when people begin suffering the negative effects of ageing.
- These negative effects include impaired functions and loss of physical, mental, and cognitive abilities resulting from the 92 conditions analysed, five of which are communicable and 81 non-communicable, along with six injuries.
UN Environment Assembly: Focus is on Plastic
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains III – Environment and Biodiversity; Plastic pollution
Key pointers:
- UN Environment Assembly is the top annual forum on the planet’s environmental crisis.
- Countries from around the world set their sights on a pivotal deal to curb plastic waste.
- The UN environment forum was held in Nairobi.
- The UN wants individual countries to sign up to “significantly” reduce plastic production, including a phasing out of single-use plastics by 2030 — a goal inspired by the 2015 Paris Agreement on voluntary reductions of carbon emissions.
Do you know?
- The world currently produces more than 300 million tonnes of plastics annually, and there are at least five trillion plastic pieces floating in our oceans.
- Microplastics have been found in the deepest sea trenches and high up the earth’s tallest peaks, and plastic consumption is growing year-on-year.
About UN Environment Assembly
- The UN Environment Assembly has the universal membership of all 193 UN Member States and the full involvement of UN organizations, specialized agencies, inter-governmental organizations, civil society and the private sector. In bringing together these varied communities, the Assembly provides a groundbreaking platform for leadership on global environmental policy.
- Latest Environment Assembly took place in Nairobi, Kenya.
DEFENCE/TECHNOLOGY
TOPIC: General Studies 2 and 3
- Important aspects of governance, transparency and accountability
- Security challenges and their management in border areas
- Achievements of Indians in science & technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
Indigenous Defence Development
Context:
- Recently, the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas Mark 1, received its long-awaited Final Operational Clearance (combat-ready and can be exploited to the limits).
- However, a day later, came a rather unwelcome report: a DRDO announcement of its decision to shelve the Kaveri turbo-jet engine project.
Do you know?
- Kaveri engine is supposed to power LCA-Tejas, which is currently powered by US manufactured GE-F404 engine.
- Two developments are of significance, for India’s national security as well as its moribund aeronautical industry.
India’s dependence on technology
- Historically, all major aerospace powers have possessed the capability to design airframes as well as power-plants.
- Until India can design and produce its own aero-engines, the performance and capabilities of any indigenously designed/built aircraft will be seriously limited by the technology that we are permitted to import.
- India has already had two bitter experiences in this regard. For example, the Hindustan Aeronautics Limited’s sleek and elegant HF-24 Marut fighter, of the 1960s and 1970s, failed to achieve its huge potential as a supersonic fighter for want of a suitable engine.
- Similarly, many of the problems the Tejas faced emanate from lack of engine thrust.
- Even as the Kaveri has failed to make an appearance, U.S.-made alternatives such as the General Electric F-404 engine, or even the more powerful F-414, do not deliver adequate thrust for the Tejas Mk 1, to meet all its missions.
- For the Tejas Mk I, Mk II, the LCA Navy, and other aircraft programmes such as the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft, India will need turbo-jet engines of even greater thrust.
Need for Indigenous Aircraft Industry
- It is vital for India to develop a family of homegrown jet engines to power indigenous combat aircraft as well as re-engine imported ones.
- In this context, it is necessary to recognise that both the Tejas and Kaveri projects — which have seen more than their share of headwinds and uncertainty — form key components of India’s technological aspirations.
- Unless carefully guided, protected and nurtured, their failure could spell the end of India’s aeronautical industry, or condemn it forever to licensed production.
- A long production run of, say, 250-300 aircraft for the Tejas and its advanced derivatives is essential if the industry is to hone its design and production skills.
Conclusion:
- It is still not too late for the government to declare both these projects as ‘national missions’ and initiate urgent remedial actions.
- The success of both the Kaveri and Tejas programmes will transform the aerospace scene, and put India in the front ranks of aeronautical nations, perhaps even ahead of China, if the desired degree of resolve and professional rigour can be brought to the fore.
- If we miss this opportunity, we will remain abjectly import-dependent forever in this vital area.
Connecting the dots:
- Does India’s Defence Procurement Policy give impetus to indigenisation? Critically examine.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Featured Comments and comments Up-voted by IASbaba are the “correct answers”.
- IASbaba App users – Team IASbaba will provide correct answers in comment section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1) Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) is responsible for Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) relating to
- Geographical Indication of goods
- Copyrights
- Semiconductor integrated circuits’ layout design
Select the correct code:
- 1 and 2
- Only 2
- 2 and 3
- All of the above
Q.2) Which of the following statements are true regarding the GI tag?
- GI tags are given on the basis of the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999.
- A GI tag connects the quality and authenticity of a given product to a particular geographical origin, thereby ensuring that no one other than the authorised user can use the popular product’s name.
- The first product to be included in the GI list was Chanderi Sarees.
Select the correct option
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- None of the above
Q.3) Meghamalai Wildlife Sanctuary is located in –
- Assam
- Kerala
- Tamil Nadu
- Meghalaya
Q.4) Consider the following statements about United Nations Environment Assembly:
- It is the world’s highest-level decision-making body on the environment.
- It has a universal membership of all UN members.
- The Environment Assembly meets triennially.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- All of the above
MUST READ
A case for aggressive diplomacy: on India-Pakistan relations
The Huawei debate
Kashmiris must be made to feel so included that Article 370 matters less
India’s broken criminal justice system cannot support the death penalty
The fiscal health of states and the limits of federalism
A battle over data is the new front in the US-China trade war











