IASbaba Prelims 60 Days Plan
ARCHIVES
PRELIMS CRACKATHON : UPSC Prelims 2019 Discussion Videos from IASbaba Topper’s
Importance of Self – Tracking: Learning from Last Year
Last year, aspirants used to type/post their answers in the comment box on a daily basis. There were huge participation and discussion below the test post. Putting answers in the comment box has been very effective to self-track yourself after updating the score. In the end, you can cross check your performance through Disqus profile.
It was highly effective in the last edition of 60 Days that propelled aspirants to monitor their performance and learn through discussion. Let you solve these questions with full honesty and write your result in the comment box. Interact with peers to know your mistakes.
The importance of this initiative stands time-bound and aggressive reverse engineering to learn the concepts. Many of you must be busy with your own strategy but let us tell you honestly that in the last few months, it is very important to revise and consolidate your learning. Just reading won’t suffice.
So, take out a few hours from your schedule and make it a revision exercise.
How can you make the best use of it?
Be honest to your effort and do not start competing with XYZ aspirants just for the sake of marks. It is more important for you to introspect and check your learning than focusing on others. Try to answer the questions in 25 minutes only.
Do not get into negative feeling that I don’t have enough knowledge to answer these questions. Feel like you are taking the real exam. What would be your response then?
The same will be replicated in the UPSC exam. Here, you get marks only and nothing else matters. So, make effort to know the answers to all questions. Do not cheat 😛
DETAILED MICRO ANALYSIS MATRIX SAMPLE– is given here. You can download this and do an assessment for yourself (the excel sheet must be modified as per this years planning. The provided excel sheet is only for reference). DOWNLOAD
- You can copy paste the same format/modify as per your need in Google Spreadsheet and update it on daily basis.
- Feedback talks about daily test results.
- Follow-up talks about daily target achieved from sources and the number of revisions to do/done and dates. Sources column is to ensure that aspirants do not run behind various sources and follow the same throughout.
Would like to end on this quote:
Either you run the day or the day runs you.
Are you ready? Let’s start!
Important Note
- Don’t forget to post your marks in the comment section. Also, let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- You can post your comments in the given format
- (1) Your Score
- (2) Matrix Meter
- (3) New Learning from the Test
Test-summary
0 of 30 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
Information
The following Test is based on the syllabus of 60 Days Plan-2019 for UPSC IAS Prelims 2019.
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 30 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 30
1. Question
Q.1) The Indian federal system is based on the –
Correct
Federalism in India describes the distribution of legal authority across national, state and local governments in India. It is imbibed from the of Canadian model federalism.
Incorrect
Federalism in India describes the distribution of legal authority across national, state and local governments in India. It is imbibed from the of Canadian model federalism.
-
Question 2 of 30
2. Question
Q.2) Consider the following features:
- Unwritten Constitution
- Rigid Constitution
- Integrated judiciary
- Bicameral legislature
- No division of powers
- Single government
Which of the above can be considered as features of Federal Government?
Correct
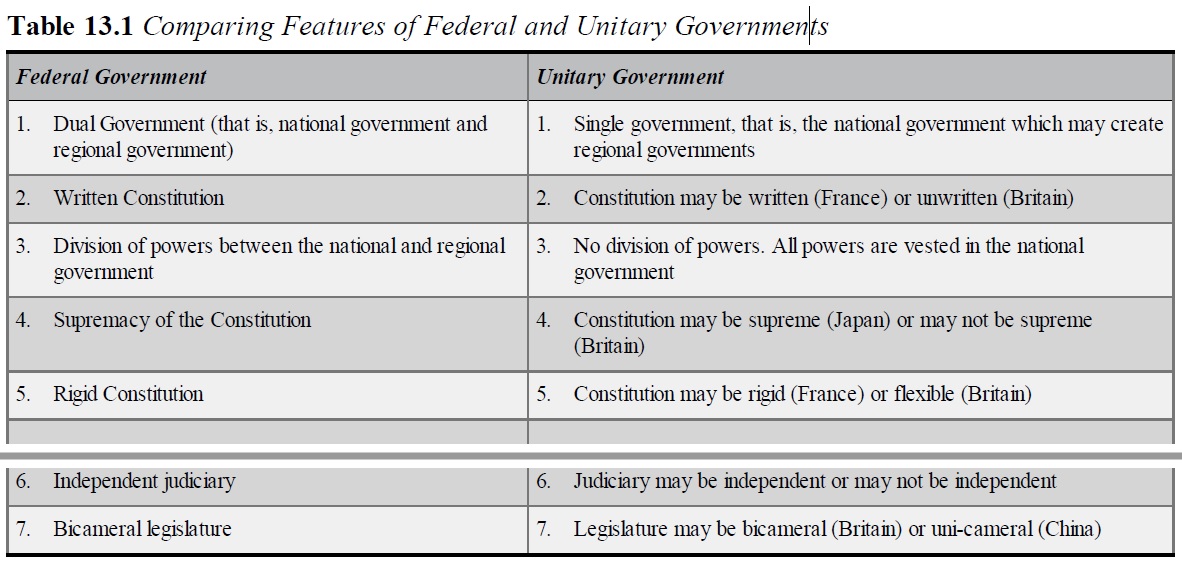
The following are the features of Federal Government:
- Dual Government (that is, national government and regional government)
- Written Constitution
- Division of powers between the national and regional government
- Supremacy of the Constitution
- Rigid Constitution
- Independent judiciary
- Bicameral legislature
 Incorrect
Incorrect
The following are the features of Federal Government:
- Dual Government (that is, national government and regional government)
- Written Constitution
- Division of powers between the national and regional government
- Supremacy of the Constitution
- Rigid Constitution
- Independent judiciary
- Bicameral legislature

-
Question 3 of 30
3. Question
Q.3) Consider the following statements:
- The Constitution of India, being federal in structure, divides all powers related to legislative, executive, judiciary and financial between the Centre and the states.
- The subject of ‘Local Government’ is mentioned in the State List under the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Statement (1) is wrong as the Constitution of India, being federal in structure, divides all powers (legislative, executive and financial) between the Centre and the states. However, there is no division of judicial power as the Constitution has established an integrated judicial system to enforce both the Central laws as well as state laws.
Statement (2) is correct. The subject of ‘Local Government’ is mentioned in the State List under the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution.
Incorrect
Statement (1) is wrong as the Constitution of India, being federal in structure, divides all powers (legislative, executive and financial) between the Centre and the states. However, there is no division of judicial power as the Constitution has established an integrated judicial system to enforce both the Central laws as well as state laws.
Statement (2) is correct. The subject of ‘Local Government’ is mentioned in the State List under the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution.
-
Question 4 of 30
4. Question
Q.4) Consider the following statements:
- President can make regulations for the peace, progress and good government of all the Union Territories.
- The governor is empowered to direct that an act of Parliament does not apply to a scheduled area in the state.
- The President is empowered to direct that an act of Parliament does not apply to tribal areas of all sixth schedule states.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
The President can make regulations for the peace, progress and good government of the four Union Territories—the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. A regulation so made has the same force and effect as an act of Parliament. It may also repeal or amend any act of Parliament in relation to these union territories. Statement (1) is wrong as it says “all the UTs”.
The governor is empowered to direct that an act of Parliament does not apply to a scheduled area in the state or apply with specified modifications and exceptions. Therefore, statement (2) is correct.
The Governor of Assam may likewise direct that an act of Parliament does not apply to a tribal area (autonomours district) in the state or apply with specified modifications and exceptions. The President enjoys the same power with respect to tribal areas (autonomous districts) in Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram. Statement (3) is wrong as President doesn’t enjoy such power in Assam.
Incorrect
The President can make regulations for the peace, progress and good government of the four Union Territories—the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. A regulation so made has the same force and effect as an act of Parliament. It may also repeal or amend any act of Parliament in relation to these union territories. Statement (1) is wrong as it says “all the UTs”.
The governor is empowered to direct that an act of Parliament does not apply to a scheduled area in the state or apply with specified modifications and exceptions. Therefore, statement (2) is correct.
The Governor of Assam may likewise direct that an act of Parliament does not apply to a tribal area (autonomours district) in the state or apply with specified modifications and exceptions. The President enjoys the same power with respect to tribal areas (autonomous districts) in Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram. Statement (3) is wrong as President doesn’t enjoy such power in Assam.
-
Question 5 of 30
5. Question
Q.5) Which among the following British-India Act provided for a three-fold emumenration, viz., federal, provincial and concurrent?
Correct
The Government of India (GoI) Act of 1935 provided for a three-fold emumenration, viz., federal, provincial and concurrent. The present Constitution follows the scheme of this act but with one difference, that is, under this act, the residuary powers were given neither to the federal legislature nor to the provincial legislature but to the governor-general of India. In this respect, India follows the Canadian precedent.
Incorrect
The Government of India (GoI) Act of 1935 provided for a three-fold emumenration, viz., federal, provincial and concurrent. The present Constitution follows the scheme of this act but with one difference, that is, under this act, the residuary powers were given neither to the federal legislature nor to the provincial legislature but to the governor-general of India. In this respect, India follows the Canadian precedent.
-
Question 6 of 30
6. Question
Q.6) Consider the below statements:
- In case of a conflict between the Central law and the state law on a subject enumerated in the Concurrent List, always the Central law prevails over the state law.
- Where there is a conflict between the Concurrent List and the State List, it is the former that should prevail.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
The Constitution expressly secure the predominance of the Union List over the State List and the Concurrent List and that of the Concurrent List over the State List. Thus, in case of overlapping between the Union List and the State List, the former should prevail. In case of overlapping between the Union List and the Concurrent List, it is again the former which should prevail. Where there is a conflict between the Concurrent List and the State List, it is the former that should prevail.
In case of a conflict between the Central law and the state law on a subject enumerated in the Concurrent List, the Central law prevails over the state law. But, there is an exception. If the state law has been reserved for the consideration of the president and has received his assent, then the state law prevails in that state. Hence, statement (1) is wrong.
Incorrect
The Constitution expressly secure the predominance of the Union List over the State List and the Concurrent List and that of the Concurrent List over the State List. Thus, in case of overlapping between the Union List and the State List, the former should prevail. In case of overlapping between the Union List and the Concurrent List, it is again the former which should prevail. Where there is a conflict between the Concurrent List and the State List, it is the former that should prevail.
In case of a conflict between the Central law and the state law on a subject enumerated in the Concurrent List, the Central law prevails over the state law. But, there is an exception. If the state law has been reserved for the consideration of the president and has received his assent, then the state law prevails in that state. Hence, statement (1) is wrong.
-
Question 7 of 30
7. Question
Q.7) Which of the following are not the federal features of Indian Constitution?
- Single Constitution
- Supremacy of Constitution
- Independent Judiciary
- All-India services
- Integrated Election Machinery
Choose correct answer from the options given below:
Correct
The federal features of the Constitution of India include –
- Dual Polity
- Written Constitution
- Division of Powers
- Supremacy of the Constitution
- Rigid Constitution
- Independent Judiciary
- Bicameralism
Indian Constitution possesses the following unitary or non-federal features:
- Strong Centre
- States Not Indestructible
- Single Constitution
- Flexibility of the Constitution
- No Equality of State Representation
- Emergency Provisions
- Single Citizenship
- Integrated Judiciary
- All-India Services
- Integrated Audit Machinery
- Parliament’s Authority Over State List
- Appointment of Governor
- Integrated Election Machinery
- Veto Over State Bills
Incorrect
The federal features of the Constitution of India include –
- Dual Polity
- Written Constitution
- Division of Powers
- Supremacy of the Constitution
- Rigid Constitution
- Independent Judiciary
- Bicameralism
Indian Constitution possesses the following unitary or non-federal features:
- Strong Centre
- States Not Indestructible
- Single Constitution
- Flexibility of the Constitution
- No Equality of State Representation
- Emergency Provisions
- Single Citizenship
- Integrated Judiciary
- All-India Services
- Integrated Audit Machinery
- Parliament’s Authority Over State List
- Appointment of Governor
- Integrated Election Machinery
- Veto Over State Bills
-
Question 8 of 30
8. Question
Q.8) Constitution empowers the Parliament to make laws on any matter enumerated in the State List under the following extraordinary circumstances?
- When Rajya Sabha Passes a Resolution supported by two-thirds of the members present and voting.
- During a National Emergency
- When States Make a Request
- To Implement International Agreements
- During Governor’s Rule
Choose the correct answer:
Correct
Constitution empowers the Parliament to make laws on any matter enumerated in the State List under the following five extraordinary circumstances:
- When Rajya Sabha Passes a Resolution. Such a resolution must be supported by two-thirds of the members present and voting.
- During a National Emergency, the Parliament acquires the power to legislate with respect to matters in the State List.
- When the legislatures of two or more states pass resolutions requesting the Parliament to enact laws on a matter in the State List.
- The Parliament can make laws on any matter in the State List for implementing the international treaties, agreements or conventions.
- When the President’s rule (not Governor’s rule) is imposed in a state, the Parliament becomes empowered to make laws with respect to any matter in the State List in relation to that state. Hence, option (c) is correct answer.
Incorrect
Constitution empowers the Parliament to make laws on any matter enumerated in the State List under the following five extraordinary circumstances:
- When Rajya Sabha Passes a Resolution. Such a resolution must be supported by two-thirds of the members present and voting.
- During a National Emergency, the Parliament acquires the power to legislate with respect to matters in the State List.
- When the legislatures of two or more states pass resolutions requesting the Parliament to enact laws on a matter in the State List.
- The Parliament can make laws on any matter in the State List for implementing the international treaties, agreements or conventions.
- When the President’s rule (not Governor’s rule) is imposed in a state, the Parliament becomes empowered to make laws with respect to any matter in the State List in relation to that state. Hence, option (c) is correct answer.
-
Question 9 of 30
9. Question
Q.9) Consider the below statements:
- The Constitution provides for inter-government delegation of legislative functions between the Centre and the states in order to mitigate rigidity and avoid a situation of deadlock.
- The Constitution also makes a provision for the entrustment of the executive functions of the Centre to a state without the consent of that state.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
Statement (1) is wrong as the distribution of legislative powers between the Centre and the states is rigid. Consequently, the Centre cannot delegate its legislative powers to the states and a single state cannot request the Parliament to make a law on a state subject.
The distribution of executive power in general follows the distribution of legislative powers. But, such a rigid division in the executive sphere may lead to occasional conflicts between the two. Hence, the Constitution provides for inter-government delegation of executive functions (not legislative) in order to mitigate rigidity and avoid a situation of deadlock.
Accordingly, the President may, with the consent of the state government, entrust to that government any of the executive functions of the Centre. Conversely, the governor of a state may, with the consent of the Central government, entrust to that government any of the executive functions of the state. This mutual delegation of administrative functions may be conditional or unconditional.
Statement (2) is correct as the Constitution also makes a provision for the entrustment of the executive functions of the Centre to a state without the consent of that state. But, in this case, the delegation is by the Parliament and not by the president. Thus, a law made by the Parliament on a subject of the Union List can confer powers and impose duties on a state, or authorise the conferring of powers and imposition of duties by the Centre upon a state (irrespective of the consent of the state concerned). Notably, the same thing cannot be done by the state legislature.
From the above, it is clear that the mutual delegation of functions between the Centre and the state can take place either under an agreement or by a legislation. While the Centre can use both the methods, a state can use only the first method.
Incorrect
Statement (1) is wrong as the distribution of legislative powers between the Centre and the states is rigid. Consequently, the Centre cannot delegate its legislative powers to the states and a single state cannot request the Parliament to make a law on a state subject.
The distribution of executive power in general follows the distribution of legislative powers. But, such a rigid division in the executive sphere may lead to occasional conflicts between the two. Hence, the Constitution provides for inter-government delegation of executive functions (not legislative) in order to mitigate rigidity and avoid a situation of deadlock.
Accordingly, the President may, with the consent of the state government, entrust to that government any of the executive functions of the Centre. Conversely, the governor of a state may, with the consent of the Central government, entrust to that government any of the executive functions of the state. This mutual delegation of administrative functions may be conditional or unconditional.
Statement (2) is correct as the Constitution also makes a provision for the entrustment of the executive functions of the Centre to a state without the consent of that state. But, in this case, the delegation is by the Parliament and not by the president. Thus, a law made by the Parliament on a subject of the Union List can confer powers and impose duties on a state, or authorise the conferring of powers and imposition of duties by the Centre upon a state (irrespective of the consent of the state concerned). Notably, the same thing cannot be done by the state legislature.
From the above, it is clear that the mutual delegation of functions between the Centre and the state can take place either under an agreement or by a legislation. While the Centre can use both the methods, a state can use only the first method.
-
Question 10 of 30
10. Question
Q.10) In order to secure cooperation and coordination between the Centre and the states –
Correct
The Constitution contains the following provisions to secure cooperation and coordination between the Centre and the states:
- The Parliament can provide for the adjudication of any dispute or complaint with respect to the use, distribution and control of waters of any inter-state river and river valley.
- The President can establish (under Article 263) an Inter-State Council to investigate and discuss subject of common interest between the Centre and the states.
- Full faith and credit is to be given throughout the territory of India to public acts, records and judicial proceedings of the Centre and every state.
- The Parliament can appoint an appropriate authority to carry out the purposes of the constitutional provisions relating to the interstate freedom of trade, commerce and intercourse. But, no such authority has been appointed so far.
Incorrect
The Constitution contains the following provisions to secure cooperation and coordination between the Centre and the states:
- The Parliament can provide for the adjudication of any dispute or complaint with respect to the use, distribution and control of waters of any inter-state river and river valley.
- The President can establish (under Article 263) an Inter-State Council to investigate and discuss subject of common interest between the Centre and the states.
- Full faith and credit is to be given throughout the territory of India to public acts, records and judicial proceedings of the Centre and every state.
- The Parliament can appoint an appropriate authority to carry out the purposes of the constitutional provisions relating to the interstate freedom of trade, commerce and intercourse. But, no such authority has been appointed so far.
-
Question 11 of 30
11. Question
Q.11) Which of the following statements are incorrect for Statutory Grants?
Correct
Grants-in-Aid to the States
Besides sharing of taxes between the Centre and the states, the Constitution provides for grants-in-aid to the states from the Central resources. There are two types of grants-in-aid, viz, statutory grants and discretionary grants.
Statutory Grants
- Article 275 empowers the Parliament to make grants to the states which are in need of financial assistance and not to every state. Also, different sums may be fixed for different states. These sums are charged on the Consolidated Fund of India every year.
- Apart from this general provision, the Constitution also provides for specific grants for promoting the welfare of the scheduled tribes in a state or for raising the level of administration of the scheduled areas in a state including the State of Assam.
- The statutory grants under Article 275 (both general and specific) are given to the states on the recommendation of the Finance Commission.
Discretionary Grants
- Article 282 empowers both the Centre and the states to make any grants for any public purpose, even if it is not within their respective legislative competence.
Incorrect
Grants-in-Aid to the States
Besides sharing of taxes between the Centre and the states, the Constitution provides for grants-in-aid to the states from the Central resources. There are two types of grants-in-aid, viz, statutory grants and discretionary grants.
Statutory Grants
- Article 275 empowers the Parliament to make grants to the states which are in need of financial assistance and not to every state. Also, different sums may be fixed for different states. These sums are charged on the Consolidated Fund of India every year.
- Apart from this general provision, the Constitution also provides for specific grants for promoting the welfare of the scheduled tribes in a state or for raising the level of administration of the scheduled areas in a state including the State of Assam.
- The statutory grants under Article 275 (both general and specific) are given to the states on the recommendation of the Finance Commission.
Discretionary Grants
- Article 282 empowers both the Centre and the states to make any grants for any public purpose, even if it is not within their respective legislative competence.
-
Question 12 of 30
12. Question
Q.12) Which among the following is envisaged by the Constitution of India as the balancing wheel of fiscal federalism in India?
Correct
The Constitution of India envisaged the Finance commission as the balancing wheel of fiscal federalism in India.
Article 280 provides for a Finance Commission as a quasi-judicial body. It is constituted by the President every fifth year or even earlier.
Incorrect
The Constitution of India envisaged the Finance commission as the balancing wheel of fiscal federalism in India.
Article 280 provides for a Finance Commission as a quasi-judicial body. It is constituted by the President every fifth year or even earlier.
-
Question 13 of 30
13. Question
Q.13) Consider the following with regard to Joint State Public Service Commission (JSPSC) and identify the incorrect statement:
Correct
The Constitution makes a provision for the establishment of a Joint State Public Service Commission (JSPSC) for two or more states. While the UPSC and the SPSC are created directly by the Constitution, a JSPSC can be created by an act of Parliament on the request of the state legislatures concerned. Thus, a JSPSC is a statutory and not a constitutional body.
A JSPSC presents its annual performance report to each of the concerned state governors. Each governor places the report before the state legislature.
Incorrect
The Constitution makes a provision for the establishment of a Joint State Public Service Commission (JSPSC) for two or more states. While the UPSC and the SPSC are created directly by the Constitution, a JSPSC can be created by an act of Parliament on the request of the state legislatures concerned. Thus, a JSPSC is a statutory and not a constitutional body.
A JSPSC presents its annual performance report to each of the concerned state governors. Each governor places the report before the state legislature.
-
Question 14 of 30
14. Question
Q.14) Consider the following statements with regard to UPSC and the President and identify the incorrect statement:
Correct
The UPSC presents, annually, to the president a report on its performance. The President places this report before both the Houses of Parliament, along with a memorandum explaining the cases where the advice of the Commission was not accepted and the reasons for such non-acceptance.
The president can exclude posts, services and matters from the purview of the UPSC.
Statement (d) is incorrect, because the additional functions relating to the services of the Union can be conferred on UPSC by the Parliament. It can also place the personnel system of any authority, corporate body or public institution within the jurisdiction of the UPSC. Hence the jurisdiction of UPSC can be extended by an act made by the Parliament. (not the President)
Incorrect
The UPSC presents, annually, to the president a report on its performance. The President places this report before both the Houses of Parliament, along with a memorandum explaining the cases where the advice of the Commission was not accepted and the reasons for such non-acceptance.
The president can exclude posts, services and matters from the purview of the UPSC.
Statement (d) is incorrect, because the additional functions relating to the services of the Union can be conferred on UPSC by the Parliament. It can also place the personnel system of any authority, corporate body or public institution within the jurisdiction of the UPSC. Hence the jurisdiction of UPSC can be extended by an act made by the Parliament. (not the President)
-
Question 15 of 30
15. Question
Q.15) Original jurisdiction of the Supreme Court does not extend to which of the following?
Correct
As a federal court, the Supreme Court decides the disputes between different units of the Indian Federation. More elaborately, any dispute between:
- the Centre and one or more states; or
- the Centre and any state or states on one side and one or more states on the other; or
- between two or more states.
In the above federal disputes, the Supreme Court has exclusive original jurisdiction. Exclusive means, no other court can decide such disputes and original means, the power to hear such disputes in the first instance, not by way of appeal.
However, this jurisdiction of the Supreme Court does not extend to the following:
- A dispute arising out of any pre-Constitution treaty, agreement, covenant, engagement, or other similar instrument.
- A dispute arising out of any treaty, agreement, etc., which specifically provides that the said jurisdiction does not extent to such a dispute.
- Inter-state water disputes.
- Matters referred to the Finance Commission.
- Adjustment of certain expenses and pensions between the Centre and the states.
- Ordinary dispute of Commercial nature between the Centre and the states.
- Recovery of damages by a state against the Centre.
Incorrect
As a federal court, the Supreme Court decides the disputes between different units of the Indian Federation. More elaborately, any dispute between:
- the Centre and one or more states; or
- the Centre and any state or states on one side and one or more states on the other; or
- between two or more states.
In the above federal disputes, the Supreme Court has exclusive original jurisdiction. Exclusive means, no other court can decide such disputes and original means, the power to hear such disputes in the first instance, not by way of appeal.
However, this jurisdiction of the Supreme Court does not extend to the following:
- A dispute arising out of any pre-Constitution treaty, agreement, covenant, engagement, or other similar instrument.
- A dispute arising out of any treaty, agreement, etc., which specifically provides that the said jurisdiction does not extent to such a dispute.
- Inter-state water disputes.
- Matters referred to the Finance Commission.
- Adjustment of certain expenses and pensions between the Centre and the states.
- Ordinary dispute of Commercial nature between the Centre and the states.
- Recovery of damages by a state against the Centre.
-
Question 16 of 30
16. Question
Q.16) Which of the below given statement(s) about Fifth Schedule areas is/are correct?
- The provisions of Part IX of the constitution relating to the Panchayats are not applicable to the Fifth Schedule areas.
- Fifth Schedule areas deals with the administration of the tribal areas in the four northeastern states of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
Select appropriate answer:
Correct
The provisions of Part IX of the constitution relating to the Panchayats are not applicable to the Fifth Schedule areas.
5th Schedule deals with administration and control of scheduled areas and scheduled tribes in any state except the four states of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
6th Schedule deals with the administration of the tribal areas in the four northeastern states of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
Incorrect
The provisions of Part IX of the constitution relating to the Panchayats are not applicable to the Fifth Schedule areas.
5th Schedule deals with administration and control of scheduled areas and scheduled tribes in any state except the four states of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
6th Schedule deals with the administration of the tribal areas in the four northeastern states of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
-
Question 17 of 30
17. Question
Q.17) Consider the below statements with regard to Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana and identify the incorrect statement:
Correct
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana
The Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY), was launched by the Govt. of India to provide connectivity to unconnected Habitations as part of a poverty reduction strategy.
The Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) is a 100% Centrally Sponsored Scheme. 50% of the Cess on High Speed Diesel (HSD) is earmarked for this Programme.
According to latest figures (as of March 2019) made available by the State Governments under a survey to identify Core Network as part of the PMGSY programme, about 1.67 lakh Unconnected Habitations are eligible for coverage under the programme. Hence, statement (c) is wrong.
The target of connecting 1,78,184 eligibile habitations under PMGSY was expected to be completed by March 2019. Almost 95% of these habitations had been sanctioned road connectivity and 91% habitations had been connected.
(For more details: refer https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/nod-for-extending-pmgsy-beyond-12th-five-year-plan/article24646349.ece)
Objectives:
- The primary objective of the PMGSY is to provide Connectivity, by way of an All-weather Road (with necessary culverts and cross-drainage structures, which is operable throughout the year), to the eligible unconnected Habitations in the rural areas with a population of 500 persons and above in Plain areas.
- In respect of the Hill States (North-East, Sikkim, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir and Uttarakhand), the Desert Areas (as identified in the Desert Development Programme), the Tribal (Schedule V) areas and Selected Tribal and Backward Districts, the objective would be to connect eligible unconnected Habitations with a population of 250 persons and above.
Do you know?
- The PMGSY shall cover only the rural areas. Urban roads are excluded from the purview of this Programme.
- Even in the rural areas, PMGSY covers only the Rural Roads i.e., Roads that were formerly classified as ‘Other District Roads’ (ODR) and ‘Village Roads’ (VR).
- Major District Roads, State Highways and National Highways cannot be covered under the PMGSY, even if they happen to be in rural areas.
Incorrect
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana
The Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY), was launched by the Govt. of India to provide connectivity to unconnected Habitations as part of a poverty reduction strategy.
The Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) is a 100% Centrally Sponsored Scheme. 50% of the Cess on High Speed Diesel (HSD) is earmarked for this Programme.
According to latest figures (as of March 2019) made available by the State Governments under a survey to identify Core Network as part of the PMGSY programme, about 1.67 lakh Unconnected Habitations are eligible for coverage under the programme. Hence, statement (c) is wrong.
The target of connecting 1,78,184 eligibile habitations under PMGSY was expected to be completed by March 2019. Almost 95% of these habitations had been sanctioned road connectivity and 91% habitations had been connected.
(For more details: refer https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/nod-for-extending-pmgsy-beyond-12th-five-year-plan/article24646349.ece)
Objectives:
- The primary objective of the PMGSY is to provide Connectivity, by way of an All-weather Road (with necessary culverts and cross-drainage structures, which is operable throughout the year), to the eligible unconnected Habitations in the rural areas with a population of 500 persons and above in Plain areas.
- In respect of the Hill States (North-East, Sikkim, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir and Uttarakhand), the Desert Areas (as identified in the Desert Development Programme), the Tribal (Schedule V) areas and Selected Tribal and Backward Districts, the objective would be to connect eligible unconnected Habitations with a population of 250 persons and above.
Do you know?
- The PMGSY shall cover only the rural areas. Urban roads are excluded from the purview of this Programme.
- Even in the rural areas, PMGSY covers only the Rural Roads i.e., Roads that were formerly classified as ‘Other District Roads’ (ODR) and ‘Village Roads’ (VR).
- Major District Roads, State Highways and National Highways cannot be covered under the PMGSY, even if they happen to be in rural areas.
-
Question 18 of 30
18. Question
Q.18) Consider the below statements with regard to Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY) scheme:
- It was launched by Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- As of now the Scheme is being implemented in only 12 identified Cities.
- It is a central sector scheme, where 100% funding will be provided by Government of India.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Correct
The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Government of India, launched the National Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY) scheme on 21st January, 2015, with a focus on holistic development of heritage cities. The scheme aims to preserve and revitalise soul of the heritage city to reflect the city’s unique character by encouraging aesthetically appealing, accessible, informative & secured environment.
HRIDAY is a central sector scheme, where 100% funding will be provided by Government of India.
With a duration of 4 years 3 months (up to March, 2019) and a total outlay of INR 500 Crores, the Scheme is being implemented in 12 identified Cities namely, Ajmer, Amaravati, Amritsar, Badami, Dwarka, Gaya, Kanchipuram, Mathura, Puri, Varanasi, Velankanni and Warangal. The scheme is implemented in a mission mode.
Incorrect
The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Government of India, launched the National Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY) scheme on 21st January, 2015, with a focus on holistic development of heritage cities. The scheme aims to preserve and revitalise soul of the heritage city to reflect the city’s unique character by encouraging aesthetically appealing, accessible, informative & secured environment.
HRIDAY is a central sector scheme, where 100% funding will be provided by Government of India.
With a duration of 4 years 3 months (up to March, 2019) and a total outlay of INR 500 Crores, the Scheme is being implemented in 12 identified Cities namely, Ajmer, Amaravati, Amritsar, Badami, Dwarka, Gaya, Kanchipuram, Mathura, Puri, Varanasi, Velankanni and Warangal. The scheme is implemented in a mission mode.
-
Question 19 of 30
19. Question
Q.19) Recently launched ‘Saubhagya Yojana’, is also known as
Correct
The Saubhagya Scheme or Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana is an Indian government project to provide electricity to all households.
The project was announced in September 2017 and the aim was to complete the electrification process by December 2018.
Fore more: https://www.india.gov.in/spotlight/pradhan-mantri-sahaj-bijli-har-ghar-yojana-saubhagya
Incorrect
The Saubhagya Scheme or Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana is an Indian government project to provide electricity to all households.
The project was announced in September 2017 and the aim was to complete the electrification process by December 2018.
Fore more: https://www.india.gov.in/spotlight/pradhan-mantri-sahaj-bijli-har-ghar-yojana-saubhagya
-
Question 20 of 30
20. Question
Q.20) Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Correct
Pratyaksh Hastantrit Labh (PAHAL) scheme was introduced for direct transfer of LPG subsidies to the consumers’ bank accounts.
The Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY) was launched as its principal vehicle to achieve the goal of electricity for all by 2022.
Incorrect
Pratyaksh Hastantrit Labh (PAHAL) scheme was introduced for direct transfer of LPG subsidies to the consumers’ bank accounts.
The Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY) was launched as its principal vehicle to achieve the goal of electricity for all by 2022.
-
Question 21 of 30
21. Question
Q.21) ‘Kuchinoerabujima Island’ was in news recently. Where is it located?
-
Question 22 of 30
22. Question
Q.22) Consider the following statements
- ‘Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX)’ will be funded and managed by a ‘Defence Innovation Organization (DIO)’
- ‘Defence Innovation Organization (DIO)’ has been formed as a ‘not for profit’ company as per Section 8 of the Companies Act 2013
Select the correct statements
Correct
Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) launched by the Governmentin April 2018, primarily aims at creation of an ecosystem to foster innovation and technology development in Defence and Aerospace by engaging Industries including MSMEs, start-ups, individual innovators, R&D institutes & academia, and provide them grants/funding and other support to carry out R&D which has good potential for future adoption for Indian defence and aerospace needs.
iDEX will be funded and managed by a ‘Defence Innovation Organization (DIO)’ which has been formed as a ‘not for profit’ company as per Section 8 of the Companies Act 2013 for this purpose, by the two founder members i.e. Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs) – HAL & BEL. iDEX will function as the executive arm of DIO, carrying out all the required activities while DIO will provide high level policy guidance to iDEX.
Incorrect
Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) launched by the Governmentin April 2018, primarily aims at creation of an ecosystem to foster innovation and technology development in Defence and Aerospace by engaging Industries including MSMEs, start-ups, individual innovators, R&D institutes & academia, and provide them grants/funding and other support to carry out R&D which has good potential for future adoption for Indian defence and aerospace needs.
iDEX will be funded and managed by a ‘Defence Innovation Organization (DIO)’ which has been formed as a ‘not for profit’ company as per Section 8 of the Companies Act 2013 for this purpose, by the two founder members i.e. Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs) – HAL & BEL. iDEX will function as the executive arm of DIO, carrying out all the required activities while DIO will provide high level policy guidance to iDEX.
-
Question 23 of 30
23. Question
Q.23) Consider the following statements with respect to ‘Global Solar Council’
- It is an intergovernmental organization of tropical countries
- It was launched during the United Nations Climate Change Conference (UN COP 24)
Select the correct statements
Correct
Global Solar Council is an international non-profit association of the national, regional and international associations in solar energy and the world.
The Global Solar Council (GSC) was launched on December 6, 2015, following the historic United Nations Climate Change Conference (UN COP 21). The GSC came into being as International Coalition of more than 30 nations, utilising maximum solar energy, decided to harness the renewable energy for the greater good.
Incorrect
Global Solar Council is an international non-profit association of the national, regional and international associations in solar energy and the world.
The Global Solar Council (GSC) was launched on December 6, 2015, following the historic United Nations Climate Change Conference (UN COP 21). The GSC came into being as International Coalition of more than 30 nations, utilising maximum solar energy, decided to harness the renewable energy for the greater good.
-
Question 24 of 30
24. Question
Q.24) ‘Operation Kabaddi’ is associated with
Correct
Operation Kabaddi’ in the post-Kargil scenario, aimed at preventing cross-border infiltration.
Incorrect
Operation Kabaddi’ in the post-Kargil scenario, aimed at preventing cross-border infiltration.
-
Question 25 of 30
25. Question
Q.25) The term ‘Quadrantids’ was in news recently. What is it associated with
Correct
The Quadrantids (QUA) are a January meteor shower. The zenithal hourly rate (ZHR) of this shower can be as high as that of two other reliably rich meteor showers, the Perseids in August and the Geminids in December, yet Quadrantid meteors are not seen as often as meteors in these other two showers, because the peak intensity is exceedingly sharp, sometimes lasting only hours. Additionally, the meteors are quite faint (mean magnitude 3-6 mag).
Incorrect
The Quadrantids (QUA) are a January meteor shower. The zenithal hourly rate (ZHR) of this shower can be as high as that of two other reliably rich meteor showers, the Perseids in August and the Geminids in December, yet Quadrantid meteors are not seen as often as meteors in these other two showers, because the peak intensity is exceedingly sharp, sometimes lasting only hours. Additionally, the meteors are quite faint (mean magnitude 3-6 mag).
-
Question 26 of 30
26. Question
Q.26) One of the prominent mudras of Lord Shiva is said to be ‘Cin Mudra or Chin Mudra’. What is the meaning of ‘Cin’ here?
Correct
Jnana mudra and cin mudra are very similar, both consisting of bringing the index finger and thumb together. These mudras are most commonly used during meditation practices.
Jnana means knowledge. When the index finger and thumb are placed together and the hands are placed facing down on the knees this is called Jnana mudra. Cin means consciousness. When the index finger and thumb are placed together and the hands are placed facing up on the knees (or thighs) this is called cin mudra.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/society/history-and-culture/find-the-missing-you/article25898165.ece
Incorrect
Jnana mudra and cin mudra are very similar, both consisting of bringing the index finger and thumb together. These mudras are most commonly used during meditation practices.
Jnana means knowledge. When the index finger and thumb are placed together and the hands are placed facing down on the knees this is called Jnana mudra. Cin means consciousness. When the index finger and thumb are placed together and the hands are placed facing up on the knees (or thighs) this is called cin mudra.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/society/history-and-culture/find-the-missing-you/article25898165.ece
-
Question 27 of 30
27. Question
Q.27) The Krishnakriti Festival is the largest and oldest art and culture festival in:
Correct
The Krishnakriti Festival is the largest and oldest art and culture festival in Hyderabad. (16th edition)
The theme ‘Urban Frames — visual practices and transitions’.
The Krishnakriti Foundation each year organizes the most prominent art and culture festival of Hyderabad in the month of January.
The festival brings together the artists, curators, musicians, dancers, theatre personalities, performers, authors, poets, actors, scholars, academicians and art and cultural enthusiasts from across the country.
‘Ahmedabad Walls and Hyderabad Biophilia’ exhibition held as part of Krishnakriti Festival 2019 was the most sought one by Robert Stephens.
‘Ahmedabad Walls’ by Mumbai-based architect and artist Robert Stephens has its roots in the study and report of Ahmedabad by Scottish polymath Patrick Geddes in the early 20th century. Patrick Geddes visited Ahmedabad in April 1915. The municipality sought him out for town planning advice. He was asked if the 500-year-old city walls should be demolished or retained. A three-day circumambulation later, Patrick Geddes emphasised that the walls must be preserved and presented his analysis in ‘Notes on Ahmedabad’.
A century later, Robert Stephens conceived the tactile travelling exhibition ‘Ahmedabad Walls’, juxtaposing Geddes’s report with aerial photographs of Ahmedabad, covering every portion of the city walls as they exist today.
Robert’s similar visual exploration of Hyderabad began in November 2018. Robert tells us that “Hyderabad Biophilia is an exploration of man’s affinity towards the natural world, in Hyderabad specifically, through the unrealised planning work of Scottish polymath Patrick Geddes and Indian town planner Mohammed Fayazuddin (Fayazuddin (1903-1977) was Hyderabad’s architect and recognised as India’s first town planner. Several landmark buildings, including Ravindra Bharathi, were designed by him).
Note- The biophilia hypothesis also called BET suggests that humans possess an innate tendency to seek connections with nature and other forms of life. Edward O. Wilson introduced and popularized the hypothesis in his book, Biophilia.
Incorrect
The Krishnakriti Festival is the largest and oldest art and culture festival in Hyderabad. (16th edition)
The theme ‘Urban Frames — visual practices and transitions’.
The Krishnakriti Foundation each year organizes the most prominent art and culture festival of Hyderabad in the month of January.
The festival brings together the artists, curators, musicians, dancers, theatre personalities, performers, authors, poets, actors, scholars, academicians and art and cultural enthusiasts from across the country.
‘Ahmedabad Walls and Hyderabad Biophilia’ exhibition held as part of Krishnakriti Festival 2019 was the most sought one by Robert Stephens.
‘Ahmedabad Walls’ by Mumbai-based architect and artist Robert Stephens has its roots in the study and report of Ahmedabad by Scottish polymath Patrick Geddes in the early 20th century. Patrick Geddes visited Ahmedabad in April 1915. The municipality sought him out for town planning advice. He was asked if the 500-year-old city walls should be demolished or retained. A three-day circumambulation later, Patrick Geddes emphasised that the walls must be preserved and presented his analysis in ‘Notes on Ahmedabad’.
A century later, Robert Stephens conceived the tactile travelling exhibition ‘Ahmedabad Walls’, juxtaposing Geddes’s report with aerial photographs of Ahmedabad, covering every portion of the city walls as they exist today.
Robert’s similar visual exploration of Hyderabad began in November 2018. Robert tells us that “Hyderabad Biophilia is an exploration of man’s affinity towards the natural world, in Hyderabad specifically, through the unrealised planning work of Scottish polymath Patrick Geddes and Indian town planner Mohammed Fayazuddin (Fayazuddin (1903-1977) was Hyderabad’s architect and recognised as India’s first town planner. Several landmark buildings, including Ravindra Bharathi, were designed by him).
Note- The biophilia hypothesis also called BET suggests that humans possess an innate tendency to seek connections with nature and other forms of life. Edward O. Wilson introduced and popularized the hypothesis in his book, Biophilia.
-
Question 28 of 30
28. Question
Q.28) Consider the following and select the correct match:
- Kardameshvara Temple:: Varanasi
- Sculpture Heritage of Pragjyotishpur:: Assam
- The Blue City:: Jodhpur
Select from the code below:
Correct
Kardameshvara Temple- Oldest surviving temple of Varanasi
Pragjyotishpur, the present day Guwahati, Assam. Guwahati has always been a center of Art and Culture in the northeastern part of India. Known as ancient sculptural heritage in and around the city. Also Guwahati is believed to have been a major school of Art, the Ambari School of Art.
Jodhpur is a popular tourist destination, featuring many palaces, forts and temples, set in the stark landscape of the Thar Desert. It is popularly known as Blue city and Sun city among people of Rajasthan and all over India.
Incorrect
Kardameshvara Temple- Oldest surviving temple of Varanasi
Pragjyotishpur, the present day Guwahati, Assam. Guwahati has always been a center of Art and Culture in the northeastern part of India. Known as ancient sculptural heritage in and around the city. Also Guwahati is believed to have been a major school of Art, the Ambari School of Art.
Jodhpur is a popular tourist destination, featuring many palaces, forts and temples, set in the stark landscape of the Thar Desert. It is popularly known as Blue city and Sun city among people of Rajasthan and all over India.
-
Question 29 of 30
29. Question
Q.29) Gilbert Hill is a 200 ft monolith column of black basalt rock in India. The rock has a sheer vertical face and was formed when molten lava was squeezed out of the Earth’s clefts during the Mesozoic Era about 66 million years ago. It is located in:
Correct
Gilbert Hill is a 200 ft (61 m) monolith column of black basalt rock at Andheri, in Mumbai, India. The rock has a sheer vertical face and was formed when molten lava was squeezed out of the Earth’s clefts during the Mesozoic Era about 66 million years ago.
Incorrect
Gilbert Hill is a 200 ft (61 m) monolith column of black basalt rock at Andheri, in Mumbai, India. The rock has a sheer vertical face and was formed when molten lava was squeezed out of the Earth’s clefts during the Mesozoic Era about 66 million years ago.
-
Question 30 of 30
30. Question
Q.30) During the 17th century, Patna became a centre of international trade. In 1620, the English East India Company established a factory in Patna for trade in calico and silk. Soon it became a trading centre for ‘X’. Francois Bernier, in Travels in the Mogul Empire, AD 1656–1668, says, “It [X] is carried down the Ganges with great facility, and the Dutch and English send large cargoes to many parts of the Indies, and to Europe”. What is X being referred above by Francois Bernier?
Correct
During the 17th century, Patna became a centre of international trade. In 1620, the English East India Company established a factory in Patna for trade in calico and silk. Soon it became a trading centre for saltpetre. Francois Bernier, in Travels in the Mogul Empire, AD 1656–1668, says, “It [saltpetre] is carried down the Ganges with great facility, and the Dutch and English send large cargoes to many parts of the Indies, and to Europe”.
Mahavir Temple and the Rizwan Castle:: The Mahavir Temple was originally established by Swami Balanand around 1730 AD. The Mahavir Mandir Trusts have the second highest budget in North India after the famous Maa Vaishno Devi shrine. The Rizwan Castle is one of the oldest heritage sites in Patna. This structure was built in the year 1890. In 1912, during the Patna Congress, Mahatma Gandhi was known to have stayed in this castle.
Source: Taken from India Heritage Walk Festival
The India Heritage Walk Festival, now in its second edition, with its month-long celebration of India’s tangible and intangible cultural heritage, led by Sahapedia in partnership with UNESCO. With its varied lineup, it explores the diversity that characterises the cultural fabric of our country, such as, food, heritage, nature, art, architecture, and so on. There will be walks, talks, workshops and Instameets across India covering a broad spectrum of Indian heritage and culture. The festival has scaled in its reach through the inclusion of over 35 cities and more than 100 events across the country. Ranging from museums, historically significant monuments and markets, to explorations of interesting natural landscapes and areas known for their rich cuisine, to women-oriented narratives, the programme is curated thematically. The focus has been to encourage and increase different forms of engagement with interesting and important heritage spaces, while also ensuring that these heritage spaces are made accessible to various audience groups. These efforts have also been specially directed towards those groups for whom engagement programmes in heritage spaces are commonly unavailable, such as children, the differently-abled, and those from economically disadvantaged backgrounds. We have also curated special walks and events with specific user groups in mind, such as students, travellers, local residents, and professional groups such as photographers, conservationists, and so on. Through the festival, Sahapedia and UNESCO aim to highlight these issues to other institutions in the culture space and emphasise the need to make heritage spaces more interesting and inclusive.
Sahapedia is an open online resource on the arts, cultures and histories of India (broadly, South Asia) based on both curated and crowd-sourced content. ‘Saha’ (Sanskrit for ‘together with’), is an invitation to explore together the richness of the Indian cultural landscape.
Incorrect
During the 17th century, Patna became a centre of international trade. In 1620, the English East India Company established a factory in Patna for trade in calico and silk. Soon it became a trading centre for saltpetre. Francois Bernier, in Travels in the Mogul Empire, AD 1656–1668, says, “It [saltpetre] is carried down the Ganges with great facility, and the Dutch and English send large cargoes to many parts of the Indies, and to Europe”.
Mahavir Temple and the Rizwan Castle:: The Mahavir Temple was originally established by Swami Balanand around 1730 AD. The Mahavir Mandir Trusts have the second highest budget in North India after the famous Maa Vaishno Devi shrine. The Rizwan Castle is one of the oldest heritage sites in Patna. This structure was built in the year 1890. In 1912, during the Patna Congress, Mahatma Gandhi was known to have stayed in this castle.
Source: Taken from India Heritage Walk Festival
The India Heritage Walk Festival, now in its second edition, with its month-long celebration of India’s tangible and intangible cultural heritage, led by Sahapedia in partnership with UNESCO. With its varied lineup, it explores the diversity that characterises the cultural fabric of our country, such as, food, heritage, nature, art, architecture, and so on. There will be walks, talks, workshops and Instameets across India covering a broad spectrum of Indian heritage and culture. The festival has scaled in its reach through the inclusion of over 35 cities and more than 100 events across the country. Ranging from museums, historically significant monuments and markets, to explorations of interesting natural landscapes and areas known for their rich cuisine, to women-oriented narratives, the programme is curated thematically. The focus has been to encourage and increase different forms of engagement with interesting and important heritage spaces, while also ensuring that these heritage spaces are made accessible to various audience groups. These efforts have also been specially directed towards those groups for whom engagement programmes in heritage spaces are commonly unavailable, such as children, the differently-abled, and those from economically disadvantaged backgrounds. We have also curated special walks and events with specific user groups in mind, such as students, travellers, local residents, and professional groups such as photographers, conservationists, and so on. Through the festival, Sahapedia and UNESCO aim to highlight these issues to other institutions in the culture space and emphasise the need to make heritage spaces more interesting and inclusive.
Sahapedia is an open online resource on the arts, cultures and histories of India (broadly, South Asia) based on both curated and crowd-sourced content. ‘Saha’ (Sanskrit for ‘together with’), is an invitation to explore together the richness of the Indian cultural landscape.











